在工业自动化和精密设备控制领域,运动控制系统是核心技术之一。无论是3D打印机、数控机床,还是自动化生产线,都离不开精确的运动控制。作为C#开发者,你是否想过如何用熟悉的技术栈来构建一个专业级的运动控制系统?
今天就带大家从零开始,用C#和WinForms打造一个功能完整的单轴运动控制器。不仅有完整的运动算法实现,还包含直观的可视化界面和实时动画效果。这不仅是一次技术实战,更是将复杂工业控制概念转化为可理解代码的绝佳案例。
🎯 核心痛点分析
工业控制软件的三大挑战
1. 实时性要求高
运动控制需要毫秒级响应,任何延迟都可能影响精度甚至造成设备损坏。
2. 复杂的运动规划
需要实现平滑的加速度曲线,避免机械冲击,同时保证运动精度。
3. 界面与控制逻辑分离
工业软件往往逻辑复杂,界面更新频繁,如何保持代码清晰和系统稳定是关键。
🚩 流程图
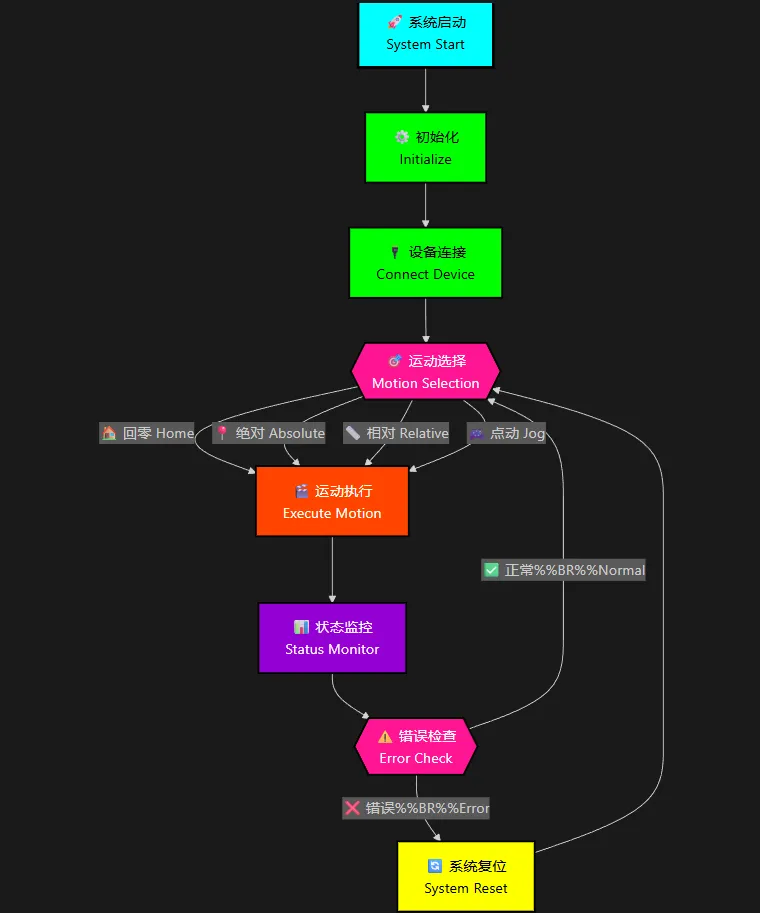
🔧 架构设计:分层解耦的智慧
核心类结构设计
我们采用事件驱动 + 异步编程的架构模式:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppSingleAxisMotionControl
{
public class MotionAxis
{
#region 事件定义
public event EventHandler<PositionChangedEventArgs> PositionChanged;
public event EventHandler<StatusChangedEventArgs> StatusChanged;
public event EventHandler<AlarmEventArgs> AlarmOccurred;
#endregion
#region 私有字段
private double _currentPosition = 0;
private double _currentVelocity = 0;
private bool _isConnected = false;
private bool _isHomed = false;
private bool _isMoving = false;
private bool _hasAlarm = false;
private double? _targetPosition = null;
private double _startPosition = 0;
private CancellationTokenSource _moveCancellation;
private System.Threading.Timer _simulationTimer;
private Random _random = new Random();
#endregion
#region 属性
public double CurrentPosition
{
get => _currentPosition;
private set
{
if (Math.Abs(_currentPosition - value) > 0.001)
{
_currentPosition = value;
PositionChanged?.Invoke(this, new PositionChangedEventArgs(value));
}
}
}
public double CurrentVelocity
{
get => _currentVelocity;
private set => _currentVelocity = value;
}
public bool IsConnected => _isConnected;
public bool IsHomed => _isHomed;
public bool IsMoving => _isMoving;
public bool HasAlarm => _hasAlarm;
public double? TargetPosition => _targetPosition;
public double StartPosition => _startPosition;
#endregion
#region 公共方法
public void Connect(string port)
{
if (_isConnected)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备已连接");
// 模拟连接过程
Thread.Sleep(500);
_isConnected = true;
_simulationTimer = new System.Threading.Timer(SimulationUpdate, null, 0, 50);
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("设备已连接"));
}
public void Disconnect()
{
if (!_isConnected)
return;
_simulationTimer?.Dispose();
_simulationTimer = null;
_moveCancellation?.Cancel();
_isConnected = false;
_isMoving = false;
_currentVelocity = 0;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("设备已断开"));
}
public void Home()
{
if (!_isConnected)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备未连接");
if (_isMoving)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备正在运动中");
_isMoving = true;
_startPosition = _currentPosition;
_targetPosition = 0;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("开始回零"));
// 模拟回零过程
Task.Run(() =>
{
try
{
SimulateMotion(0, 20, 100, CancellationToken.None);
_isHomed = true;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("回零完成"));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
AlarmOccurred?.Invoke(this, new AlarmEventArgs($"回零失败: {ex.Message}"));
}
finally
{
_isMoving = false;
_currentVelocity = 0;
_targetPosition = null;
}
});
}
public void MoveAbsolute(double position, double velocity, double acceleration, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (!_isConnected)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备未连接");
if (_isMoving)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备正在运动中");
// 参数验证和日志
if (velocity <= 0) velocity = 10; // 默认值
if (acceleration <= 0) acceleration = 100; // 默认值
// 添加调试信息
Console.WriteLine($"MoveAbsolute: 位置={position:F3}, 速度={velocity:F2}, 加速度={acceleration:F1}");
_isMoving = true;
_startPosition = _currentPosition;
_targetPosition = position;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs($"开始绝对运动至 {position:F3}mm,速度{velocity:F1}mm/s"));
try
{
SimulateMotion(position, velocity, acceleration, cancellationToken);
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("绝对运动完成"));
}
finally
{
_isMoving = false;
_currentVelocity = 0;
_targetPosition = null;
}
}
public void MoveRelative(double distance, double velocity, double acceleration, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (!_isConnected)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备未连接");
if (_isMoving)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备正在运动中");
double targetPos = _currentPosition + distance;
MoveAbsolute(targetPos, velocity, acceleration, cancellationToken);
}
public void StartJog(double velocity)
{
if (!_isConnected)
throw new InvalidOperationException("设备未连接");
_currentVelocity = velocity;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs($"开始点动,速度: {velocity:F2}mm/s"));
}
public void StopJog()
{
_currentVelocity = 0;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("停止点动"));
}
public void Stop()
{
_moveCancellation?.Cancel();
_currentVelocity = 0;
_isMoving = false;
_targetPosition = null;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("急停执行"));
}
public void Reset()
{
_hasAlarm = false;
StatusChanged?.Invoke(this, new StatusChangedEventArgs("报警复位"));
}
#endregion
#region 私有方法
private void SimulateMotion(double targetPosition, double velocity, double acceleration, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
double startPos = _currentPosition;
double totalDistance = Math.Abs(targetPosition - startPos);
double direction = Math.Sign(targetPosition - startPos);
if (totalDistance < 0.001)
return;
// 添加调试日志
Console.WriteLine($"SimulateMotion: 起始={startPos:F3}, 目标={targetPosition:F3}, 速度={velocity:F2}, 加速度={acceleration:F1}");
DateTime startTime = DateTime.Now;
// 运动规划计算
double timeToMaxVelocity = velocity / acceleration;
double distanceToMaxVelocity = 0.5 * acceleration * timeToMaxVelocity * timeToMaxVelocity;
bool hasConstantVelocityPhase = totalDistance > 2 * distanceToMaxVelocity;
double actualMaxVelocity;
double totalTime;
double accelTime, constTime, decelTime;
double accelDist, constDist, decelDist;
if (hasConstantVelocityPhase)
{
// 梯形速度曲线
actualMaxVelocity = velocity;
accelTime = decelTime = actualMaxVelocity / acceleration;
accelDist = decelDist = 0.5 * acceleration * accelTime * accelTime;
constDist = totalDistance - accelDist - decelDist;
constTime = constDist / actualMaxVelocity;
totalTime = accelTime + constTime + decelTime;
Console.WriteLine($"梯形曲线: 最大速度={actualMaxVelocity:F2}, 总时间={totalTime:F2}s");
Console.WriteLine($"加速时间={accelTime:F2}s, 匀速时间={constTime:F2}s, 减速时间={decelTime:F2}s");
}
else
{
// 三角形速度曲线
actualMaxVelocity = Math.Sqrt(totalDistance * acceleration);
accelTime = decelTime = actualMaxVelocity / acceleration;
constTime = 0;
accelDist = decelDist = totalDistance / 2;
constDist = 0;
totalTime = accelTime + decelTime;
Console.WriteLine($"三角形曲线: 最大速度={actualMaxVelocity:F2}, 总时间={totalTime:F2}s");
}
// 执行运动仿真
while (Math.Abs(_currentPosition - targetPosition) > 0.001 && !cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
double elapsedTime = (DateTime.Now - startTime).TotalSeconds;
double newPosition;
double newVelocity;
string phase = "";
if (elapsedTime >= totalTime)
{
newPosition = targetPosition;
newVelocity = 0;
phase = "完成";
}
else if (elapsedTime <= accelTime)
{
// 加速阶段
newVelocity = acceleration * elapsedTime;
newPosition = startPos + direction * (0.5 * acceleration * elapsedTime * elapsedTime);
phase = "加速";
}
else if (elapsedTime <= accelTime + constTime)
{
// 匀速阶段
double constElapsed = elapsedTime - accelTime;
newVelocity = actualMaxVelocity;
newPosition = startPos + direction * (accelDist + actualMaxVelocity * constElapsed);
phase = "匀速";
}
else
{
// 减速阶段
double decelElapsed = elapsedTime - accelTime - constTime;
newVelocity = actualMaxVelocity - acceleration * decelElapsed;
newPosition = startPos + direction * (accelDist + constDist +
actualMaxVelocity * decelElapsed - 0.5 * acceleration * decelElapsed * decelElapsed);
phase = "减速";
}
// 限制位置范围
if (direction > 0)
newPosition = Math.Min(newPosition, targetPosition);
else
newPosition = Math.Max(newPosition, targetPosition);
CurrentPosition = newPosition;
CurrentVelocity = direction * Math.Abs(newVelocity);
// 输出调试信息
if ((int)(elapsedTime * 10) % 1 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"时间={elapsedTime:F2}s, 阶段={phase}, 位置={newPosition:F3}, 速度={CurrentVelocity:F2}");
}
Thread.Sleep(20);
}
CurrentPosition = targetPosition;
CurrentVelocity = 0;
Console.WriteLine("运动仿真结束");
}
private void SimulationUpdate(object state)
{
if (!_isConnected)
return;
// 模拟点动运动
if (!_isMoving && Math.Abs(_currentVelocity) > 0.001)
{
CurrentPosition += _currentVelocity * 0.05;
// 添加微小的位置抖动以模拟真实系统
CurrentPosition += (_random.NextDouble() - 0.5) * 0.001;
}
// 模拟随机报警
if (_random.NextDouble() < 0.0001)
{
_hasAlarm = true;
AlarmOccurred?.Invoke(this, new AlarmEventArgs("模拟系统报警"));
}
}
#endregion
}
#region 事件参数类
public class PositionChangedEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public double Position { get; }
public PositionChangedEventArgs(double position)
{
Position = position;
}
}
public class StatusChangedEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public string Status { get; }
public StatusChangedEventArgs(string status)
{
Status = status;
}
}
public class AlarmEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public string AlarmMessage { get; }
public AlarmEventArgs(string alarmMessage)
{
AlarmMessage = alarmMessage;
}
}
#endregion
}
🎯 设计亮点:
- 事件驱动:界面与业务逻辑完全解耦
- 属性保护:关键状态只能内部修改,外部只读
- 异步支持:所有运动操作支持取消和超时控制
在Windows窗体应用程序开发中,自定义控件的设计是展示UI设计能力和提升用户体验的重要方式。本文将详细介绍如何使用SkiaSharp图形库创建一个功能完善、视觉效果精美的时钟控件。我们将从基础实现开始,循序渐进地增加美化元素,最终打造出一个既实用又美观的自定义控件,SkiaSharp比系统自带的drawing要好一少。
SkiaSharp简介
SkiaSharp是Google Skia图形引擎的.NET绑定,提供了强大的2D绘图功能。它具有以下优势:
- 跨平台支持,可在Windows、macOS和Linux上运行
- 高性能渲染,适合实时绘制和动画
- 丰富的绘图API,包括路径、变换、渐变等
- 与.NET无缝集成
在Windows Forms应用程序中,可以通过SKControl控件轻松集成SkiaSharp的绘图能力。
基础时钟控件实现
控件结构设计
我们的时钟控件将继承自SKControl,主要包含以下核心组件:
- 表盘和刻度
- 时针、分针和秒针
- 中心点装饰
- 计时器用于更新时间显示
初始化与计时器设置
C#public ClockControl()
{
// 设置控件基本属性
BackColor = Color.White;
Size = new Size(300, 300);
// 初始化计时器,每秒更新一次
_timer = new System.Timers.Timer(1000);
_timer.Elapsed += OnTimerElapsed;
_timer.AutoReset = true;
_timer.Enabled = true;
}
private void OnTimerElapsed(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
// 在UI线程上刷新控件
if (InvokeRequired)
{
BeginInvoke(new Action(() => Invalidate()));
}
else
{
Invalidate();
}
}
这段代码创建了一个300x300像素的时钟控件,并设置一个每秒触发一次的计时器,用于更新控件显示。通过Invalidate()方法触发重绘,确保时钟指针根据当前时间实时更新。
绘制表盘和刻度
表盘是时钟的基础部分,包括外圈、刻度线和数字标记:
C#private void DrawClockFace(SKCanvas canvas, float centerX, float centerY, float radius)
{
// 绘制外圆
using var paint = new SKPaint
{
Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke,
Color = SKColors.Black,
StrokeWidth = 2,
IsAntialias = true
};
canvas.DrawCircle(centerX, centerY, radius, paint);
// 绘制刻度线和数字
for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++)
{
float angle = i * 6; // 每分钟6度
bool isHourMark = i % 5 == 0;
// 根据是否小时刻度设置不同长度和粗细
float innerRadius = isHourMark ? radius - 15 : radius - 5;
float strokeWidth = isHourMark ? 3 : 1;
// 绘制刻度线...
// 绘制小时数字...
}
}
这段代码使用SkiaSharp的绘图API绘制表盘和刻度。我们使用三角函数计算每个刻度的位置,并区分小时刻度(更粗、更长)和分钟刻度。
在网络安全日益重要的今天,你是否遇到过这样的困扰:网络异常时无法快速定位问题源头?想要监控应用程序的网络流量却无从下手?
作为一名C#开发者,掌握网络数据包捕获技术不仅能提升你的技术实力,更能在实际项目中发挥重要作用。无论是网络故障排查、性能监控,还是安全分析,数据包监控都是必备技能。
今天,我将带你用C#从零构建一个专业级的网络数据包过滤器,不仅界面美观、功能完整,还支持实时捕获、智能过滤、16进制分析等高级功能。学会这套技术,你就能轻松应对各种网络监控需求!
💡 问题分析:为什么需要自己开发数据包监控工具?
🔍 市面工具的局限性
- Wireshark:功能强大但对普通用户过于复杂
- Fiddler:仅支持HTTP/HTTPS协议
- 商业软件:成本高昂且不够灵活
🎯 自研优势
- 定制化:完全按业务需求设计
- 集成性:可无缝集成到现有系统
- 扩展性:后续功能迭代更加灵活
- 成本控制:一次开发长期使用
🚀 解决方案架构设计
我们将使用以下技术栈构建这个工具:
核心组件
- SharpPcap:网络数据包捕获库
- PacketDotNet:数据包解析引擎
- WinForms:用户界面框架
- Npcap:底层数据包捕获驱动
功能模块
- 网络接口管理:自动识别网卡设备
- 数据包捕获:实时抓取网络流量
- 协议解析:支持TCP/UDP/ICMP/HTTP等
- 智能过滤:多维度数据筛选
- 数据分析:16进制与文本双重展示
💻 代码实战:核心功能实现
🔧 环境准备
首先安装必要的NuGet包:
Bash<PackageReference Include="PacketDotNet" Version="1.4.8" />
<PackageReference Include="SharpPcap" Version="6.3.1" />
重要提醒:必须以管理员权限运行,并确保安装了Npcap驱动。
🏗️ 核心数据结构设计
C#public class PacketInfo
{
public DateTime Timestamp { get; set; }
public string SourceIP { get; set; } = "";
public string DestinationIP { get; set; } = "";
public string Protocol { get; set; } = "";
public int SourcePort { get; set; }
public int DestinationPort { get; set; }
public int Size { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; } = "";
public byte[] RawData { get; set; } = new byte[0]; // 原始数据存储
}
作为C#开发者,你是否经常为Dictionary的性能瓶颈而苦恼?在高并发场景下,标准的Dictionary和ConcurrentDictionary往往成为系统的性能短板。今天给大家介绍一个性能怪兽级的开源库——Faster.Map,它能让你的键值对操作速度提升数倍!
想象一下,当你的应用需要处理1.34亿条数据的查询、插入、更新操作时,传统Dictionary可能需要几秒钟,而Faster.Map只需要几十毫秒。这不是科幻,这是现实!本文将深入解析这个神器的使用方法和最佳实践。
🔍 传统Dictionary的痛点分析
在实际开发中,我们经常遇到这些性能问题:
1. 高负载因子下性能急剧下降
当Dictionary填充率超过75%时,哈希冲突增加,查询性能呈指数级下降。
2. 并发场景下的锁竞争
ConcurrentDictionary虽然线程安全,但在高并发下仍存在锁竞争问题。
3. 内存使用效率低下
传统Dictionary在处理大量数据时,内存碎片化严重,影响缓存命中率。
🔆 Nuget 安装包
注意:只有在.net 9以上版本,才支持CMap,其实在github下载src引用项目靠谱多了。
Markdownhttps://github.com/Wsm2110/Faster.Map?tab=readme-ov-file
在工业4.0时代,网络安全已成为制造业的生命线。想象一下:凌晨3点,工厂PLC突然离线,生产线停摆,损失以分钟计算...这样的噩梦每天都在全球工厂上演。
传统的网络监控工具往往只能告诉你"出问题了",却无法像资深工程师一样分析根因、预测风险。今天,我将手把手带你构建一个具备AI智能的工业网络监控系统,让机器拥有专家级的诊断能力。
本文将解决三个核心痛点:如何实时捕获工业网络异常、怎样让AI理解工业协议特征、如何构建可扩展的智能诊断架构。
🔍 问题分析:工业网络监控的三大挑战
挑战一:数据复杂性
工业网络不同于普通IT网络,涉及Modbus、EtherNet/IP、OPC-UA等专业协议,传统监控工具"看不懂"这些协议的业务含义。
挑战二:实时性要求
工业控制系统对延迟极其敏感,毫秒级的异常可能导致设备损坏,需要实时分析和即时响应。
挑战三:专业知识门槛
网络异常的根因分析需要深厚的工业自动化经验,普通运维人员往往力不从心。
💡 解决方案:Semantic Kernel + 实时数据流
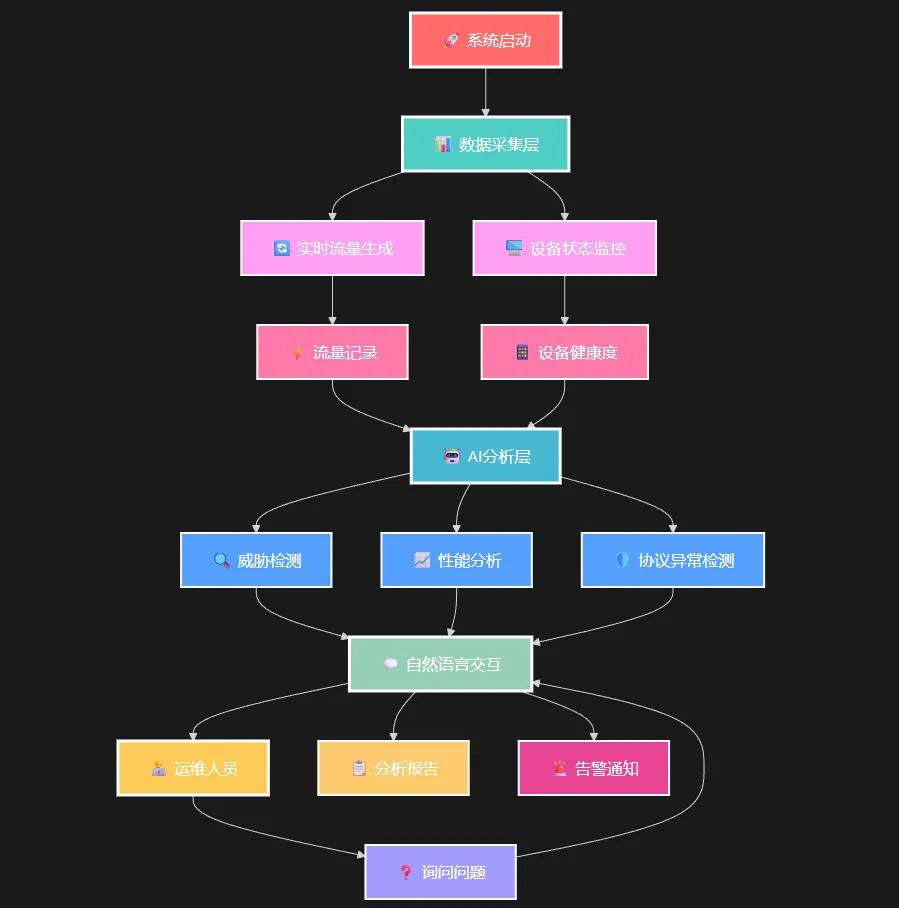
🏗️ 架构设计思路
我们采用三层架构:
- 数据采集层:实时生成工业网络流量数据
- AI分析层:基于Semantic Kernel的智能诊断引擎
- 交互层:自然语言对话式运维界面
核心优势:让AI成为你的网络专家助手,用对话方式获取专业洞察。
🚩 设计流程
🛠️ 代码实战:构建智能监控系统
📊 第一步:定义工业网络数据模型
C#public enum NetworkProtocol
{
TCP, UDP, HTTP, HTTPS,
Modbus, // 工业串行通信协议
EtherNetIP, // 以太网工业协议
OPCua, // 开放平台通信统一架构
Profinet, // 西门子工业以太网
EtherCAT // 实时以太网
}
public enum NetworkSegment
{
OTNetwork, // 操作技术网络
ITNetwork, // 信息技术网络
DMZ, // 非军事化区域
ControlNetwork, // 控制网络
SafetyNetwork, // 安全网络
WirelessNetwork // 无线网络
}
public class NetworkTrafficRecord
{
public string Id { get; set; } = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
public DateTime Timestamp { get; set; }
public string SourceIP { get; set; }
public string DestinationIP { get; set; }
public NetworkProtocol Protocol { get; set; }
public long BytesSent { get; set; }
public long BytesReceived { get; set; }
public double Latency { get; set; }
public double PacketLoss { get; set; }
public TrafficType TrafficType { get; set; }
public NetworkSegment Segment { get; set; }
public string AlertMessage { get; set; }
}