目录
你是否曾经为了处理未知结构的JSON而写了一大堆反射代码?是否为了实现灵活的API而让代码变得臃肿不堪?今天我们来聊聊C#中一个被严重低估的特性——动态编程(Dynamic Programming)。
掌握System.Dynamic命名空间,你将告别繁琐的反射操作,让代码变得更加优雅和高效。本文将通过5个实战场景,带你深入理解并应用C#的动态特性。
🎯 为什么需要动态编程?
在实际开发中,我们经常遇到这些痛点:
- JSON数据结构不固定:接口返回的数据格式经常变化
- 配置文件灵活性不够:需要支持动态添加属性
- 插件系统扩展困难:第三方组件接口不统一
- 反射性能问题:大量使用反射导致性能下降
💡 解决方案:System.Dynamic全家桶
🚀 方案一:ExpandoObject - 动态对象的最佳选择
ExpandoObject是动态编程的明星类,它允许我们在运行时动态添加和删除成员。这是个好东西,还没有这个出来前处理这个挺麻烦的。
c#// 使用ExpandoObject的优雅方式
public class DynamicApproach
{
public void ProcessJson(string json)
{
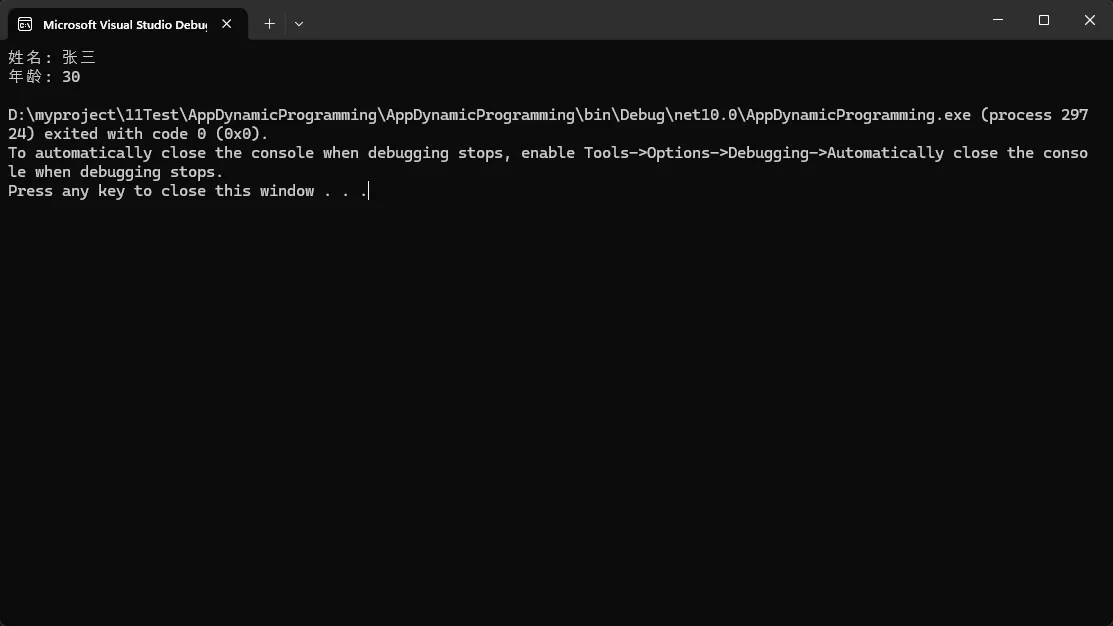
dynamic obj = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<ExpandoObject>(json);
// 直接访问属性,如同静态类型一样自然
Console.WriteLine($"姓名: {obj.name}");
Console.WriteLine($"年龄: {obj.age}");
// 动态添加新属性
obj.processTime = DateTime.Now;
obj.status = "已处理";
}
}
💰 实际应用场景:
- API响应处理
- 配置文件读取
- 临时数据容器
⚠️ 坑点提醒:
- 没有编译时类型检查,拼写错误只能在运行时发现
- 性能略低于静态类型
🔧 方案二:DynamicObject - 自定义动态行为
当ExpandoObject无法满足复杂需求时,继承DynamicObject可以实现完全自定义的动态行为。
c#using System.Dynamic;
using System.Net.Http.Json;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
namespace AppDynamicProgramming
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
dynamic config = new SmartConfig();
// 动态设置属性
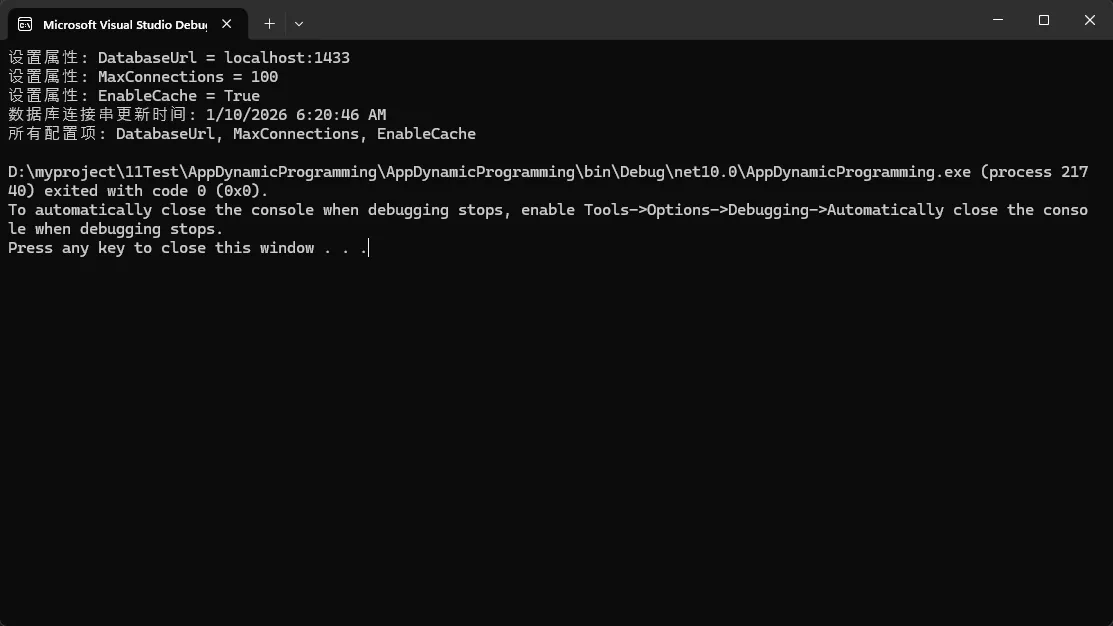
config.DatabaseUrl = "localhost:1433";
config.MaxConnections = 100;
config.EnableCache = true;
// 动态调用方法
var updateTime = config.GetUpdateTime("DatabaseUrl");
var allProps = config.GetAllProperties();
Console.WriteLine($"数据库连接串更新时间: {updateTime}");
Console.WriteLine($"所有配置项: {string.Join(", ", allProps)}");
}
}
public class SmartConfig : DynamicObject
{
private Dictionary<string, object> _properties = new Dictionary<string, object>();
private Dictionary<string, DateTime> _updateTimes = new Dictionary<string, DateTime>();
// 重写获取成员的行为
public override bool TryGetMember(GetMemberBinder binder, out object result)
{
string propertyName = binder.Name;
// 添加日志记录
Console.WriteLine($"访问属性: {propertyName}");
return _properties.TryGetValue(propertyName, out result);
}
// 重写设置成员的行为
public override bool TrySetMember(SetMemberBinder binder, object value)
{
string propertyName = binder.Name;
// 自动记录更新时间
_updateTimes[propertyName] = DateTime.Now;
_properties[propertyName] = value;
Console.WriteLine($"设置属性: {propertyName} = {value}");
return true;
}
// 自定义方法调用
public override bool TryInvokeMember(InvokeMemberBinder binder, object[] args, out object result)
{
result = null;
switch (binder.Name)
{
case "GetUpdateTime":
if (args.Length == 1 && args[0] is string propName)
{
result = _updateTimes.TryGetValue(propName, out DateTime time) ? time : (DateTime?)null;
return true;
}
break;
case "GetAllProperties":
result = _properties.Keys.ToList();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
💰 实际应用场景:
- 智能配置系统
- ORM框架
- 插件接口适配器
🌟 方案三:dynamic关键字 - 延迟绑定的魅力
dynamic关键字让我们可以绕过编译时类型检查,实现真正的鸭子类型编程。不过大量用这个dynamic效率肯定会低一些的,这块需要自己把握 。
c#public class DynamicDemo
{
// 通用的对象处理方法
public void ProcessAnyObject(dynamic obj)
{
// 不管obj是什么类型,只要有这些成员就能正常工作
try
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {obj.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($"Value: {obj.Value}");
obj.Process();
}
catch (RuntimeBinderException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"动态绑定失败: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// COM组件交互的完美解决方案
public void WorkWithExcel()
{
// 不需要引用Office PIA程序集
Type excelType = Type.GetTypeFromProgID("Excel.Application");
dynamic excel = Activator.CreateInstance(excelType);
excel.Visible = true;
dynamic workbook = excel.Workbooks.Add();
dynamic worksheet = workbook.ActiveSheet;
// 直接操作Excel对象,如同本地对象一样
worksheet.Cells[1, 1].Value = "Hello Dynamic!";
worksheet.Cells[1, 2].Value = DateTime.Now;
// 清理资源
workbook.Close();
excel.Quit();
}
}
// 测试不同类型的对象
public class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; } = "张三";
public int Value { get; set; } = 100;
public void Process() => Console.WriteLine("Person.Process() called");
}
public class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; } = "iPhone";
public decimal Value { get; set; } = 9999;
public void Process() => Console.WriteLine("Product.Process() called");
}
💰 实际应用场景:
- COM组件交互,当年调用excel,word这块还是挺费事的,每个要找接口,用dynamic确定简单不少,不过这些年基本没用过什么com组件了。
- 第三方库封装
- 动态代理实现
🎨 方案四:IDynamicMetaObjectProvider - 高级定制接口
对于需要完全控制动态行为的场景,实现IDynamicMetaObjectProvider接口提供了最大的灵活性。
c#using Microsoft.CSharp.RuntimeBinder;
using System;
using System.Dynamic;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
namespace AppDynamicProgramming
{
public class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Value { get; set; }
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
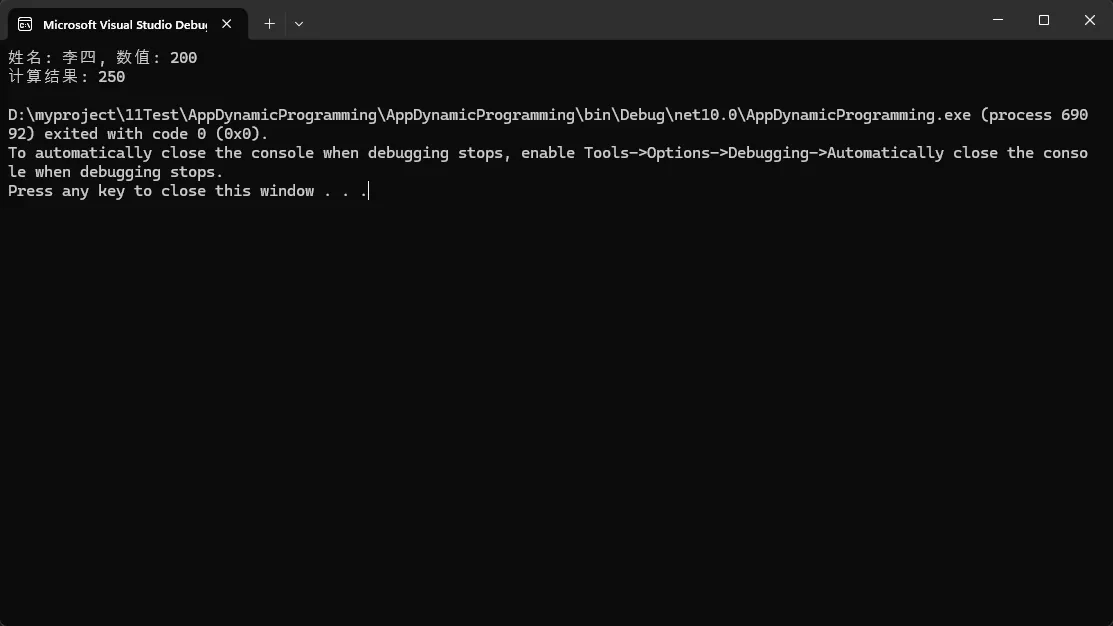
var person = new Person { Name = "李四", Value = 200 };
dynamic proxy = new FlexibleProxy(person);
var flexProxy = (FlexibleProxy)proxy; // 转换为具体类型
flexProxy.AddMethod("GetInfo", args => $"姓名: {person.Name}, 数值: {person.Value}");
flexProxy.AddMethod("Calculate", args => (int)args[0] + person.Value);
Console.WriteLine(proxy.GetInfo());
Console.WriteLine($"计算结果: {proxy.Calculate(50)}");
}
}
public class FlexibleProxy : IDynamicMetaObjectProvider
{
private readonly object _target;
private readonly Dictionary<string, Func<object[], object>> _customMethods;
public FlexibleProxy(object target)
{
_target = target;
_customMethods = new Dictionary<string, Func<object[], object>>();
}
// 添加自定义方法
public void AddMethod(string name, Func<object[], object> method)
{
_customMethods[name] = method;
}
public DynamicMetaObject GetMetaObject(Expression parameter)
{
return new FlexibleProxyMetaObject(parameter, this, _target);
}
internal bool TryInvokeCustomMethod(string name, object[] args, out object result)
{
if (_customMethods.TryGetValue(name, out var method))
{
result = method(args);
return true;
}
result = null;
return false;
}
}
// 自定义MetaObject实现
public class FlexibleProxyMetaObject : DynamicMetaObject
{
private readonly FlexibleProxy _proxy;
private readonly object _target;
public FlexibleProxyMetaObject(Expression expression, FlexibleProxy proxy, object target)
: base(expression, BindingRestrictions.Empty, proxy)
{
_proxy = proxy;
_target = target;
}
public override DynamicMetaObject BindInvokeMember(InvokeMemberBinder binder, DynamicMetaObject[] args)
{
var resultVar = Expression.Variable(typeof(object), "result");
var argExprs = args.Select(a => Expression.Convert(a.Expression, typeof(object)));
var argsArray = Expression.NewArrayInit(typeof(object), argExprs);
var tryCustomMethodCall = Expression.Call(
Expression.Constant(_proxy),
typeof(FlexibleProxy).GetMethod("TryInvokeCustomMethod", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance),
Expression.Constant(binder.Name),
argsArray,
resultVar
);
var condition = Expression.Condition(
tryCustomMethodCall,
resultVar,
Expression.Throw(
Expression.New(
typeof(MissingMethodException).GetConstructor(new[] { typeof(string) }),
Expression.Constant($"Method '{binder.Name}' not found.")
),
typeof(object)
),
typeof(object)
);
var block = Expression.Block(
new[] { resultVar },
condition
);
return new DynamicMetaObject(block, BindingRestrictions.GetTypeRestriction(Expression, LimitType));
}
}
}
🛡️ 方案五:性能优化与最佳实践,你认为的可能不对?
c#public class PerformanceOptimizedDynamic
{
// 缓存CallSite以提高性能
private static readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object>>>
GetMemberSites = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object>>>();
private static readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object, object>>>
SetMemberSites = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object, object>>>();
public static object GetMember(object target, string memberName)
{
var site = GetMemberSites.GetOrAdd(memberName, name =>
CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object>>.Create(
Binder.GetMember(CSharpBinderFlags.None, name, typeof(PerformanceOptimizedDynamic),
new[] { CSharpArgumentInfo.Create(CSharpArgumentInfoFlags.None, null) })
)
);
return site.Target(site, target);
}
public static void SetMember(object target, string memberName, object value)
{
var site = SetMemberSites.GetOrAdd(memberName, name =>
CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object, object>>.Create(
Binder.SetMember(CSharpBinderFlags.None, name, typeof(PerformanceOptimizedDynamic),
new[] {
CSharpArgumentInfo.Create(CSharpArgumentInfoFlags.None, null),
CSharpArgumentInfo.Create(CSharpArgumentInfoFlags.None, null)
})
)
);
site.Target(site, target, value);
}
// 性能测试对比
public static void PerformanceTest()
{
var obj = new ExpandoObject();
dynamic dynamicObj = obj;
// 预热
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
dynamicObj.TestProperty = i;
var value = dynamicObj.TestProperty;
}
// 测试直接dynamic调用
var sw1 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
dynamicObj.TestProperty = i;
var value = dynamicObj.TestProperty;
}
sw1.Stop();
// 测试缓存CallSite调用
var sw2 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
SetMember(obj, "TestProperty", i);
var value = GetMember(obj, "TestProperty");
}
sw2.Stop();
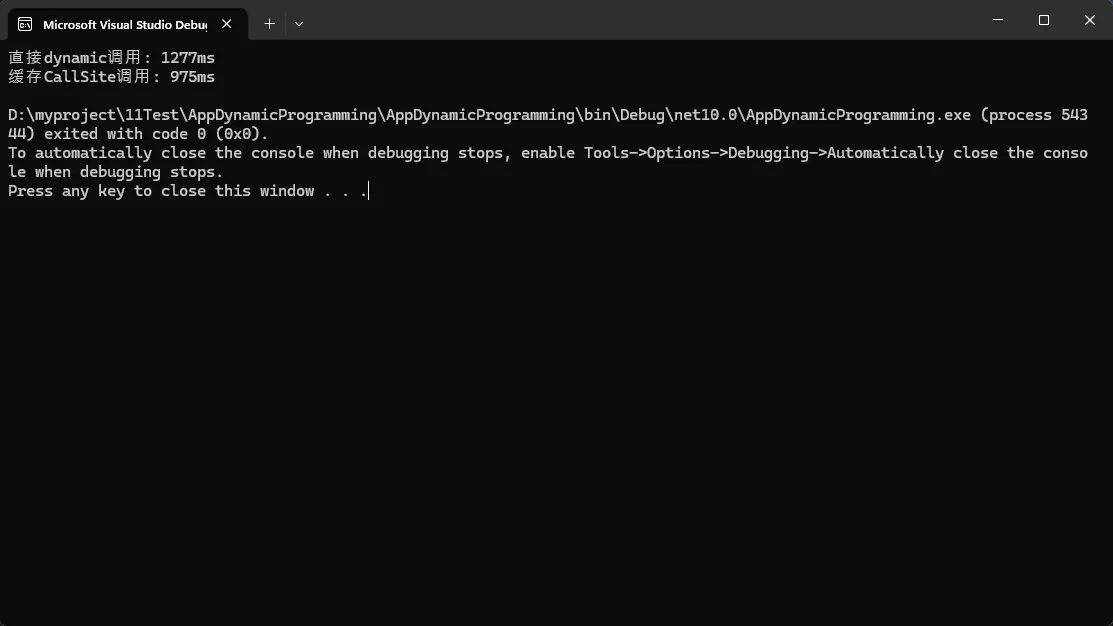
Console.WriteLine($"直接dynamic调用: {sw1.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Console.WriteLine($"缓存CallSite调用: {sw2.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
}
}
按一惯逻辑,写一缓存肯定效率上去,实际上dynamic每个调用点生成CallSite,效率更快。
上面版本需要修改一下,缓存版本才会快一些。
c#// 获取缓存的CallSite(避免循环中的字典查找)
var setSite = SetMemberSites.GetOrAdd("TestProperty", name =>
CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object, object>>.Create(
Binder.SetMember(CSharpBinderFlags.None, name, typeof(PerformanceOptimizedDynamic),
new[] {
CSharpArgumentInfo.Create(CSharpArgumentInfoFlags.None, null),
CSharpArgumentInfo.Create(CSharpArgumentInfoFlags.None, null)
})
)
);
var getSite = GetMemberSites.GetOrAdd("TestProperty", name =>
CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, object>>.Create(
Binder.GetMember(CSharpBinderFlags.None, name, typeof(PerformanceOptimizedDynamic),
new[] { CSharpArgumentInfo.Create(CSharpArgumentInfoFlags.None, null) })
)
);
// 测试缓存CallSite调用
var sw2 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
setSite.Target(setSite, obj, i);
var value = getSite.Target(getSite, obj);
}
sw2.Stop();
🔍 常见坑点与解决方案
❌ 常犯错误1:过度使用dynamic
c#// 错误示例 - 能用静态类型就别用dynamic
public dynamic ProcessData(dynamic input)
{
return new { Result = input.Value * 2 };
}
// 正确示例 - 明确输入输出类型
public ProcessResult ProcessData<T>(T input) where T : IProcessable
{
return new ProcessResult { Value = input.Process() };
}
在属性名固定的情况下,直接使用
dynamic是最优选择;在属性名动态变化时,缓存CallSite才能体现出优势。
❌ 常犯错误2:忽略异常处理
c#// 错误示例 - 没有异常处理
public void BadExample(dynamic obj)
{
var result = obj.SomeMethod(); // 可能抛出RuntimeBinderException
}
// 正确示例 - 完善的异常处理
public void GoodExample(dynamic obj)
{
try
{
if (HasMethod(obj, "SomeMethod"))
{
var result = obj.SomeMethod();
}
}
catch (RuntimeBinderException ex)
{
// 记录日志并提供降级方案
Logger.LogWarning($"动态调用失败: {ex.Message}");
}
}
private bool HasMethod(object obj, string methodName)
{
return obj.GetType().GetMethod(methodName) != null;
}
💎 三个收藏级代码模板
1. 通用JSON动态处理器
c#public static class JsonDynamicHelper
{
public static dynamic ParseAndEnhance(string json)
{
dynamic obj = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<ExpandoObject>(json);
var dict = (IDictionary<string, object>)obj;
// 添加元数据
dict["_parseTime"] = DateTime.Now;
dict["_hasError"] = false;
return obj;
}
}
2. 安全的动态属性访问器
c#public static class SafeDynamic
{
public static T GetValue<T>(dynamic obj, string propertyName, T defaultValue = default(T))
{
try
{
var dict = obj as IDictionary<string, object>;
if (dict?.ContainsKey(propertyName) == true)
{
return (T)Convert.ChangeType(dict[propertyName], typeof(T));
}
return defaultValue;
}
catch
{
return defaultValue;
}
}
}
3. 动态对象构建器
c#public class DynamicBuilder
{
private readonly ExpandoObject _obj = new ExpandoObject();
public DynamicBuilder Set(string key, object value)
{
((IDictionary<string, object>)_obj)[key] = value;
return this;
}
public dynamic Build() => _obj;
}
🎯 总结与展望
通过本文的学习,我们掌握了C#动态编程的精髓:
- ExpandoObject:最简单实用的动态对象解决方案
- DynamicObject:自定义动态行为的强大基类
- dynamic关键字:实现鸭子类型编程的利器
动态编程不是银弹,但在正确的场景下使用,能让我们的代码更加优雅和灵活。记住:能用静态类型就用静态类型,需要灵活性时才考虑动态特性。
🤔 思考题:
- 在你的项目中,有哪些场景可以用动态编程来简化代码?
- 你觉得动态编程的最大优势和劣势分别是什么?
💬 互动时间:
如果你在使用C#动态特性时遇到过什么有趣的问题或有独特的应用场景,欢迎在评论区分享!让我们一起探讨更多动态编程的可能性。
觉得这篇文章对你有帮助吗?请转发给更多需要的C#开发同行,让更多人受益于动态编程的强大威力!
关注我,获取更多C#开发实战技巧和最佳实践分享!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!