目录
🚀 .NET 8新特性解析:FrozenDictionary让你的应用性能起飞!
你还在为频繁的字典查询拖慢应用性能而头疼吗?还在纠结内存占用过高的问题吗?C#开发者的福音来了!.NET 8引入的FrozenDictionary<TKey,TValue>,专为高频查询场景而生,让你的应用性能瞬间提升30%+!
本文将深度解析这个性能优化神器的使用技巧,带你掌握从入门到精通的完整攻略。无论你是初级开发者还是资深架构师,都能从中获得实用的编程技巧和性能优化方案。
🎯 问题分析:传统Dictionary的性能瓶颈
📊 性能痛点梳理
在企业级应用开发中,我们经常遇到这些场景:
- 配置数据查询:系统启动时加载,运行期间频繁读取
- 枚举映射表:状态码对应关系,查询密集但修改极少
- 缓存数据访问:热点数据反复查询,写入频率极低
- 路由映射表:URL路径匹配,高并发场景下的性能瓶颈
传统的Dictionary<TKey,TValue>虽然功能强大,但在这些 "一次写入,多次读取" 的场景中存在明显短板:
🔥 核心问题分析
- 内存开销过大:为了支持动态修改,预留了大量冗余空间
- 哈希冲突处理:通用哈希策略无法针对特定数据集优化
- 线程安全开销:并发读取时的同步机制影响性能
💡 解决方案:FrozenDictionary的五大核心优势
🎯 1. 极致的查询性能优化
FrozenDictionary在创建时会分析你的数据特征,量身定制最优的哈希策略:
c#using System.Collections.Frozen;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AppFrozenDictionary
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var normalDict = new Dictionary<string, int>
{
{ "Success", 200 },
{ "NotFound", 404 },
{ "ServerError", 500 }
};
// 性能优化方式:查询速度提升 30%+(取决于场景与平台)
var frozenDict = new Dictionary<string, int>
{
{ "Success", 200 },
{ "NotFound", 404 },
{ "ServerError", 500 }
}.ToFrozenDictionary();
const int iterations = 1_000_000;
// 热身(JIT、缓存)
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
var s1 = normalDict["Success"];
var s2 = frozenDict["Success"];
}
// 测试传统 Dictionary
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
int result1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
result1 += normalDict["Success"];
}
sw.Stop();
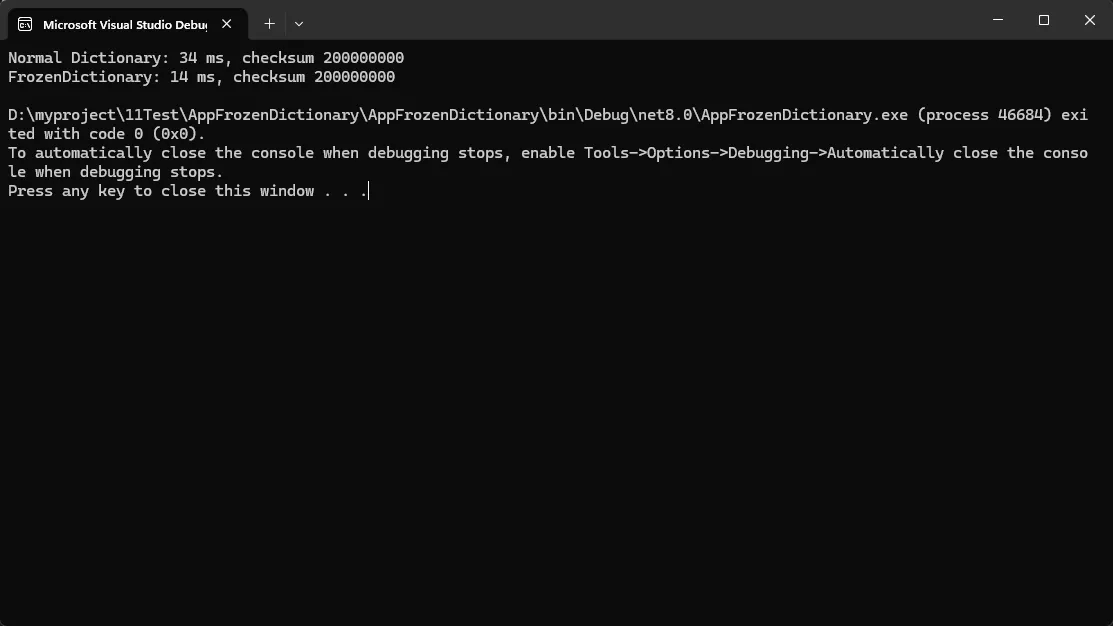
Console.WriteLine($"Normal Dictionary: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms, checksum {result1}");
// 测试 FrozenDictionary
sw.Restart();
int result2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
result2 += frozenDict["Success"];
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"FrozenDictionary: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms, checksum {result2}");
}
}
}
⚡ 性能提升秘密:
- 内部使用完美哈希算法,几乎零冲突
- 针对具体数据集优化的哈希函数
- 内存布局紧凑,CPU缓存友好
🎯 2. 线程安全的天然优势
c#// 高并发场景的最佳实践
public class ConfigurationService
{
// 🔒 天然线程安全,无需额外同步机制
private static readonly FrozenDictionary<string, string> _configs;
static ConfigurationService()
{
// 启动时一次性加载配置(模拟)
var configDict = LoadConfigFromDatabase();
// 直接从源字典构建 frozen(避免不必要的多余副本)
_configs = configDict.ToFrozenDictionary();
}
// 高并发访问,零锁开销
public string GetConfig(string key) =>
_configs.TryGetValue(key, out var value) ? value : string.Empty;
// 支持安全的并行查询
public Dictionary<string, string> GetMultipleConfigs(IEnumerable<string> keys)
{
// AsParallel + ToDictionary 的组合适合中等量并行查询并利用多个内核
return keys
.AsParallel()
.Where(key => _configs.ContainsKey(key))
.ToDictionary(key => key, key => _configs[key]);
}
// 此处生成大量配置以模拟真实场景
private static Dictionary<string, string> LoadConfigFromDatabase(int count = 100_000)
{
var dict = new Dictionary<string, string>(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
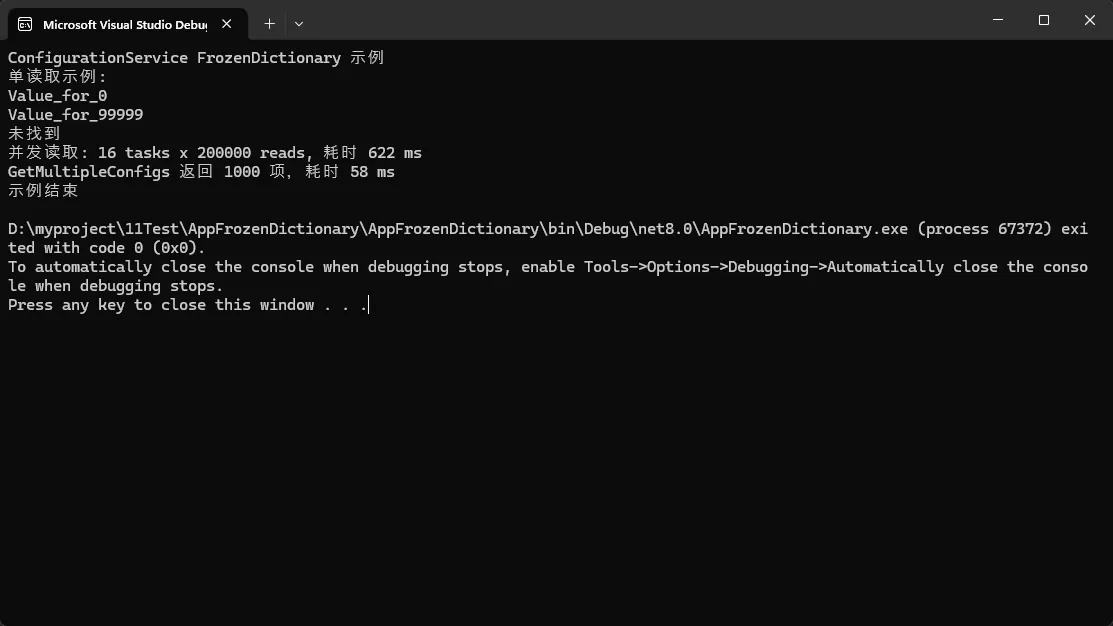
dict[$"Key_{i}"] = $"Value_for_{i}";
}
return dict;
}
}
🎯 3. 智能的创建优化策略
c#using System.Collections.Frozen;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AppFrozenDictionary
{
public static class DataMappingFactory
{
public static FrozenDictionary<TKey, TValue> CreateOptimized<TKey, TValue>(
IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> source)
where TKey : notnull
{
var pairs = source is KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>[] arr ? arr : source.ToArray();
return pairs.Length switch
{
0 => FrozenDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Empty,
< 10 => pairs.ToFrozenDictionary(),
_ => pairs.ToFrozenDictionary(EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default)
};
}
}
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("DataMappingFactory 示例");
var empty = DataMappingFactory.CreateOptimized<string, string>(Enumerable.Empty<KeyValuePair<string, string>>());
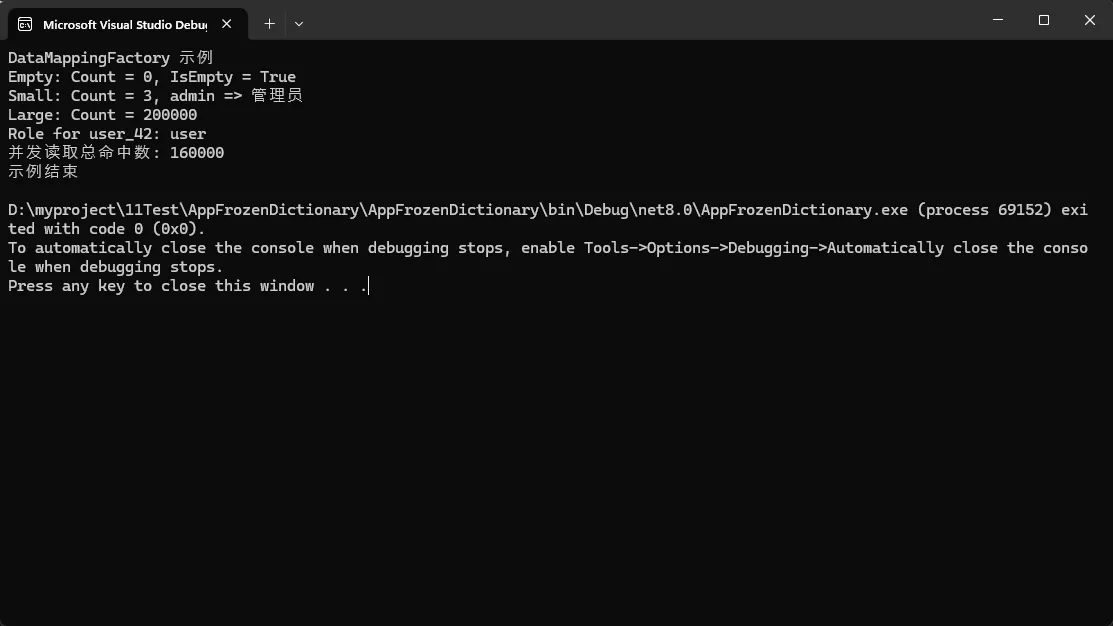
Console.WriteLine($"Empty: Count = {empty.Count}, IsEmpty = {ReferenceEquals(empty, FrozenDictionary<string, string>.Empty)}");
var smallSource = new[]
{
new KeyValuePair<string,string>("admin", "管理员"),
new KeyValuePair<string,string>("user", "普通用户"),
new KeyValuePair<string,string>("guest", "访客")
};
var small = DataMappingFactory.CreateOptimized(smallSource);
Console.WriteLine($"Small: Count = {small.Count}, admin => {small["admin"]}");
var userRolePairs = await GetUserRolesFromDatabaseAsync(200_000);
var large = DataMappingFactory.CreateOptimized(userRolePairs);
Console.WriteLine($"Large: Count = {large.Count}");
Console.WriteLine($"Role for user_42: {(large.TryGetValue("user_42", out var r) ? r : "未找到")}");
var tasks = Enumerable.Range(0, Environment.ProcessorCount)
.Select(_ => Task.Run(() =>
{
int hits = 0;
var rnd = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
var key = "user_" + rnd.Next(0, large.Count);
if (large.ContainsKey(key)) hits++;
}
return hits;
}))
.ToArray();
var results = await Task.WhenAll(tasks);
Console.WriteLine($"并发读取总命中数: {results.Sum()}");
Console.WriteLine("示例结束");
}
private static Task<IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, string>>> GetUserRolesFromDatabaseAsync(int count = 1000)
{
return Task.Run<IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, string>>>(() =>
{
var list = new List<KeyValuePair<string, string>>(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
var key = $"user_{i}";
var role = (i % 100 == 0) ? "admin" : "user";
list.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, string>(key, role));
}
return list;
});
}
}
}
🎯 4. LINQ扩展的完美支持
c#public class Product
{
public string Sku { get; init; }
public string Name { get; init; }
public decimal Price { get; init; }
public Product(string sku, string name, decimal price)
{
Sku = sku ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(sku));
Name = name ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(name));
Price = price;
}
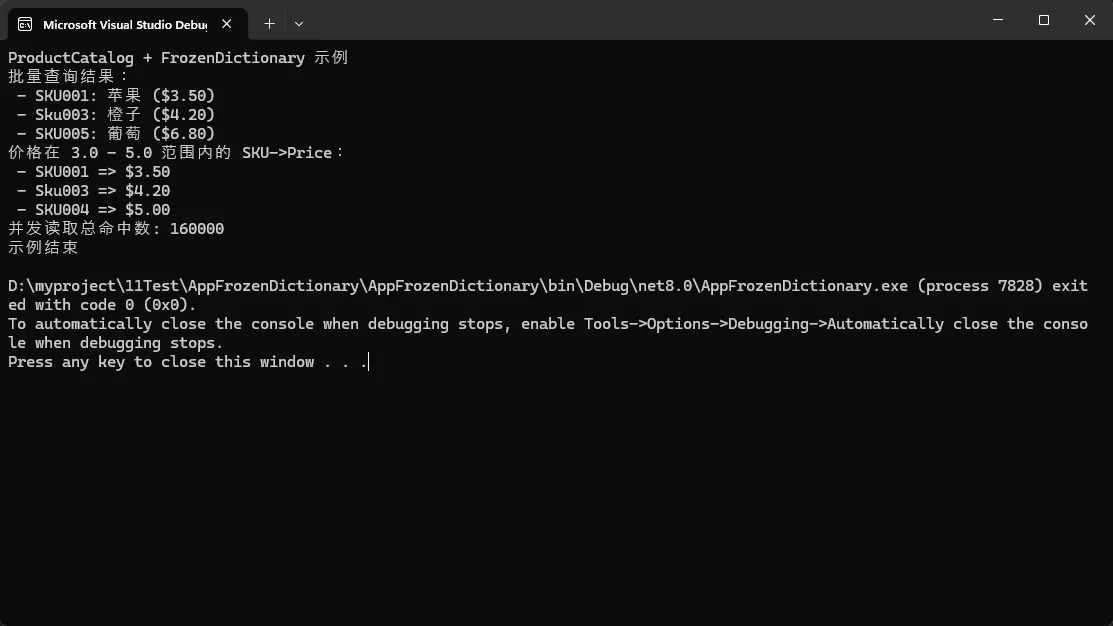
public override string ToString() => $"{Sku}: {Name} ({Price:C})";
}
public class ProductCatalog
{
private readonly FrozenDictionary<string, Product> _products;
public ProductCatalog(IEnumerable<Product> products)
{
_products = products.ToFrozenDictionary(
p => p.Sku,
p => p,
StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
}
public IEnumerable<Product> GetProductsBatch(IEnumerable<string> skus)
{
return skus.Select(sku => _products.TryGetValue(sku, out var product) ? product : null)
.Where(p => p != null)!;
}
public FrozenDictionary<string, decimal> GetPricesInRange(decimal minPrice, decimal maxPrice)
{
return _products.Where(kvp => kvp.Value.Price >= minPrice && kvp.Value.Price <= maxPrice)
.ToFrozenDictionary(kvp => kvp.Key, kvp => kvp.Value.Price);
}
}
🔥 收藏级代码模板
模板1:高性能配置管理器
c#// 配置源接口
public interface IConfigSource<T> where T : class
{
Task<IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, T>>> LoadAsync(CancellationToken ct = default);
}
public class MemoryConfigSource<T> : IConfigSource<T> where T : class
{
private readonly Func<int, IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, T>>> _factory;
private int _version;
public MemoryConfigSource(Func<int, IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, T>>> factory, int startVersion = 0)
{
_factory = factory ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(factory));
_version = startVersion;
}
public void BumpVersion() => Interlocked.Increment(ref _version);
public Task<IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, T>>> LoadAsync(CancellationToken ct = default)
{
int v = Volatile.Read(ref _version);
var data = _factory(v);
return Task.FromResult(data);
}
}
public sealed class HighPerformanceConfigManager<T> : IDisposable where T : class
{
private volatile FrozenDictionary<string, T> _configs = FrozenDictionary<string, T>.Empty;
private readonly ReaderWriterLockSlim _lock = new(LockRecursionPolicy.NoRecursion);
private readonly IConfigSource<T> _source;
private readonly CancellationTokenSource _cts = new();
private readonly Task? _backgroundRefresher;
public event Action<int>? OnReloaded;
public HighPerformanceConfigManager(IConfigSource<T> source, TimeSpan? periodicReload = null)
{
_source = source ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(source));
RefreshConfigsAsync().GetAwaiter().GetResult();
if (periodicReload.HasValue && periodicReload.Value > TimeSpan.Zero)
{
_backgroundRefresher = Task.Run(() => PeriodicReloadLoop(periodicReload.Value, _cts.Token));
}
}
public T? GetConfig(string key) =>
_configs.TryGetValue(key, out var config) ? config : null;
public IReadOnlyDictionary<string, T> GetConfigs(IEnumerable<string> keys) =>
keys.AsParallel()
.Where(key => _configs.ContainsKey(key))
.ToDictionary(key => key, key => _configs[key]);
public void RefreshConfigs()
=> RefreshConfigsAsync().GetAwaiter().GetResult();
public async Task RefreshConfigsAsync(CancellationToken ct = default)
{
var newEntries = await _source.LoadAsync(ct).ConfigureAwait(false);
var frozen = newEntries.ToFrozenDictionary(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
_lock.EnterWriteLock();
try
{
_configs = frozen;
}
finally
{
_lock.ExitWriteLock();
}
OnReloaded?.Invoke(frozen.Count);
}
private async Task PeriodicReloadLoop(TimeSpan interval, CancellationToken ct)
{
try
{
while (!ct.IsCancellationRequested)
{
await Task.Delay(interval, ct).ConfigureAwait(false);
try
{
await RefreshConfigsAsync(ct).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException) when (ct.IsCancellationRequested)
{
break;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Debug.WriteLine($"Periodic reload failed: {ex}");
}
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException) { }
}
public void Dispose()
{
_cts.Cancel();
try { _backgroundRefresher?.Wait(); } catch { }
_lock.Dispose();
_cts.Dispose();
}
}
模板2:多级缓存查询优化器
c#/// <summary>
/// 多级缓存查询优化器 - 结合FrozenDictionary实现极致性能
/// </summary>
public class MultiLevelQueryOptimizer<TKey, TValue>
where TKey : notnull
where TValue : class
{
private readonly FrozenDictionary<TKey, TValue> _l1Cache;
private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue> _l2Cache;
private readonly Func<TKey, Task<TValue?>> _dataLoader;
public MultiLevelQueryOptimizer(
IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> hotData,
Func<TKey, Task<TValue?>> dataLoader)
{
_l1Cache = hotData.ToFrozenDictionary(); // 热点数据冻结
_l2Cache = new ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>();
_dataLoader = dataLoader;
}
public async ValueTask<TValue?> GetAsync(TKey key)
{
// L1: 冻结字典查询 - 最快
if (_l1Cache.TryGetValue(key, out var hotValue))
return hotValue;
// L2: 并发字典查询 - 次快
if (_l2Cache.TryGetValue(key, out var cachedValue))
return cachedValue;
// L3: 数据源加载 - 最慢,但会缓存结果
var loadedValue = await _dataLoader(key).ConfigureAwait(false);
if (loadedValue != null)
{
_l2Cache.TryAdd(key, loadedValue);
}
return loadedValue;
}
// 批量查询优化
public async Task<Dictionary<TKey, TValue>> GetBatchAsync(IEnumerable<TKey> keys)
{
var keyList = keys.ToList();
var result = new Dictionary<TKey, TValue>(keyList.Count);
// 并行处理L1和L2缓存(保持线程安全)
var cacheResults = keyList.AsParallel()
.Select(key => new { Key = key, Value = GetFromCache(key) })
.Where(x => x.Value != null)
.ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value!);
foreach (var kvp in cacheResults)
result[kvp.Key] = kvp.Value;
// 加载缺失的数据(并行发起加载)
var missingKeys = keyList.Except(result.Keys).ToList();
if (missingKeys.Count > 0)
{
var loadTasks = missingKeys.Select(async key =>
new { Key = key, Value = await _dataLoader(key).ConfigureAwait(false) });
var loadResults = await Task.WhenAll(loadTasks).ConfigureAwait(false);
foreach (var item in loadResults.Where(x => x.Value != null))
{
result[item.Key] = item.Value!;
_l2Cache.TryAdd(item.Key, item.Value!);
}
}
return result;
}
private TValue? GetFromCache(TKey key) =>
_l1Cache.TryGetValue(key, out var l1Value) ? l1Value :
_l2Cache.TryGetValue(key, out var l2Value) ? l2Value : null;
}
🎯 核心要点总结
三个关键性能提升点:
- 查询速度提升30-50% - 完美哈希算法 + 紧凑内存布局
- 内存占用减少40% - 去除冗余空间 + 优化数据结构
- 并发性能零开销 - 天然不可变 + 无锁读取
最佳使用场景:
- ✅ 配置数据、枚举映射、路由表
- ✅ 缓存热点数据、常量查询表
- ✅ 高并发只读场景、启动时预加载数据
避免使用场景:
- ❌ 频繁修改的动态数据
- ❌ 小数据集(<10项)的临时查询
- ❌ 创建开销敏感的热路径
💬 互动讨论时间
- 你的项目中有哪些高频查询场景可以用FrozenDictionary优化?
- 在实际应用中,你遇到过哪些Dictionary性能瓶颈问题?
欢迎在评论区分享你的使用经验和遇到的问题!如果这篇文章对你有帮助,请转发给更多同行,让我们一起提升.NET应用的性能表现!
🔗 延伸学习建议:
- 深入了解.NET 8的其他集合优化特性
- 学习内存分析工具的使用技巧
- 探索更多LINQ性能优化方案
觉得内容有用请点赞收藏,持续分享更多实用的C#开发技巧!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录