作为Python开发者,你是否还在用传统的for循环处理列表、字典和集合?是否觉得代码冗长且难以维护?今天我们来聊聊Python中最优雅的特性之一——推导式(Comprehensions)。无论你是刚入门的新手,还是有经验的开发者,掌握推导式都能让你的代码更加简洁、高效。本文将从实际开发场景出发,深入浅出地讲解列表推导式、字典推导式和集合推导式的核心用法,帮你在日常的Python开发和上位机开发中写出更加Pythonic的代码。
🎯 什么是推导式?为什么要用它?
问题分析
在日常编程中,我们经常需要对数据进行筛选、转换和处理。传统做法通常是这样的:
Python# 传统方式:获取1-10中的偶数平方
result = []
for i in range(1, 11):
if i % 2 == 0:
result.append(i ** 2)
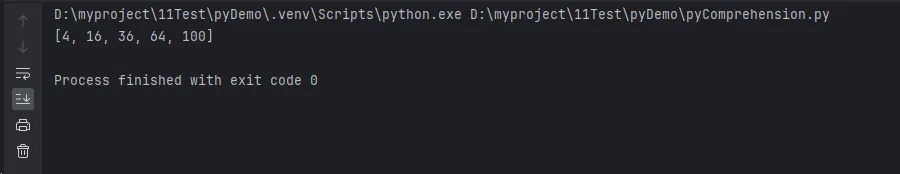
print(result) # [4, 16, 36, 64, 100]
这种写法虽然清晰,但代码量大,需要3-4行才能完成一个简单的数据处理任务。
解决方案
Python推导式提供了一种更加简洁和高效的解决方案:
Python# 推导式方式:一行搞定
result = [i ** 2 for i in range(1, 11) if i % 2 == 0]
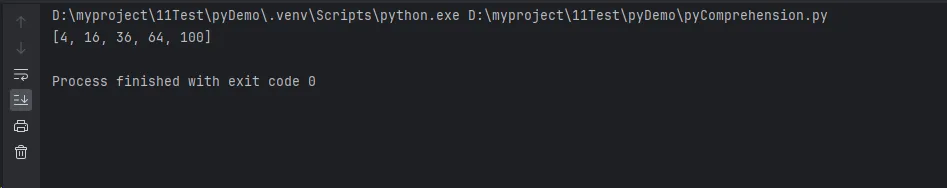
print(result) # [4, 16, 36, 64, 100]
在Python开发中,经常会遇到需要处理重复数据、进行集合运算或快速判断元素是否存在的场景。比如在上位机开发中处理传感器数据去重,或者在数据分析时需要找出两个数据集的交集、并集等。今天我们就来深入探讨Python集合(set)的强大功能,从基础概念到实战应用,让你彻底掌握这个高效的数据结构。无论你是刚接触Python编程技巧的新手,还是想要提升代码性能的开发者,这篇文章都将为你提供实用的解决方案。
🎯 什么是Python集合?为什么要用它?
问题分析
在实际Python开发中,我们经常遇到以下问题:
- 列表中有大量重复数据需要去重
- 需要快速判断某个元素是否存在于大量数据中
- 要对两个数据集进行交集、并集、差集运算
- 需要一个高性能的数据结构来存储唯一值
解决方案
Python的集合(set)正是为解决这些问题而生的数据结构,它具有以下特点:
- 唯一性:自动去除重复元素
- 无序性:元素没有固定顺序
- 可变性:可以动态添加和删除元素
- 高效性:查找、添加、删除操作的时间复杂度都是O(1)
🔥 集合的创建与基本操作
创建集合的多种方式
Python# 方式1:使用花括号创建
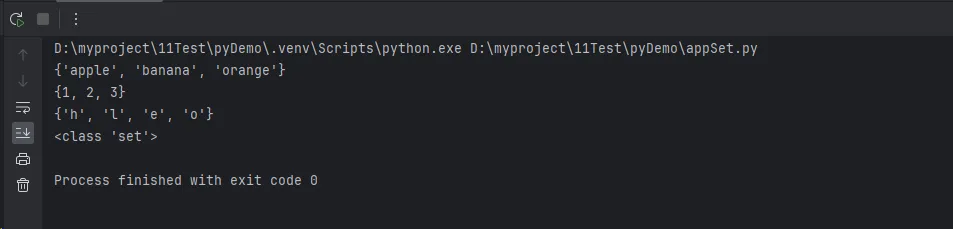
fruits = {'apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'apple'} # 重复的'apple'会被自动去除
print(fruits)
# 方式2:使用set()函数
numbers = set([1, 2, 3, 2, 1])
print(numbers) # {1, 2, 3}
# 方式3:从字符串创建
chars = set('hello')
print(chars)
# 方式4:创建空集合(注意不能用{},那是字典)
empty_set = set()
print(type(empty_set))
作为一名C#开发者,你是否曾想过尝试Java开发,却被复杂的环境搭建步骤劝退?与C#的Visual Studio一站式体验不同,Java的开发环境需要我们手动配置JDK、选择IDE、熟悉构建工具。不用担心,本文将以C#开发者的视角,用最实用的方式带你快速搭建Java开发环境,让你在30分钟内写出第一个Java程序。无论你是想拓展技术栈,还是项目需要,这篇文章都能让你轻松上手Java开发。
🎯 为什么Java环境搭建对C#开发者是个挑战?
对于习惯了C#开发的我们来说,Java环境搭建确实存在几个痛点:
1. 概念差异大
- C#:.NET Framework/Core自带运行时,Visual Studio集成一切
- Java:需要单独安装JDK,IDE和构建工具分离(这块可能是新转型最不好接受的)
2. 版本选择困难
- JDK版本众多(8、11、17、21),每个都有不同特性
- IDE选择多样(IntelliJ IDEA、Eclipse、NetBeans)
3. 配置复杂
- 环境变量配置(JAVA_HOME、PATH)
- 构建工具学习成本(Maven vs Gradle)
Python Complete Guide to INI Configuration File Handling: Make Your App Configuration Management More Elegant
In Python development on the Windows platform, we often need to deal with various configuration files. Whether it's a desktop application, automation script, or HMI program, proper configuration management is key to project success. Today we'll dive into the most classic configuration file format in Python — the INI file — and its read/write operations. This article starts from real development needs and, through rich code examples, helps you master all INI file handling techniques to easily handle various configuration management scenarios.
🤔 Why Choose INI Configuration Files?
Among many configuration file formats, INI files have unique advantages:
Clear structure: Use sections and key-value pairs; even non-technical users can easily understand it
Strong compatibility: Native support on Windows; many legacy applications use this format
Good readability: Plain text format, supports comments, easy to maintain and debug
A typical INI file structure:
Ini; 这是注释
[database]
host = localhost
port = 3306
username = admin
password = 123456
[logging]
level = INFO
file_path = ./logs/app.log
max_size = 10MB
🛠️ Python Built-in Tool: configparser Module
The Python standard library provides the configparser module, the first-choice tool for handling INI files. Let's start from basic usage:
📖 Reading INI Configuration Files
Pythonimport configparser
def read_config():
# Create ConfigParser object
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
# Read configuration file
config.read('config.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# Get all section names
sections = config.sections()
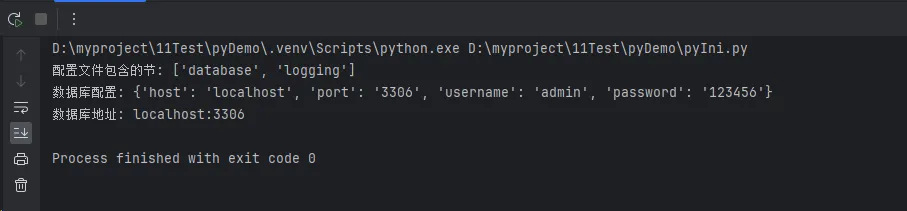
print(f"配置文件包含的节: {sections}")
# Read all key-value pairs of a specific section
db_config = dict(config['database'])
print(f"数据库配置: {db_config}")
# Read specific configuration items
host = config.get('database', 'host')
port = config.getint('database', 'port') # Automatically converted to int
print(f"数据库地址: {host}:{port}")
return config
# Usage example
if __name__ == "__main__":
config = read_config()
在Windows平台的Python开发中,我们经常需要处理各种配置文件。无论是桌面应用、自动化脚本还是上位机程序,合理的配置管理都是项目成功的关键。今天就来深入探讨Python中最经典的配置文件格式——ini文件的读写操作。本文将从实际开发需求出发,通过丰富的代码示例,让你掌握ini文件操作的所有技巧,轻松应对各种配置管理场景。
🤔 为什么选择ini配置文件?
在众多配置文件格式中,ini文件有着独特的优势:
结构清晰:采用节(section)和键值对的层次结构,即使非技术人员也能轻松理解
兼容性强:Windows系统原生支持,许多传统软件都使用这种格式
可读性好:纯文本格式,支持注释,便于维护和调试
典型的ini文件结构如下:
Ini; 这是注释
[database]
host = localhost
port = 3306
username = admin
password = 123456
[logging]
level = INFO
file_path = ./logs/app.log
max_size = 10MB
🛠️ Python内置工具:configparser模块
Python标准库提供了configparser模块,这是处理ini文件的首选工具。让我们从基础用法开始:
📖 读取ini配置文件
Pythonimport configparser
def read_config():
# 创建ConfigParser对象
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
# 读取配置文件
config.read('config.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# 获取所有节名
sections = config.sections()
print(f"配置文件包含的节: {sections}")
# 读取特定节的所有键值对
db_config = dict(config['database'])
print(f"数据库配置: {db_config}")
# 读取具体的配置项
host = config.get('database', 'host')
port = config.getint('database', 'port') # 自动转换为整数
print(f"数据库地址: {host}:{port}")
return config
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
config = read_config()
