在Windows桌面开发中,WinForm曾经是主流的技术栈,但随着界面设计和交互需求越来越丰富,WPF(Windows Presentation Foundation)以更强大的UI渲染、可扩展的样式和更灵活的数据绑定特性吸引了众多开发者转向。
WinForm与WPF在绘图方面的差异
-
渲染引擎
WinForm基于GDI+,需要手动处理绘制逻辑、重绘、坐标转换等;WPF使用基于DirectX的矢量渲染引擎,UI可自动响应分辨率、缩放和动画等需求。
-
布局系统
WinForm一般使用
Dock、Anchor或手动绝对坐标;WPF提供了丰富的布局容器(如Grid、StackPanel、Canvas),并支持自动伸缩和自适应,大幅减少手动定位的工作量。 -
可视化与样式
在WinForm中对控件进行自定义样式常常需要重写
OnPaint;WPF中提供了ControlTemplate、Style以及基于XAML的可视化树,能自定义任意形状、颜色和动画效果。
Ellipse的基本用法
在WPF中,Ellipse是一个通用的“图形”控件,用于绘制圆形或椭圆形。与WinForm相比,WPF中的Ellipse使用更加简单明了。
在窗口中直接使用Ellipse
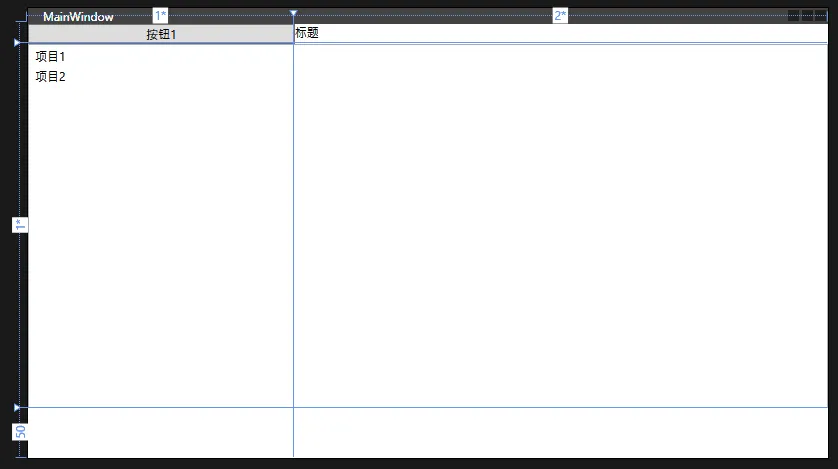
下面是一个最简单的示例,展示了如何在WPF窗口中创建和使用椭圆。该示例展示了一个包含红色椭圆的窗口:
XML<Window x:Class="AppEllipse.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppEllipse"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
<Ellipse Width="100"
Height="100"
Fill="Red"
Stroke="Black"
StrokeThickness="2" />
</Grid>
</Window>
前言
在从 Windows Forms (WinForm) 转到 Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 的过程中,初学者常常会被全新的布局系统与控件体系所困扰。WPF 提供了许多新的控件和特性来帮助简化 UI 构建,其中一个常用控件就是 Border。本文将结合具体示例,介绍在 WPF 中如何使用 Border,并与 WinForm 的常见做法进行对比。
WinForm 与 WPF 的边框区别
- 在 WinForm 中,自定义控件或 Panel 可能通过设置
BorderStyle等属性来显示简单边框。要想进一步美化或调整更多外观细节,就需要借助第三方控件或自己绘制。 - 在 WPF 中,Border 是一个专门用于为单个子元素添加边框、背景、圆角和边距的容器控件,开发者无需自行绘制即可完成丰富的样式配置。
基础用法
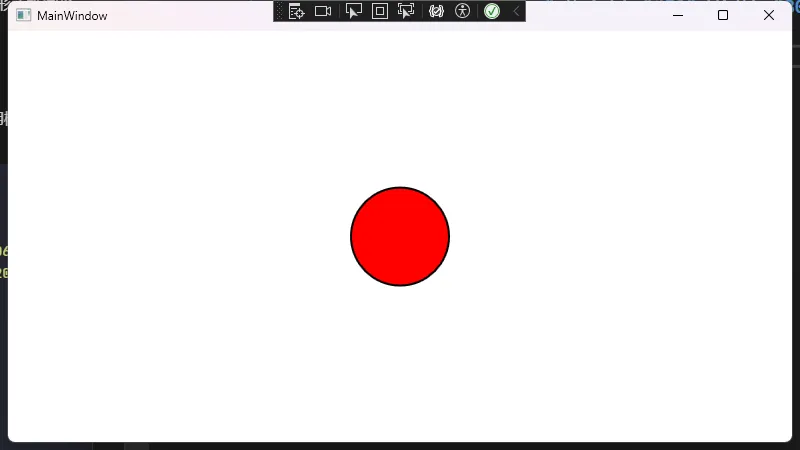
以下示例展示了最基本的 Border 用法,包括设置背景色、边框厚度和颜色等。
XML<Window x:Class="AppBorder.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppBorder"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
<Border
BorderThickness="2"
BorderBrush="LightBlue"
Background="AliceBlue"
Padding="10"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="我是被Border包裹的内容"
Foreground="DarkBlue"
FontSize="16"/>
</Border>
</Grid>
</Window>
在从 WinForm 向 WPF 转型的过程中,很多开发者都会思考如何在 WPF 中实现各种自定义图形的绘制。WinForm 中通常通过 GDI+或者直接在控件的 Paint 事件中手动绘图。而在 WPF 中,使用 Shape 派生类(例如 Rectangle, Ellipse, Line 等)就可以更直观地在界面上绘制图形。本篇文章将介绍如何在 WPF 中使用 Rectangle,并说明与 WinForm 的主要差异,以及如何利用 WPF 的强大样式和动画特性让矩形图形更灵活多变。
Rectangle 在 WinForm 与 WPF 中的差异
WinForm:
- 通常需要在
OnPaint或Paint事件内通过Graphics对象手动调用DrawRectangle等方法进行绘制。 - 若想改变矩形的位置、大小或颜色,通常需要触发重绘(
Invalidate/Refresh)或联动其它 UI 事件。
WPF:
- 通过
System.Windows.Shapes.Rectangle控件来绘制矩形。可以把它看作一个 UIElement,天然支持布局系统。 - 可直接在 XAML 中声明,或在后台代码创建并添加到容器中。
- 可以使用依赖属性(如
Width,Height,Fill,Stroke等)进行绑定或使用样式,轻松调整或动画化。 - 几乎无需手动处理重绘,WPF 会自动计算并渲染界面。
一个简单的 Rectangle 示例
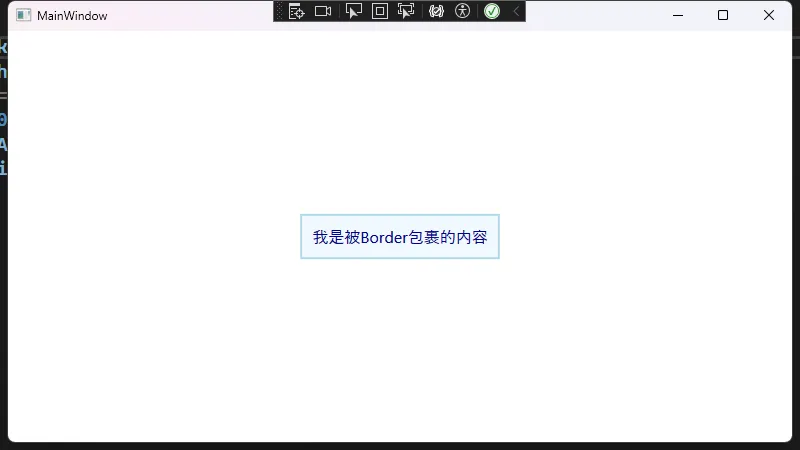
下面是一个最基础的示例,展示如何在 XAML 中使用 Rectangle 控件:
XML<Window x:Class="AppRectangle.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppRectangle"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
<Rectangle Width="200" Height="100"
Fill="LightBlue"
Stroke="DarkBlue"
StrokeThickness="2"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center" />
</Grid>
</Window>
 在此示例中:
在此示例中:
从WinForm转型到WPF开发时,最显著的变化之一就是布局系统的差异。WPF提供了更加灵活和强大的响应式布局能力,本文将详细介绍WPF中实现响应式布局的多种方式。
Grid布局 - 使用星号和Auto实现响应式
Grid是WPF中最灵活的布局容器之一,通过设置列宽和行高的比例,可以轻松实现响应式布局。
XML<Window x:Class="AppResponsive.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppResponsive"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window1" Height="450" Width="800">
<DockPanel LastChildFill="True">
<!-- 顶部工具栏 -->
<StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Top" Background="LightBlue" Height="50">
<TextBlock Text="顶部工具栏" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
<!-- 左侧导航 -->
<StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Left" Background="LightGreen" Width="150">
<TextBlock Text="左侧导航" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
<!-- 右侧面板 -->
<StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Right" Background="LightPink" Width="200">
<TextBlock Text="右侧面板" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
<!-- 底部状态栏 -->
<StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Bottom" Background="LightGray" Height="30">
<TextBlock Text="底部状态栏" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
<!-- 主内容区域(自动填充剩余空间) -->
<Grid Background="White">
<TextBlock Text="主内容区域" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</Grid>
</DockPanel>
</Window>
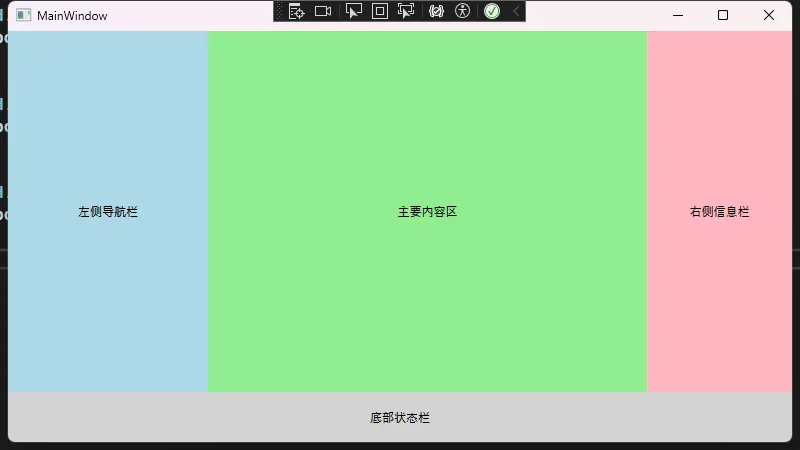
前言
从WinForm转向WPF开发时,最需要转变的思维就是布局方式。WPF提供了更加灵活和强大的布局系统,可以轻松实现自适应布局设计。本文将详细介绍WPF中常用的布局控件及其应用。
Grid布局 - 最常用的布局控件
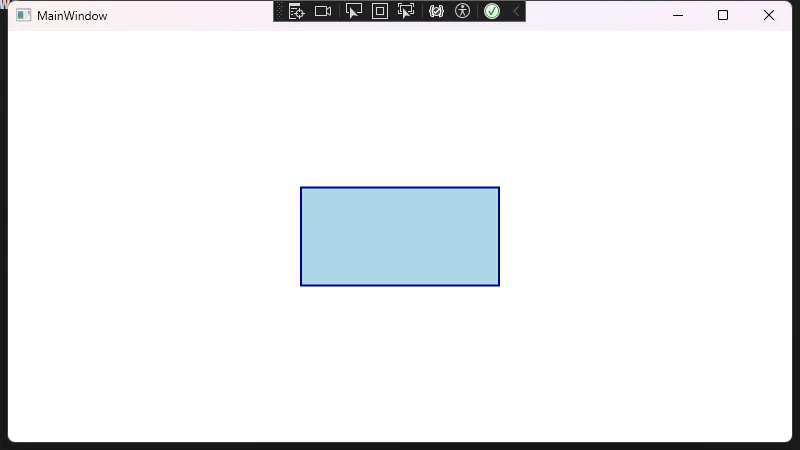
Grid是WPF中最灵活的布局控件,类似于HTML中的表格布局。它允许你定义行和列,并可以设置比例或固定大小。
基础Grid示例
XML<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<!-- 第一行高度为Auto,根据内容自动调整 -->
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<!-- 第二行高度为* ,占用剩余所有空间 -->
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<!-- 第三行固定高度50 -->
<RowDefinition Height="50"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<!-- 第一列宽度占比1 -->
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<!-- 第二列宽度占比2 -->
<ColumnDefinition Width="2*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<!-- 放置在第0行第0列的按钮 -->
<Button Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Content="按钮1"/>
<!-- 放置在第0行,跨越2列的文本块 -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1" Text="标题"/>
<!-- 放置在第1行,跨越2列的列表 -->
<ListBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.ColumnSpan="2">
<ListBoxItem>项目1</ListBoxItem>
<ListBoxItem>项目2</ListBoxItem>
</ListBox>
</Grid>