目录
作为一名C#开发者,你是否遇到过这样的困扰:用户在表单中按Tab键切换控件时,焦点跳转顺序混乱不堪?明明希望用户从姓名输入框跳到电话号码框,结果却跳到了页面底部的取消按钮?或者某些控件根本无法通过Tab键访问?
这些问题看似细微,却直接影响用户体验,尤其是对于数据录入频繁的业务系统。今天我们就来彻底解决这个问题,掌握TabIndex和TabStop这两个关键属性,让你的WinForm应用拥有丝滑般的焦点切换体验。
🔍 问题分析:为什么焦点切换如此重要?
用户体验痛点
在实际开发中,不合理的焦点切换会导致:
- 录入效率低下:用户需要频繁使用鼠标定位
- 操作流程混乱:逻辑顺序与Tab顺序不一致
- 无障碍访问困难:键盘用户无法正常操作
- 专业性质疑:给用户留下"不专业"的印象
技术原理解析
WinForm中的焦点切换机制基于两个核心属性:
- TabIndex:决定控件的Tab顺序(数值越小优先级越高)
- TabStop:决定控件是否参与Tab导航(true/false)
💡 解决方案:5个实战技巧让焦点切换更优雅
🎯 技巧一:建立清晰的TabIndex规划
应用场景:表单控件众多,需要建立合理的导航顺序
c#namespace AppWinformTab
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private TextBox txtName;
private TextBox txtPhone;
private TextBox txtEmail;
private ComboBox cmbDepartment;
private TextBox txtProvince;
private TextBox txtCity;
private TextBox txtAddress;
private Button btnSave;
private Button btnCancel;
private Button btnReset;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 初始化控件并设置位置与大小(简单示例)
this.txtName = new TextBox() { Left = 20, Top = 20, Width = 200, Name = "txtName", PlaceholderText = "姓名" };
this.txtPhone = new TextBox() { Left = 20, Top = 55, Width = 200, Name = "txtPhone", PlaceholderText = "电话" };
this.txtEmail = new TextBox() { Left = 20, Top = 90, Width = 200, Name = "txtEmail", PlaceholderText = "邮件" };
this.cmbDepartment = new ComboBox() { Left = 240, Top = 20, Width = 150, Name = "cmbDepartment" };
this.cmbDepartment.Items.AddRange(new object[] { "技术", "产品", "运营", "市场" });
this.txtProvince = new TextBox() { Left = 20, Top = 140, Width = 200, Name = "txtProvince", PlaceholderText = "省" };
this.txtCity = new TextBox() { Left = 240, Top = 140, Width = 150, Name = "txtCity", PlaceholderText = "市" };
this.txtAddress = new TextBox() { Left = 20, Top = 175, Width = 370, Name = "txtAddress", PlaceholderText = "详细地址" };
this.btnSave = new Button() { Left = 20, Top = 220, Width = 80, Text = "保存", Name = "btnSave" };
this.btnCancel = new Button() { Left = 110, Top = 220, Width = 80, Text = "取消", Name = "btnCancel" };
this.btnReset = new Button() { Left = 200, Top = 220, Width = 80, Text = "重置", Name = "btnReset" };
// 按钮事件(示例)
this.btnSave.Click += BtnSave_Click;
this.btnCancel.Click += BtnCancel_Click;
this.btnReset.Click += BtnReset_Click;
// 添加控件到表单
this.Controls.AddRange(new Control[] {
txtName, txtPhone, txtEmail, cmbDepartment,
txtProvince, txtCity, txtAddress,
btnSave, btnCancel, btnReset
});
// 表单属性
this.Text = "用户信息";
this.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(420, 280);
SetupTabOrder();
}
private void SetupTabOrder()
{
// 主要信息区域 (0-9)
txtName.TabIndex = 0;
txtPhone.TabIndex = 1;
txtEmail.TabIndex = 2;
cmbDepartment.TabIndex = 3;
// 地址信息区域 (10-19)
txtProvince.TabIndex = 10;
txtCity.TabIndex = 11;
txtAddress.TabIndex = 12;
// 操作按钮区域 (90-99)
btnSave.TabIndex = 90;
btnCancel.TabIndex = 91;
btnReset.TabIndex = 92;
// 设置 AcceptButton / CancelButton
this.AcceptButton = btnSave; // 回车触发保存
this.CancelButton = btnCancel; // Esc 触发取消
}
private void BtnSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("保存成功", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
private void BtnCancel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void BtnReset_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
txtName.Text = "";
txtPhone.Text = "";
txtEmail.Text = "";
cmbDepartment.SelectedIndex = -1;
txtProvince.Text = "";
txtCity.Text = "";
txtAddress.Text = "";
txtName.Focus();
}
}
}
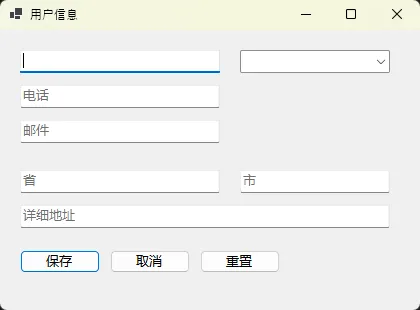
💡 最佳实践:
- 使用区间分组:基础信息0-9,扩展信息10-19,按钮90-99
- 预留空隙:便于后期插入新控件
- 逻辑优先:按用户操作流程设置顺序
🚀 技巧二:动态控制TabStop优化用户体验
应用场景:根据业务逻辑动态控制哪些控件参与Tab导航
c#using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AppWinformTab
{
public enum UserRole
{
Viewer,
Editor
}
public static class SmartTabManager
{
// 禁用只读或不可用控件的 Tab 导航,递归子控件
public static void DisableTabForReadOnlyControls(Control parent)
{
foreach (Control control in parent.Controls)
{
if (control is TextBox textBox)
{
textBox.TabStop = !textBox.ReadOnly;
}
else if (control is ComboBox comboBox)
{
comboBox.TabStop = comboBox.Enabled;
}
else if (control is CheckBox checkBox)
{
checkBox.TabStop = checkBox.Enabled;
}
if (control.HasChildren)
{
DisableTabForReadOnlyControls(control);
}
}
}
// 根据用户角色设置哪些控件可 Tab
public static void SetTabOrderByUserRole(Form form, UserRole role)
{
// 先默认禁用所有输入控件的 TabStop(但不改变可视状态)
foreach (var ctl in form.Controls.Cast<Control>())
{
if (ctl is TextBox || ctl is ComboBox || ctl is Button || ctl is CheckBox)
{
ctl.TabStop = false;
}
}
switch (role)
{
case UserRole.Viewer:
// 观察者只能访问带 "Query" 名称的按钮
form.Controls.OfType<Button>()
.Where(btn => btn.Name.Contains("Query"))
.ToList()
.ForEach(btn => btn.TabStop = true);
break;
case UserRole.Editor:
// 编辑者可以访问所有输入控件(非只读/可用)
EnableAllInputControls(form);
break;
}
}
private static void EnableAllInputControls(Control parent)
{
foreach (Control control in parent.Controls)
{
if (control is TextBox textBox)
{
textBox.TabStop = !textBox.ReadOnly && textBox.Enabled;
}
else if (control is ComboBox comboBox)
{
comboBox.TabStop = comboBox.Enabled;
}
else if (control is Button button)
{
button.TabStop = button.Enabled;
}
else if (control is CheckBox checkBox)
{
checkBox.TabStop = checkBox.Enabled;
}
if (control.HasChildren)
EnableAllInputControls(control);
}
}
}
}
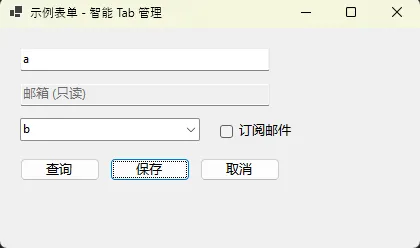
⚠️ 常见坑点:
- Label控件默认TabStop为false,这是正确的
- Panel和GroupBox不要设置TabStop为true
- 隐藏控件会自动跳过Tab导航
🎨 技巧三:创建自定义Tab导航组件
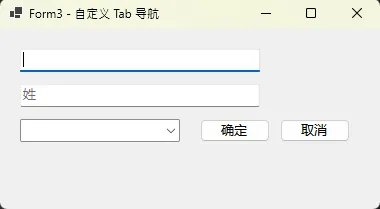
应用场景:复杂表单需要更精细的焦点控制
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AppWinformTab
{
public class TabNavigationManager
{
private List<Control> _tabSequence;
private int _currentIndex;
public TabNavigationManager()
{
_tabSequence = new List<Control>();
_currentIndex = -1;
}
// 添加控件到导航序列(会订阅 KeyDown)
public void AddControl(Control control)
{
if (control == null) return;
_tabSequence.Add(control);
control.KeyDown += Control_KeyDown;
}
private void Control_KeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
// 处理 Tab 和 Enter 导航
if (e.KeyCode == Keys.Tab)
{
e.Handled = true;
e.SuppressKeyPress = true;
if (e.Shift)
MoveToPrevious();
else
MoveToNext();
}
else if (e.KeyCode == Keys.Enter)
{
e.Handled = true;
e.SuppressKeyPress = true;
MoveToNext();
}
}
private void MoveToNext()
{
if (_tabSequence.Count == 0) return;
_currentIndex = (_currentIndex + 1) % _tabSequence.Count;
FocusCurrentControl();
}
private void MoveToPrevious()
{
if (_tabSequence.Count == 0) return;
_currentIndex = _currentIndex <= 0 ? _tabSequence.Count - 1 : _currentIndex - 1;
FocusCurrentControl();
}
private void FocusCurrentControl()
{
if (_currentIndex < 0 || _currentIndex >= _tabSequence.Count) return;
var control = _tabSequence[_currentIndex];
// 跳过不可见或不可用控件,尝试下一个(避免死循环)
for (int i = 0; i < _tabSequence.Count; i++)
{
if (control.Visible && control.Enabled)
{
control.Focus();
if (control is TextBox textBox)
textBox.SelectAll();
return;
}
// 移动到下一个候选
_currentIndex = (_currentIndex + 1) % _tabSequence.Count;
control = _tabSequence[_currentIndex];
}
}
}
}
🔧 技巧四:可视化设计器快速设置TabOrder
应用场景:大量控件需要快速设置Tab顺序
在Visual Studio设计器中的操作步骤:
c#public static class TabOrderHelper
{
public static void SetTabOrderByLocation(Control parent)
{
var controls = parent.Controls
.Cast<Control>()
.Where(c => c.TabStop)
.OrderBy(c => c.Top)
.ThenBy(c => c.Left)
.ToList();
for (int i = 0; i < controls.Count; i++)
{
controls[i].TabIndex = i;
}
}
// 根据控件名称排序
public static void SetTabOrderByName(Control parent)
{
var controls = parent.Controls
.Cast<Control>()
.Where(c => c.TabStop)
.OrderBy(c => c.Name)
.ToList();
for (int i = 0; i < controls.Count; i++)
{
controls[i].TabIndex = i;
}
}
}
🎯 技巧五:处理特殊场景的焦点切换
应用场景:DataGridView、用户控件等特殊控件的焦点管理
c#public class SpecialControlTabHandler
{
// DataGridView的Tab处理
public static void SetupDataGridViewTab(DataGridView dgv)
{
dgv.KeyDown += (sender, e) =>
{
if (e.KeyCode == Keys.Tab && dgv.CurrentCell != null)
{
// 在最后一行最后一列时Tab到下一个控件
if (dgv.CurrentCell.RowIndex == dgv.Rows.Count - 1 &&
dgv.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex == dgv.Columns.Count - 1)
{
e.Handled = true;
SendKeys.Send("{TAB}");
}
}
};
}
// UserControl内部Tab循环
public static void EnableInternalTabCycle(UserControl userControl)
{
var controls = GetTabOrderedControls(userControl);
if (controls.Count > 0)
{
var firstControl = controls.First();
var lastControl = controls.Last();
lastControl.KeyDown += (sender, e) =>
{
if (e.KeyCode == Keys.Tab && !e.Shift)
{
e.Handled = true;
firstControl.Focus();
}
};
firstControl.KeyDown += (sender, e) =>
{
if (e.KeyCode == Keys.Tab && e.Shift)
{
e.Handled = true;
lastControl.Focus();
}
};
}
}
private static List<Control> GetTabOrderedControls(Control parent)
{
return parent.Controls
.Cast<Control>()
.Where(c => c.TabStop && c.CanFocus)
.OrderBy(c => c.TabIndex)
.ToList();
}
}
🏆 最佳实践总结
📋 Tab顺序设计原则
- 从左到右,从上到下:符合用户阅读习惯
- 逻辑分组:相关控件TabIndex连续
- 按钮置后:操作按钮放在输入控件之后
- 预留间隔:便于后期维护和扩展
🎯 结尾总结
掌握TabIndex与TabStop的使用技巧,是提升WinForm应用用户体验的关键一步。通过本文的5个实战技巧,我们学会了:
- 建立清晰的TabIndex规划 - 用区间分组法组织控件导航顺序
- 动态控制TabStop - 根据业务逻辑智能调整可访问控件
- 自定义导航组件 - 为复杂表单创建更精细的焦点控制
记住这句话:优秀的软件不仅功能强大,更要细节完美。一个流畅的Tab导航,往往能让用户对你的应用留下专业、贴心的印象。
💬 互动时间:
你在项目中遇到过哪些特殊的焦点切换需求?有没有自己独特的解决方案?欢迎在评论区分享你的经验!
🔥 觉得这些技巧实用?请转发给更多C#开发同行,让我们一起提升.NET生态的整体开发水平!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录