目录
在Python开发中,布尔类型(bool)看似简单,只有True和False两个值,但它却是程序逻辑控制的基石。无论是条件判断、循环控制,还是函数返回值的设计,布尔类型都发挥着举足轻重的作用。
很多初学者在使用布尔类型时,往往只停留在基础的True/False判断上,却忽略了Python中强大的布尔上下文机制和短路逻辑特性。这些高级特性不仅能让代码更加优雅简洁,还能显著提升程序性能。
本文将从实战角度深入解析Python布尔类型的三大核心应用:基础布尔操作、布尔上下文的灵活运用以及短路逻辑的性能优化,帮助你全面掌握这个看似简单却功能强大的数据类型。
🔍 问题分析:布尔类型的常见误区
在Windows应用开发中,我经常看到开发者对布尔类型的使用存在以下误区:
误区一:认为布尔类型只能存储True/False
误区二:不理解Python的布尔上下文机制
误区三:忽略短路逻辑带来的性能优势
让我们通过实际代码来分析这些问题。
💡 解决方案:布尔类型的三大核心特性
🎯 特性一:布尔类型的本质与创建
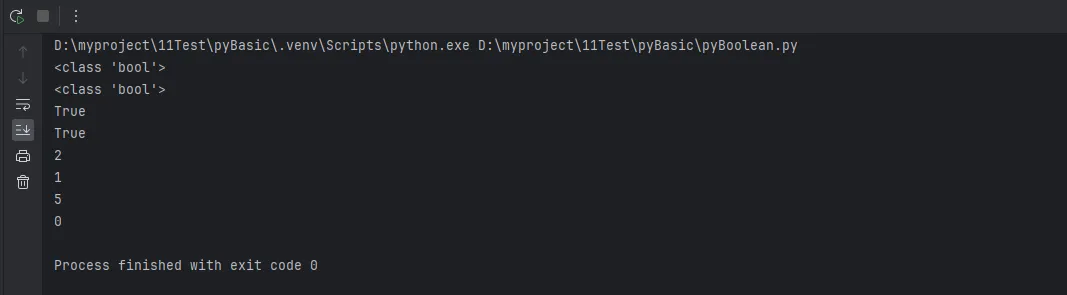
Python# 布尔类型的创建方式
print(type(True)) # <class 'bool'>
print(type(False)) # <class 'bool'>
# 布尔类型继承自int
print(isinstance(True, int)) # True
print(isinstance(False, int)) # True
# 布尔值的数值表示
print(True + 1) # 2
print(False + 1) # 1
print(True * 5) # 5
print(False * 5) # 0
实战应用:在Windows应用开发中,这个特性常用于状态计数:
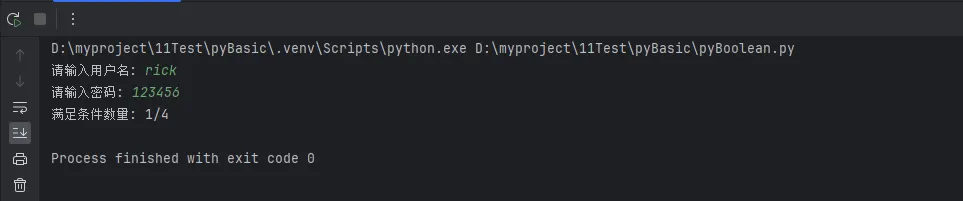
Python# 统计多个条件满足的个数
username = input("请输入用户名: ")
password = input("请输入密码: ")
conditions = [
len(username) >= 6,
any(c.isdigit() for c in password),
any(c.isupper() for c in password),
any(c.islower() for c in password)
]
satisfied_count = sum(conditions) # 利用布尔值的数值特性
print(f"满足条件数量: {satisfied_count}/4")
🔥 特性二:布尔上下文的强大机制
Python中的布尔上下文是指任何对象都可以在需要布尔值的场景中使用。这是Python的一个强大特性:
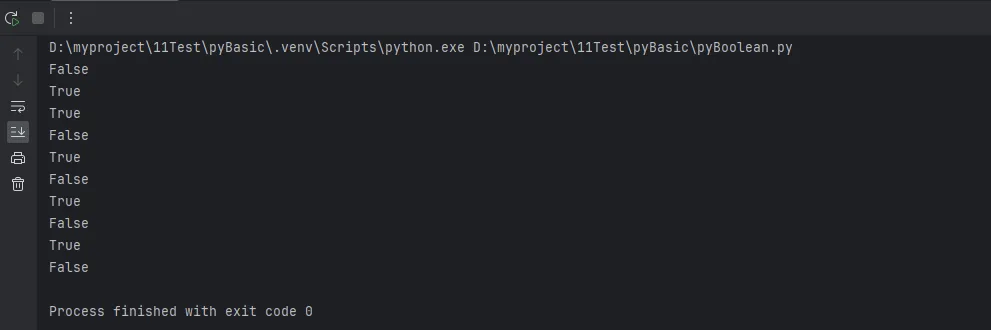
Python# 数字的布尔上下文
print(bool(0))
print(bool(42))
print(bool(-1))
# 字符串的布尔上下文
print(bool(""))
print(bool("hello"))
# 容器的布尔上下文
print(bool([]))
print(bool([1,2]))
print(bool({}))
print(bool({"key": "value"}))
# None的布尔上下文
print(bool(None))
实战案例:用户输入验证的优雅写法
Pythondef validate_user_input(data):
"""用户输入验证 - 利用布尔上下文简化代码"""
# 传统写法(冗余)
if data is not None and len(data) > 0 and data.strip() != "":
return True
else:
return False
# 布尔上下文优雅写法
return bool(data and data.strip())
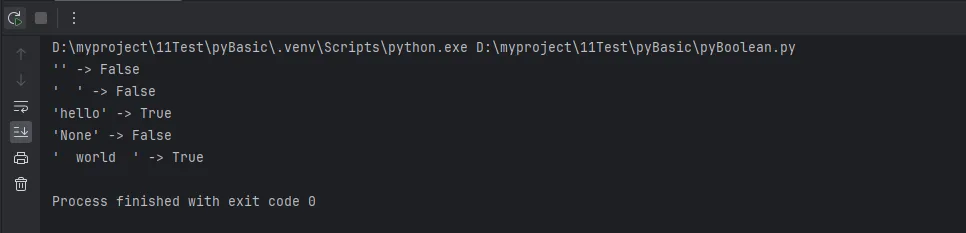
# 测试用例
test_cases = ["", " ", "hello", None, " world "]
for case in test_cases:
print(f"'{case}' -> {validate_user_input(case)}")
实用技巧:配置文件处理中的应用
Pythonclass ConfigManager:
def __init__(self, config_dict):
self.config = config_dict
def get_setting(self, key, default=None):
"""获取配置项,利用布尔上下文提供默认值"""
value = self.config.get(key)
return value if value else default
def is_feature_enabled(self, feature):
"""检查功能是否启用"""
return bool(self.config.get(feature))
# 使用示例
config = {
"debug_mode": True,
"max_connections": 100,
"log_file": "", # 空字符串
"cache_enabled": None
}
manager = ConfigManager(config)
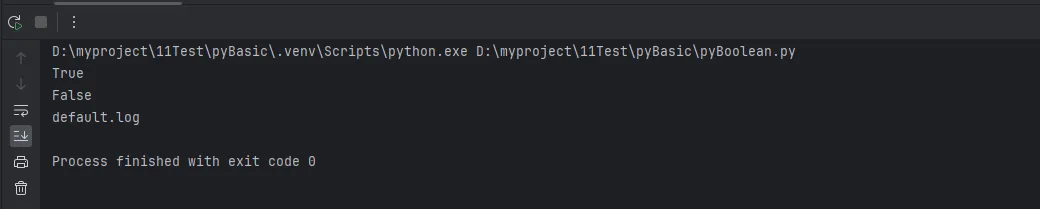
print(manager.is_feature_enabled("debug_mode")) # True
print(manager.is_feature_enabled("cache_enabled")) # False
print(manager.get_setting("log_file", "default.log")) # default.log
⚡ 特性三:短路逻辑的性能优化
短路逻辑是布尔类型最实用的特性之一,能够显著提升程序性能:
Pythonimport time
def expensive_operation():
"""模拟耗时操作"""
time.sleep(0.1)
return True
def quick_check():
"""快速检查"""
return False
# and短路逻辑演示
start_time = time.time()
result1 = quick_check() and expensive_operation() # expensive_operation()不会执行
end_time = time.time()
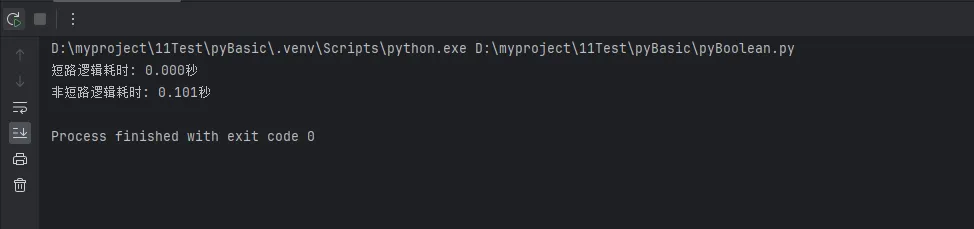
print(f"短路逻辑耗时: {end_time - start_time:.3f}秒")
# 不使用短路逻辑
start_time = time.time()
result2 = expensive_operation() and quick_check() # 两个函数都会执行
end_time = time.time()
print(f"非短路逻辑耗时: {end_time - start_time:.3f}秒")
实战应用:文件处理中的安全检查
Pythonimport os
def safe_file_operation(filepath):
"""安全的文件操作 - 利用短路逻辑避免异常"""
# 短路逻辑:只有前面条件为True时,后面才会执行
if (filepath and # 路径不为空
os.path.exists(filepath) and # 文件存在
os.path.isfile(filepath) and # 是文件而非目录
os.access(filepath, os.R_OK)): # 有读权限
with open(filepath, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
return f.read()
else:
return None
# 测试不同情况
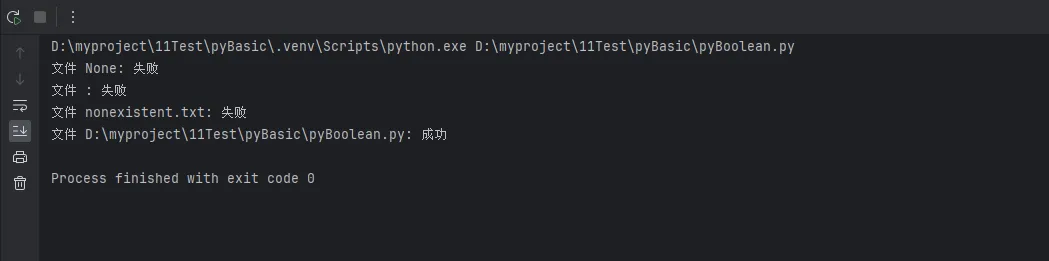
test_files = [None, "", "nonexistent.txt", __file__]
for file in test_files:
result = safe_file_operation(file)
status = "成功" if result else "失败"
print(f"文件 {file}: {status}")
🛠️ 代码实战:布尔类型的综合应用
实战案例:Windows应用的状态管理器
Pythonclass ApplicationStateManager:
"""应用状态管理器 - 综合运用布尔类型特性"""
def __init__(self):
self.states = {
'connected': False,
'authenticated': False,
'data_loaded': False,
'ui_ready': False
}
self.error_count = 0
self.max_errors = 5
def update_state(self, state_name, value):
"""更新状态"""
if state_name in self.states:
self.states[state_name] = bool(value) # 确保为布尔值
return True
return False
def can_operate(self):
"""检查是否可以执行操作 - 利用短路逻辑"""
return (self.states['connected'] and
self.states['authenticated'] and
self.states['data_loaded'] and
self.error_count < self.max_errors)
def get_readiness_score(self):
"""获取就绪分数 - 利用布尔值的数值特性"""
return sum(self.states.values()) / len(self.states)
def get_status_report(self):
"""获取状态报告"""
ready_states = sum(self.states.values()) # 布尔值求和
total_states = len(self.states)
status = "运行中" if self.can_operate() else "未就绪"
return {
'status': status,
'ready_count': ready_states,
'total_count': total_states,
'readiness_percentage': f"{ready_states/total_states*100:.1f}%",
'details': self.states.copy()
}
# 使用示例
manager = ApplicationStateManager()
# 模拟状态更新
manager.update_state('connected', True)
manager.update_state('authenticated', 1) # 非零数字转为True
manager.update_state('data_loaded', "loaded") # 非空字符串转为True
manager.update_state('ui_ready', []) # 空列表转为False
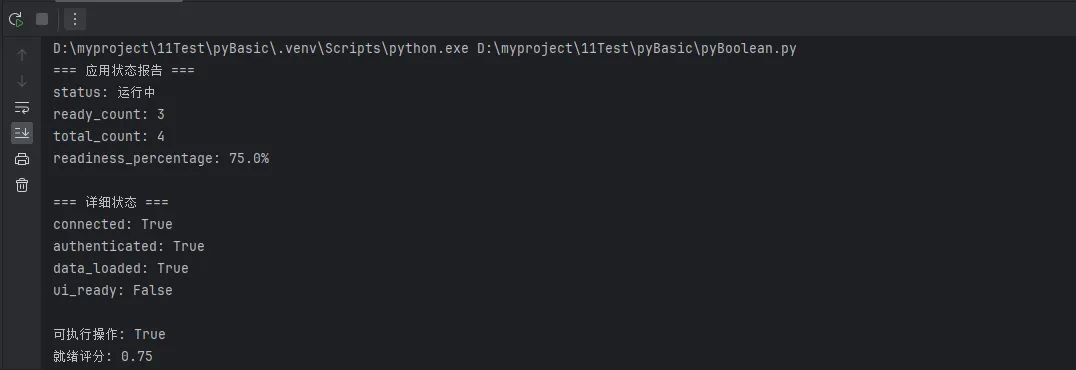
print("=== 应用状态报告 ===")
report = manager.get_status_report()
for key, value in report.items():
if key != 'details':
print(f"{key}: {value}")
print("\n=== 详细状态 ===")
for state, value in report['details'].items():
print(f"{state}: {value}")
print(f"\n可执行操作: {manager.can_operate()}")
print(f"就绪评分: {manager.get_readiness_score():.2f}")
高级技巧:自定义布尔行为
Pythonclass SmartConfig:
"""智能配置类 - 自定义布尔行为"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.config = kwargs
self.enabled_count = 0
def __bool__(self):
"""自定义布尔行为"""
# 当至少有一个配置项为真值时,整个配置对象为True
self.enabled_count = sum(bool(v) for v in self.config.values())
return self.enabled_count > 0
def __str__(self):
return f"SmartConfig(enabled: {self.enabled_count}/{len(self.config)})"
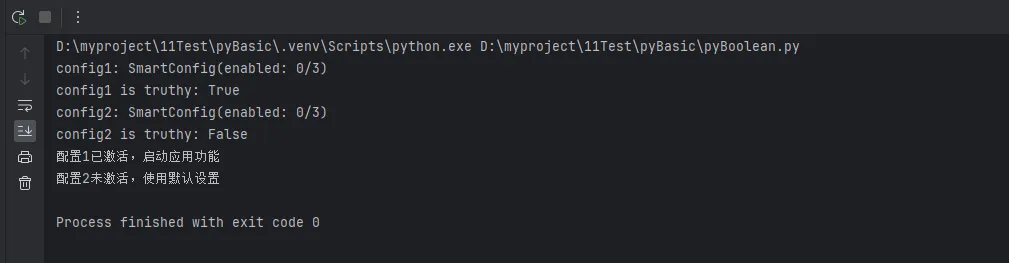
# 测试自定义布尔行为
config1 = SmartConfig(debug=True, cache=False, logs="")
config2 = SmartConfig(debug=False, cache=False, logs="")
print(f"config1: {config1}")
print(f"config1 is truthy: {bool(config1)}") # True
print(f"config2: {config2}")
print(f"config2 is truthy: {bool(config2)}") # False
# 在条件语句中使用
if config1:
print("配置1已激活,启动应用功能")
if not config2:
print("配置2未激活,使用默认设置")
🎯 核心要点总结
通过本文的深入解析,我们掌握了Python布尔类型的三大核心特性:
1. 布尔类型的数值特性:布尔值可以参与数学运算,True等于1,False等于0,这个特性在状态统计和条件计数中非常实用。
2. 布尔上下文的灵活机制:Python中任何对象都可以在布尔上下文中使用,空容器、空字符串、None、0都被视为False,其他情况为True。这个机制让代码更加简洁优雅。
3. 短路逻辑的性能优势:and和or操作符具有短路特性,能够避免不必要的函数调用和计算,显著提升程序性能。
掌握这些特性,不仅能让你的Python代码更加Pythonic,还能在实际项目开发中写出更高效、更可维护的代码。在Windows应用开发中,合理运用布尔类型的这些高级特性,将让你的程序逻辑更清晰,性能更优秀。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!