目录
在Python桌面开发中,按钮控件是用户交互的核心组件。无论你是开发数据处理工具、设备控制软件还是管理系统,Button控件都是必不可少的界面元素。本文将从零开始,深入解析Tkinter Button控件的使用方法,帮助你快速掌握Python GUI开发的核心技能。通过实际案例和最佳实践,让你的Python开发技能更上一层楼,为后续的上位机开发打下坚实基础。
🎯 Button控件核心概念
什么是Button控件
Button控件是Tkinter中最基础的交互组件,它允许用户通过点击触发特定的功能。在实际的Python开发项目中,按钮承担着连接用户操作和程序逻辑的重要桥梁作用。
Button控件的本质
从技术角度看,Button是一个可点击的矩形区域,包含文本、图片或两者的组合。当用户点击时,会触发绑定的回调函数,执行相应的业务逻辑。
🔧 基础语法与参数详解
创建Button的标准语法
Pythonimport tkinter as tk
button = tk.Button(parent, option=value, ...)
核心参数全览
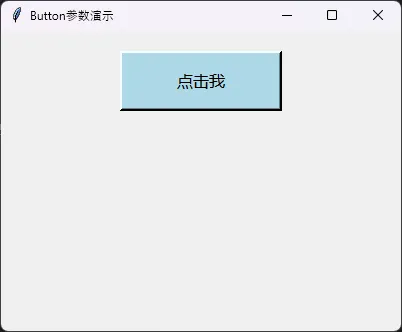
Pythonimport tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Button参数演示")
root.geometry("400x300")
# 基础按钮
basic_button = tk.Button(
root,
text="点击我", # 按钮文本
command=lambda: print("按钮被点击!"), # 点击回调函数
width=15, # 宽度(字符数)
height=2, # 高度(文本行数)
bg="lightblue", # 背景色
fg="black", # 前景色(文字颜色)
font=("微软雅黑", 12), # 字体设置
relief="raised", # 边框样式
bd=3, # 边框宽度
state="normal" # 状态:normal, disabled, active
)
basic_button.pack(pady=20)
root.mainloop()
💻 实战案例1:计算器按钮布局
让我们通过一个实际的计算器界面来理解Button的布局应用:
Pythonimport tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
class SimpleCalculator:
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk()
self.root.title("简易计算器")
self.root.geometry("300x400")
self.root.resizable(False, False)
# 显示屏
self.display_var = tk.StringVar()
self.display_var.set("0")
# 创建界面
self.create_display()
self.create_buttons()
def create_display(self):
"""创建显示屏"""
display_frame = tk.Frame(self.root, bg="black", height=80)
display_frame.pack(fill="x", padx=10, pady=10)
display_frame.pack_propagate(False)
display_label = tk.Label(
display_frame,
textvariable=self.display_var,
font=("Arial", 20, "bold"),
bg="black",
fg="white",
anchor="e"
)
display_label.pack(fill="both", expand=True, padx=10, pady=10)
def create_buttons(self):
"""创建按钮布局"""
# 按钮配置
button_config = {
'font': ('Arial', 12, 'bold'),
'width': 5,
'height': 2
}
# 创建按钮框架
button_frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
button_frame.pack(fill="both", expand=True, padx=10, pady=5)
# 按钮布局定义
buttons = [
['C', '±', '%', '÷'],
['7', '8', '9', '×'],
['4', '5', '6', '-'],
['1', '2', '3', '+'],
['0', '.', '=']
]
# 创建按钮
for i, row in enumerate(buttons):
for j, btn_text in enumerate(row):
if btn_text == '0':
# 数字0占两列
btn = tk.Button(
button_frame,
text=btn_text,
command=lambda t=btn_text: self.button_click(t),
**button_config,
bg="lightgray"
)
btn.grid(row=i, column=j, columnspan=2,
sticky="ew", padx=2, pady=2)
elif btn_text == '=':
# 等号按钮
btn = tk.Button(
button_frame,
text=btn_text,
command=lambda t=btn_text: self.button_click(t),
**button_config,
bg="orange",
fg="white"
)
btn.grid(row=i, column=j+1,
sticky="ew", padx=2, pady=2)
else:
# 其他按钮
color = "orange" if btn_text in ['÷', '×', '-', '+'] else "lightgray"
btn = tk.Button(
button_frame,
text=btn_text,
command=lambda t=btn_text: self.button_click(t),
**button_config,
bg=color,
fg="white" if color == "orange" else "black"
)
btn.grid(row=i, column=j,
sticky="ew", padx=2, pady=2)
# 配置列权重
for i in range(4):
button_frame.columnconfigure(i, weight=1)
def button_click(self, value):
"""按钮点击处理"""
current = self.display_var.get()
if value == 'C':
self.display_var.set("0")
elif value.isdigit() or value == '.':
if current == "0":
self.display_var.set(value)
else:
self.display_var.set(current + value)
elif value == '=':
try:
# 简化的计算逻辑
expression = current.replace('×', '*').replace('÷', '/')
result = eval(expression)
self.display_var.set(str(result))
except:
messagebox.showerror("错误", "计算错误")
self.display_var.set("0")
else:
# 运算符处理
self.display_var.set(current + value)
def run(self):
self.root.mainloop()
# 运行计算器
if __name__ == "__main__":
calc = SimpleCalculator()
calc.run()

🎨 实战案例2:文件操作工具
这个案例展示了Button在实际文件处理项目中的应用:
Pythonimport time
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, messagebox, scrolledtext
import os
import shutil
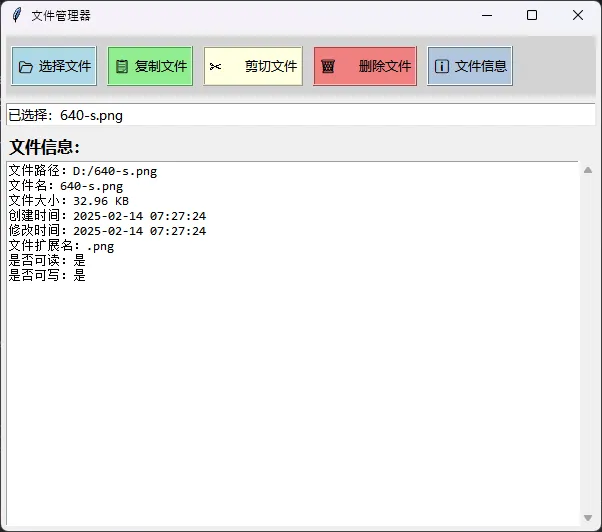
class FileManager:
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk()
self.root.title("文件管理器")
self.root.geometry("600x500")
# 当前选择的文件路径
self.current_file = None
self.create_interface()
def create_interface(self):
"""创建主界面"""
# 顶部按钮区域
top_frame = tk.Frame(self.root, bg="lightgray", height=60)
top_frame.pack(fill="x", padx=5, pady=5)
top_frame.pack_propagate(False)
# 按钮样式配置
btn_style = {
'font': ('微软雅黑', 10),
'height': 2,
'relief': 'ridge',
'bd': 2
}
# 文件操作按钮
buttons = [
("📂 选择文件", self.select_file, "lightblue"),
("📋 复制文件", self.copy_file, "lightgreen"),
("✂️ 剪切文件", self.cut_file, "lightyellow"),
("🗑️ 删除文件", self.delete_file, "lightcoral"),
("ℹ️ 文件信息", self.show_file_info, "lightsteelblue")
]
for i, (text, command, color) in enumerate(buttons):
btn = tk.Button(
top_frame,
text=text,
command=command,
bg=color,
**btn_style
)
btn.pack(side="left", padx=5, pady=10, fill="y")
# 状态显示区域
self.status_label = tk.Label(
self.root,
text="请选择一个文件",
bg="white",
relief="sunken",
bd=1,
anchor="w",
font=('微软雅黑', 10)
)
self.status_label.pack(fill="x", padx=5, pady=2)
# 文件信息显示区域
info_frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
info_frame.pack(fill="both", expand=True, padx=5, pady=5)
tk.Label(info_frame, text="文件信息:", font=('微软雅黑', 12, 'bold')).pack(anchor="w")
self.info_text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(
info_frame,
height=20,
font=('Consolas', 10),
wrap=tk.WORD
)
self.info_text.pack(fill="both", expand=True)
def select_file(self):
"""选择文件"""
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="选择文件",
filetypes=[
("所有文件", "*.*"),
("文本文件", "*.txt"),
("Python文件", "*.py"),
("图片文件", "*.jpg;*.png;*.gif")
]
)
if file_path:
self.current_file = file_path
self.status_label.config(text=f"已选择:{os.path.basename(file_path)}")
self.update_file_info()
def copy_file(self):
"""复制文件"""
if not self.current_file:
messagebox.showwarning("警告", "请先选择一个文件")
return
save_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(
title="复制文件到...",
defaultextension=os.path.splitext(self.current_file)[1],
initialfile=f"copy_{os.path.basename(self.current_file)}"
)
if save_path:
try:
shutil.copy2(self.current_file, save_path)
messagebox.showinfo("成功", f"文件已复制到:\n{save_path}")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"复制失败:{str(e)}")
def cut_file(self):
"""剪切文件"""
if not self.current_file:
messagebox.showwarning("警告", "请先选择一个文件")
return
save_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(
title="移动文件到...",
defaultextension=os.path.splitext(self.current_file)[1],
initialfile=os.path.basename(self.current_file)
)
if save_path:
try:
shutil.move(self.current_file, save_path)
messagebox.showinfo("成功", f"文件已移动到:\n{save_path}")
self.current_file = None
self.status_label.config(text="请选择一个文件")
self.info_text.delete(1.0, tk.END)
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"移动失败:{str(e)}")
def delete_file(self):
"""删除文件"""
if not self.current_file:
messagebox.showwarning("警告", "请先选择一个文件")
return
if messagebox.askyesno("确认", f"确定要删除文件吗?\n{self.current_file}"):
try:
os.remove(self.current_file)
messagebox.showinfo("成功", "文件已删除")
self.current_file = None
self.status_label.config(text="请选择一个文件")
self.info_text.delete(1.0, tk.END)
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"删除失败:{str(e)}")
def show_file_info(self):
"""显示文件详细信息"""
if not self.current_file:
messagebox.showwarning("警告", "请先选择一个文件")
return
self.update_file_info()
def update_file_info(self):
"""更新文件信息显示"""
if not self.current_file or not os.path.exists(self.current_file):
return
try:
stat = os.stat(self.current_file)
size = stat.st_size
# 格式化文件大小
if size < 1024:
size_str = f"{size} B"
elif size < 1024 * 1024:
size_str = f"{size / 1024:.2f} KB"
else:
size_str = f"{size / (1024 * 1024):.2f} MB"
info = f"""文件路径:{self.current_file}
文件名:{os.path.basename(self.current_file)}
文件大小:{size_str}
创建时间:{time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime(stat.st_ctime))}
修改时间:{time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime(stat.st_mtime))}
文件扩展名:{os.path.splitext(self.current_file)[1]}
是否可读:{'是' if os.access(self.current_file, os.R_OK) else '否'}
是否可写:{'是' if os.access(self.current_file, os.W_OK) else '否'}
"""
self.info_text.delete(1.0, tk.END)
self.info_text.insert(1.0, info)
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"获取文件信息失败:{str(e)}")
def run(self):
self.root.mainloop()
# 运行文件管理器
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = FileManager()
app.run()
🎯 高级技巧与最佳实践
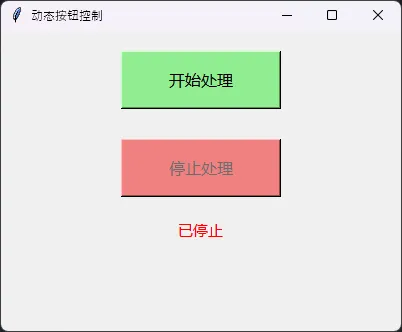
动态按钮状态控制
Pythonimport tkinter as tk
import threading
import time
class DynamicButtonDemo:
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk()
self.root.title("动态按钮控制")
self.root.geometry("400x300")
# 按钮状态标志
self.is_processing = False
self.create_buttons()
def create_buttons(self):
"""创建动态控制按钮"""
# 处理按钮
self.process_btn = tk.Button(
self.root,
text="开始处理",
command=self.start_process,
font=('微软雅黑', 12),
bg="lightgreen",
width=15,
height=2
)
self.process_btn.pack(pady=20)
# 停止按钮(初始禁用)
self.stop_btn = tk.Button(
self.root,
text="停止处理",
command=self.stop_process,
font=('微软雅黑', 12),
bg="lightcoral",
width=15,
height=2,
state="disabled" # 初始禁用
)
self.stop_btn.pack(pady=10)
# 状态标签
self.status_label = tk.Label(
self.root,
text="就绪",
font=('微软雅黑', 11),
fg="green"
)
self.status_label.pack(pady=10)
def start_process(self):
"""开始处理"""
if self.is_processing:
return
self.is_processing = True
# 更新按钮状态
self.process_btn.config(state="disabled", text="处理中...")
self.stop_btn.config(state="normal")
# 更新状态
self.status_label.config(text="正在处理...", fg="orange")
# 在新线程中执行耗时操作
thread = threading.Thread(target=self.simulate_process)
thread.daemon = True
thread.start()
def simulate_process(self):
"""模拟处理过程"""
for i in range(10):
if not self.is_processing:
break
# 更新进度
self.root.after(0, lambda i=i: self.status_label.config(
text=f"处理中... {(i+1)*10}%"
))
time.sleep(1) # 模拟处理时间
# 处理完成
if self.is_processing:
self.root.after(0, self.process_completed)
def stop_process(self):
"""停止处理"""
self.is_processing = False
# 重置按钮状态
self.process_btn.config(state="normal", text="开始处理")
self.stop_btn.config(state="disabled")
# 更新状态
self.status_label.config(text="已停止", fg="red")
def process_completed(self):
"""处理完成"""
self.is_processing = False
# 重置按钮状态
self.process_btn.config(state="normal", text="开始处理")
self.stop_btn.config(state="disabled")
# 更新状态
self.status_label.config(text="处理完成", fg="green")
def run(self):
self.root.mainloop()
# 运行演示
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo = DynamicButtonDemo()
demo.run()
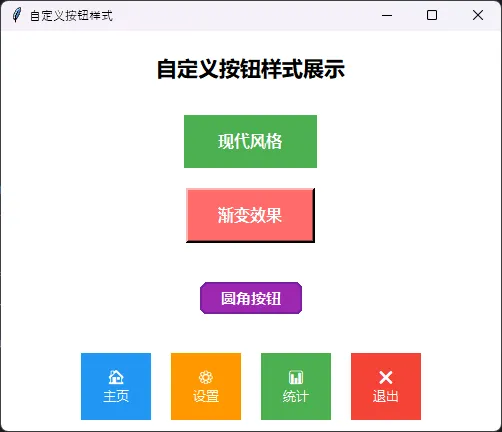
自定义按钮样式
Pythonimport tkinter as tk
class CustomButtonStyles:
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk()
self.root.title("自定义按钮样式")
self.root.geometry("500x400")
self.root.config(bg="white")
self.create_styled_buttons()
def create_styled_buttons(self):
"""创建各种样式的按钮"""
# 标题
title_label = tk.Label(
self.root,
text="自定义按钮样式展示",
font=('微软雅黑', 16, 'bold'),
bg="white"
)
title_label.pack(pady=20)
# 现代风格按钮
modern_btn = tk.Button(
self.root,
text="现代风格",
font=('微软雅黑', 12, 'bold'),
bg="#4CAF50",
fg="white",
relief="flat",
bd=0,
padx=30,
pady=10,
cursor="hand2"
)
modern_btn.pack(pady=10)
# 绑定hover效果
def on_enter(e):
modern_btn.config(bg="#45a049")
def on_leave(e):
modern_btn.config(bg="#4CAF50")
modern_btn.bind("<Enter>", on_enter)
modern_btn.bind("<Leave>", on_leave)
# 渐变效果按钮(模拟)
gradient_frame = tk.Frame(self.root, bg="white")
gradient_frame.pack(pady=10)
gradient_btn = tk.Button(
gradient_frame,
text="渐变效果",
font=('微软雅黑', 12, 'bold'),
bg="#FF6B6B",
fg="white",
relief="raised",
bd=3,
padx=25,
pady=8
)
gradient_btn.pack()
# 圆角按钮(使用Canvas模拟)
canvas = tk.Canvas(self.root, width=200, height=60, bg="white", highlightthickness=0)
canvas.pack(pady=15)
# 绘制圆角矩形
def create_rounded_button(canvas, x1, y1, x2, y2, r=10, **kwargs):
points = []
for x, y in [(x1, y1 + r), (x1, y1), (x1 + r, y1),
(x2 - r, y1), (x2, y1), (x2, y1 + r),
(x2, y2 - r), (x2, y2), (x2 - r, y2),
(x1 + r, y2), (x1, y2), (x1, y2 - r)]:
points.extend([x, y])
return canvas.create_polygon(points, smooth=True, **kwargs)
# 创建圆角按钮背景
rounded_bg = create_rounded_button(
canvas, 50, 15, 150, 45, r=15,
fill="#9C27B0", outline="#7B1FA2", width=2
)
# 添加文字
canvas.create_text(100, 30, text="圆角按钮",
fill="white", font=('微软雅黑', 11, 'bold'))
# 图标按钮
icon_frame = tk.Frame(self.root, bg="white")
icon_frame.pack(pady=10)
# 模拟图标按钮
icon_buttons = [
("🏠", "主页", "#2196F3"),
("⚙️", "设置", "#FF9800"),
("📊", "统计", "#4CAF50"),
("❌", "退出", "#F44336")
]
for icon, text, color in icon_buttons:
btn_frame = tk.Frame(icon_frame, bg="white")
btn_frame.pack(side="left", padx=10)
btn = tk.Button(
btn_frame,
text=f"{icon}\n{text}",
font=('微软雅黑', 10),
bg=color,
fg="white",
relief="flat",
bd=0,
width=8,
height=3,
cursor="hand2"
)
btn.pack()
def run(self):
self.root.mainloop()
# 运行样式演示
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo = CustomButtonStyles()
demo.run()
🎯 总结
通过本文的深入学习,我们全面掌握了Python Tkinter Button控件的核心技能。从基础的按钮创建到复杂的文件管理器开发,每个实例都体现了编程技巧在实际项目中的应用价值。
三个核心要点:
- 基础扎实:熟练掌握Button的参数配置和事件绑定机制
- 实战导向:通过计算器和文件管理器项目,理解Button在复杂界面中的应用
- 优化意识:关注性能优化和用户体验,为上位机开发奠定基础
掌握了Button控件,你已经迈出了Python GUI开发的重要一步。结合本文的实战案例和最佳实践,相信你能够开发出更加专业和实用的桌面应用程序。继续深入学习其他Tkinter控件,你的Python开发技能将会更加全面和深入!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录