目录
🚀 C#开发神器:不可变集合让你的代码更安全、更高效
在多线程横行的今天,你是否还在为集合的线程安全问题而头疼?是否因为意外修改了共享数据而导致程序崩溃?今天我们来聊聊C#中一个被严重低估的"神器"——不可变集合(Immutable Collections),它能够从根本上解决这些痛点,让你的代码既安全又优雅。
🔥 为什么你需要不可变集合?
痛点一:多线程环境下的数据竞争
c#// 传统做法:需要手动加锁
private static readonly object _lock = new object();
private static List<string> _sharedList = new List<string>();
public void AddItem(string item)
{
lock (_lock) // 每次操作都要加锁,性能开销大
{
_sharedList.Add(item);
}
}
痛点二:意外修改导致的Bug
c#public List<Product> GetProducts()
{
return _products; // 危险!外部可能会修改这个集合
}
// 调用方可能无意中修改了数据
var products = service.GetProducts();
products.Clear(); // 糟糕!原始数据被清空了
痛点三:防御性编程的性能损耗
c#public List<Product> GetProducts()
{
return new List<Product>(_products); // 每次都要复制,内存浪费
}
💡 不可变集合的五大核心优势
🎯 1. 天然线程安全
不可变集合一旦创建就无法修改,天然具备线程安全特性
c#using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建不可变列表
var originalList = ImmutableList.Create("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
// 多线程环境下安全访问,无需加锁
Task.Run(() =>
{
foreach (var item in originalList) // 完全安全,不会有数据竞争
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
});
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
🎯 2. 结构化共享,性能卓越
c#using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 添加元素时,不会复制整个集合
var list1 = ImmutableList.Create(1, 2, 3);
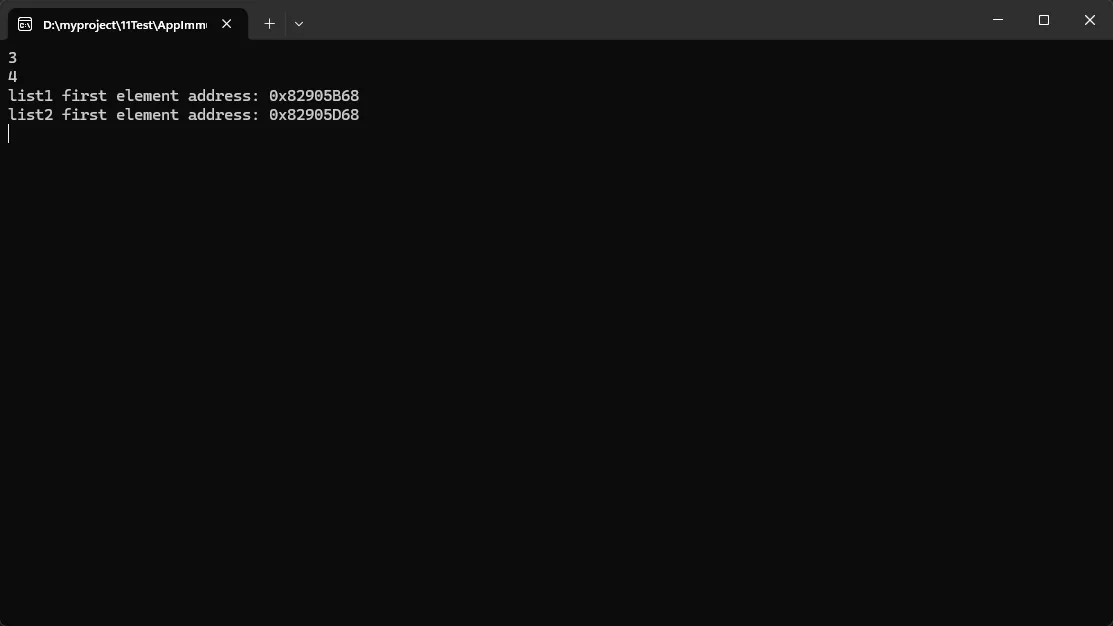
var list2 = list1.Add(4); // 只创建新的节点,共享原有数据
Console.WriteLine(list1.Count); // 3 - 原集合不变
Console.WriteLine(list2.Count); // 4 - 新集合包含新元素
var list1Buffer = list1.ToArray();
var list2Buffer = list2.ToArray();
unsafe
{
fixed (int* list1Ptr = &list1Buffer[0])
fixed (int* list2Ptr = &list2Buffer[0])
{
Console.WriteLine($"list1 first element address: 0x{(long)list1Ptr:X}");
Console.WriteLine($"list2 first element address: 0x{(long)list2Ptr:X}");
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
🎯 3. 安全的数据传递
c#public class ProductService
{
private readonly ImmutableList<Product> _products;
public ImmutableList<Product> GetProducts()
{
return _products; // 安全!外部无法修改
}
public ProductService AddProduct(Product product)
{
// 返回新实例,原实例保持不变
return new ProductService(_products.Add(product));
}
}
注意:这个问题很多发生,一定要注意
🎯 4. 支持枚举时修改
c#using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var mutableList = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
var immutableList = ImmutableList.Create(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// 可变集合:枚举时修改会抛异常
//foreach (var item in mutableList)
//{
// if (item % 2 == 0)
// mutableList.Remove(item); // InvalidOperationException!
//}
// 不可变集合:安全的"修改"操作
foreach (var item in immutableList)
{
if (item % 2 == 0)
immutableList = immutableList.Remove(item); // 完全安全!
}
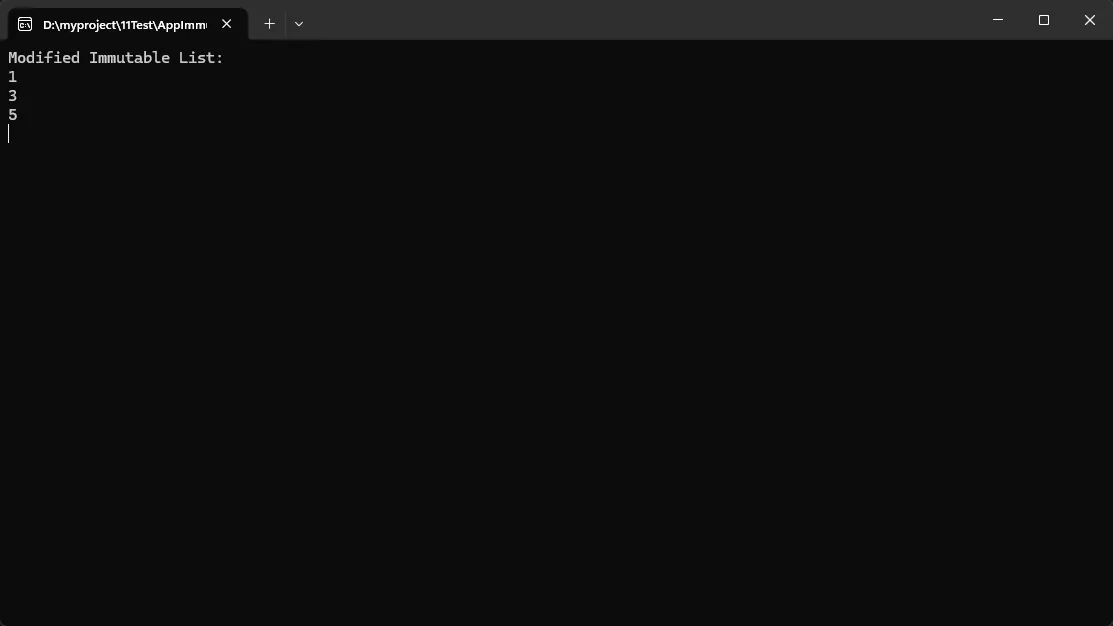
Console.WriteLine("Modified Immutable List:");
foreach (var item in immutableList)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
注意:这个在remove时,比List要靠谱不少,省事一些
🎯 5. 函数式编程友好
c#// 链式操作,代码更简洁
using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
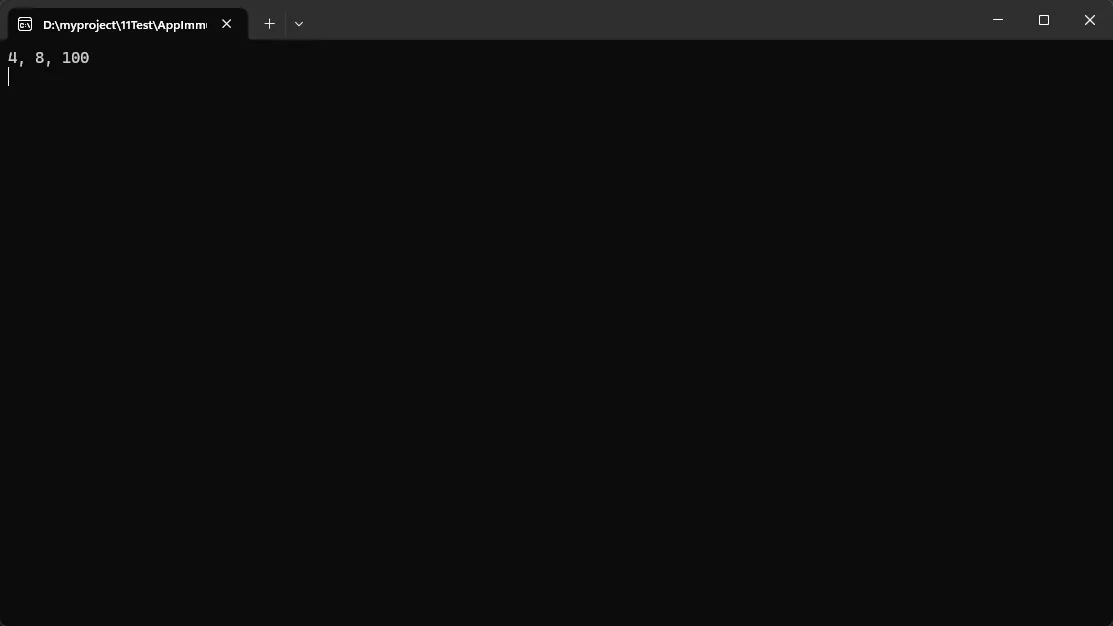
// 链式操作,代码更简洁
var result = ImmutableList.Create(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.Where(x => x % 2 == 0)
.Select(x => x * 2)
.ToImmutableList()
.Add(100)
.Sort();
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(", ", result));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
🛠️ 实战应用:五种核心集合类型
📚 1. ImmutableList<T> - 有序列表
c#using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建方式
var list = ImmutableList<string>.Empty
.Add("First")
.Add("Second")
.Add("Third");
// 或者从现有集合创建
var existingData = new[] { "Apple", "Banana", "Cherry" };
var immutableList = existingData.ToImmutableList();
// 高效批量操作
var builder = ImmutableList.CreateBuilder<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
builder.Add(i); // 使用Builder避免频繁创建新实例
}
var finalList = builder.ToImmutable();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
最佳实践: 对于频繁的批量修改操作,使用Builder模式提升性能。
🗂️ 2. ImmutableDictionary<TKey, TValue> - 键值对集合
c#using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 配置管理场景
var config = ImmutableDictionary<string, string>.Empty
.Add("DatabaseUrl", "Server=localhost;Database=MyDB")
.Add("ApiKey", "123456")
.Add("CacheTimeout", "300");
config = UpdateConfig(config, "CacheTimeout", "600"); // 更新配置
config = UpdateConfig(config, "Password", "123");
// 高效查找
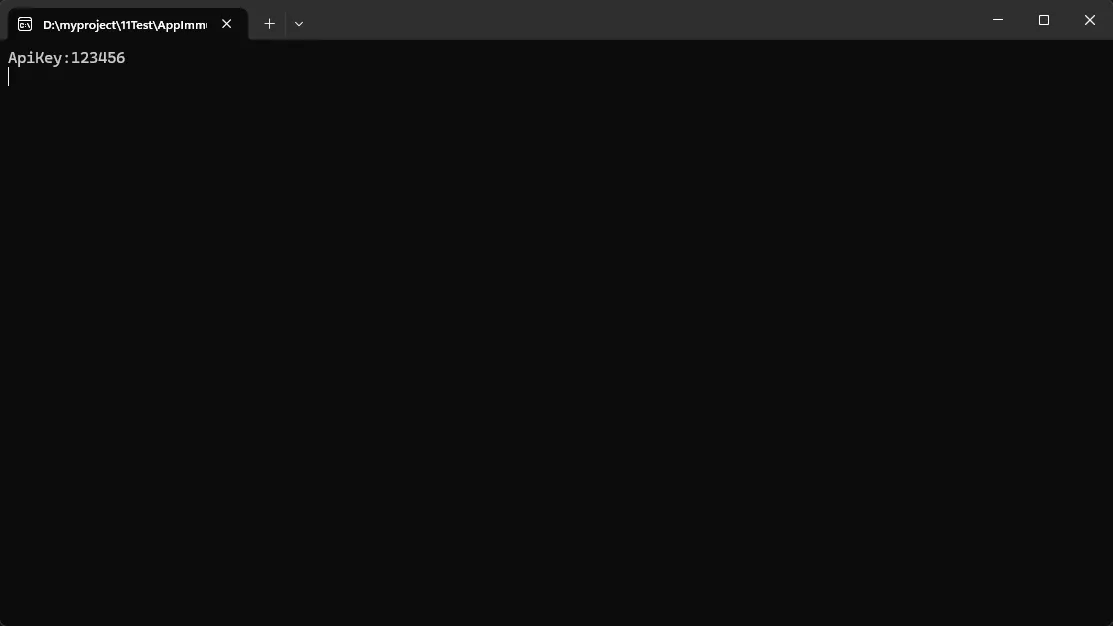
if (config.TryGetValue("ApiKey", out var apiKey))
{
Console.WriteLine("ApiKey:" + apiKey);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
// 线程安全的配置更新
private static ImmutableDictionary<string, string> UpdateConfig(
ImmutableDictionary<string, string> currentConfig,
string key,
string value)
{
return currentConfig.SetItem(key, value); // 返回新配置实例
}
}
}
🎯 3. ImmutableHashSet<T> - 唯一值集合
c#using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 权限管理系统
var adminPermissions = ImmutableHashSet.Create(
"READ_USERS",
"WRITE_USERS",
"DELETE_USERS",
"SYSTEM_CONFIG"
);
var userPermissions = ImmutableHashSet.Create(
"READ_USERS"
);
// 权限合并
var combinedPermissions = adminPermissions.Union(userPermissions);
foreach (var item in combinedPermissions)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
// 权限检查
private static bool HasPermission(ImmutableHashSet<string> userPerms, string permission)
{
return userPerms.Contains(permission); // O(1) 时间复杂度
}
}
}
📦 4. ImmutableQueue<T> 和 ImmutableStack<T> - 特殊用途集合
c#using System.Collections.Immutable;
namespace AppImmutableList
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 任务队列场景
var taskQueue = ImmutableQueue<string>.Empty
.Enqueue("Task1")
.Enqueue("Task2")
.Enqueue("Task3");
// 处理任务
while (!taskQueue.IsEmpty)
{
var task = taskQueue.Peek(); // 查看队首任务
taskQueue = taskQueue.Dequeue(); // 移除任务,返回新队列
Console.WriteLine($"Processing: {task}");
}
// 函数调用栈模拟
var callStack = ImmutableStack<string>.Empty
.Push("Main()")
.Push("ProcessData()")
.Push("ValidateInput()");
var currentMethod = callStack.Peek(); // ValidateInput()
callStack = callStack.Pop(); // 返回调用方法
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
🏗️ 5. 性能优化:Builder模式的正确使用
c#// ❌ 错误做法:频繁创建新实例
var list = ImmutableList<int>.Empty;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
list = list.Add(i); // 每次都创建新实例,性能差
}
// ✅ 正确做法:使用Builder
var builder = ImmutableList.CreateBuilder<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
builder.Add(i); // 高效的可变操作
}
var optimizedList = builder.ToImmutable(); // 一次性转换
// 真实场景:批量数据处理
public ImmutableList<ProcessedData> ProcessLargeDataset(IEnumerable<RawData> rawData)
{
var builder = ImmutableList.CreateBuilder<ProcessedData>();
foreach (var item in rawData)
{
if (IsValidData(item))
{
builder.Add(TransformData(item));
}
}
return builder.ToImmutable();
}
⚠️ 常见陷阱与最佳实践
陷阱1:误解"不可变"的含义
c#// ❌ 容易误解的代码
var list = ImmutableList.Create(new Person("John"));
list[0].Name = "Jane"; // 对象本身仍然可变!
// ✅ 正确理解:不可变的是集合结构,不是元素内容
// 如果需要元素也不可变,请使用不可变的值类型或record
public record Person(string Name, int Age);
var list = ImmutableList.Create(new Person("John", 25));
陷阱2:性能考虑
c#// ❌ 对于频繁的单个修改操作,传统集合可能更高效
var mutableList = new List<int>(capacity: 1000);
mutableList.Add(item); // O(1) 摊销时间
// ✅ 不可变集合适合读多写少的场景
var immutableList = existingList.Add(item); // O(log n) 时间
最佳实践总结
- 读多写少的场景优先考虑不可变集合
- 多线程环境下使用不可变集合避免锁开销
- 批量操作时使用Builder模式
- API设计中使用不可变集合提供安全的数据访问
- 配置管理等需要版本化的场景非常适合
🔧 安装与使用
xml<!-- 在项目文件中添加NuGet包引用 -->
<PackageReference Include="System.Collections.Immutable" Version="8.0.0" />
c#// 引入命名空间
using System.Collections.Immutable;
// 开始使用
var myList = ImmutableList.Create("Hello", "World");
🎯 总结与思考
不可变集合是现代C#开发中的一个重要工具,它能够:
- 彻底解决多线程数据竞争问题,无需手动同步
- 提供结构化共享机制,在保证安全的同时优化内存使用
- 支持函数式编程范式,让代码更加优雅和可维护
记住这三个"金句":
- "一旦不可变,永远线程安全"
- "共享结构,独立修改"
- "批量操作用Builder,单次操作用方法"
你在项目中是否遇到过因为集合修改导致的线程安全问题?或者有没有使用不可变集合的实践经验?欢迎在评论区分享你的经验和遇到的挑战!
觉得这篇文章对你的C#开发有帮助?请转发给更多同行,让我们一起写出更安全、更高效的代码! 👍
更多C#开发技巧和最佳实践,请关注我们的技术公众号!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录