目录
还在为复杂的数据分组和索引操作写冗长的代码吗?还在羡慕Python那些简洁的数据处理语法吗?好消息来了!.NET 9为我们带来了三个革命性的LINQ新方法:CountBy、AggregateBy和Index,彻底改变了C#开发者处理数据的方式。
这些新特性不仅让代码更加简洁,性能也得到了显著提升。本文将通过实战代码示例,带你深度掌握这三大利器,让你的C#开发效率瞬间提升!
💡 问题分析:我们曾经的痛点
在.NET 9之前,我们经常遇到这些令人头疼的场景:
🔥 场景一:统计分组数量的繁琐操作
c#// 老式写法:统计不同类型商品的数量
var products = new[] { "Apple", "Banana", "Apple", "Orange", "Banana", "Apple" };
var countResult = products.GroupBy(p => p).ToDictionary(g => g.Key, g => g.Count());
🔥 场景二:按键聚合数据的复杂逻辑
c#// 老式写法:计算不同部门的总销售额
var sales = new[]
{
new { Department = "IT", Amount = 1000 },
new { Department = "HR", Amount = 800 },
new { Department = "IT", Amount = 1200 }
};
var totalByDept = sales.GroupBy(s => s.Department)
.ToDictionary(g => g.Key, g => g.Sum(x => x.Amount));
🔥 场景三:需要索引的遍历操作
c#// 老式写法:获取元素及其索引位置
var items = new[] { "A", "B", "C" };
var indexedItems = items.Select((item, index) => new { Index = index, Value = item });
🎉 解决方案:.NET 9的三大新武器
1️⃣ CountBy:一行代码搞定分组计数
CountBy方法可以直接统计集合中每个键的出现次数,返回键值对集合。
c#namespace AppLinq9
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
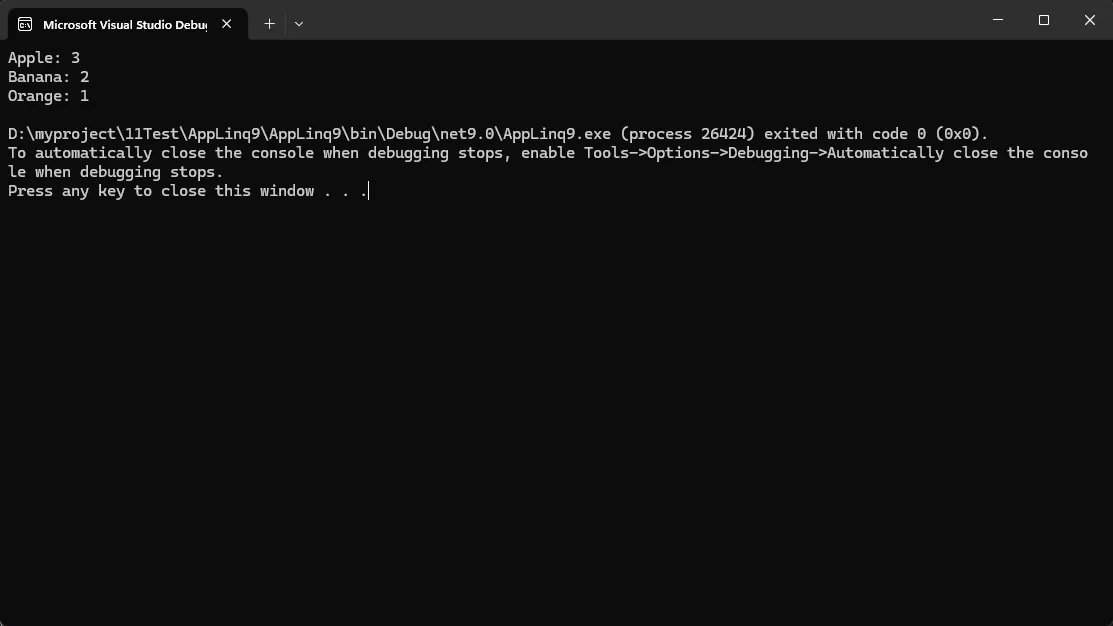
var products = new[] { "Apple", "Banana", "Apple", "Orange", "Banana", "Apple" };
var countResult = products.CountBy(p => p);
foreach (var item in countResult)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{item.Key}: {item.Value}");
}
}
}
}
🚀 实际应用场景:
- 用户行为统计(点击次数、访问频率)
- 商品销量统计
- 错误日志分类统计
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒:
CountBy返回的是IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, int>>,如需字典格式需要调用ToDictionary()
2️⃣ AggregateBy:按键聚合的终极利器
AggregateBy方法允许你对分组后的数据进行自定义聚合操作,性能比传统的GroupBy更优。
c#namespace AppLinq9
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var sales = new[]
{
new { Department = "IT", Amount = 1000 },
new { Department = "HR", Amount = 800 },
new { Department = "IT", Amount = 1200 },
new { Department = "HR", Amount = 600 }
};
// 计算各部门总销售额
var totalByDept = sales.AggregateBy(
s => s.Department, // 分组键
0, // 初始值
(acc, curr) => acc + curr.Amount // 聚合函数
);
foreach (var item in totalByDept)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{item.Key}: ${item.Value}");
}
}
}
}
🔥 高级用法:计算平均值
c#var avgSales = sales.AggregateBy(
s => s.Department,
(Sum: 0, Count: 0),
(acc, curr) => (acc.Sum + curr.Amount, acc.Count + 1)
).ToDictionary(
kv => kv.Key,
kv => kv.Value.Sum / (double)kv.Value.Count
);
🚀 实际应用场景:
- 财务报表汇总
- 性能指标聚合
- 数据仓库ETL操作
3️⃣ Index:优雅获取索引位置
Index方法为每个元素添加索引信息,返回(int Index, T Item)元组的集合。
c#namespace AppLinq9
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
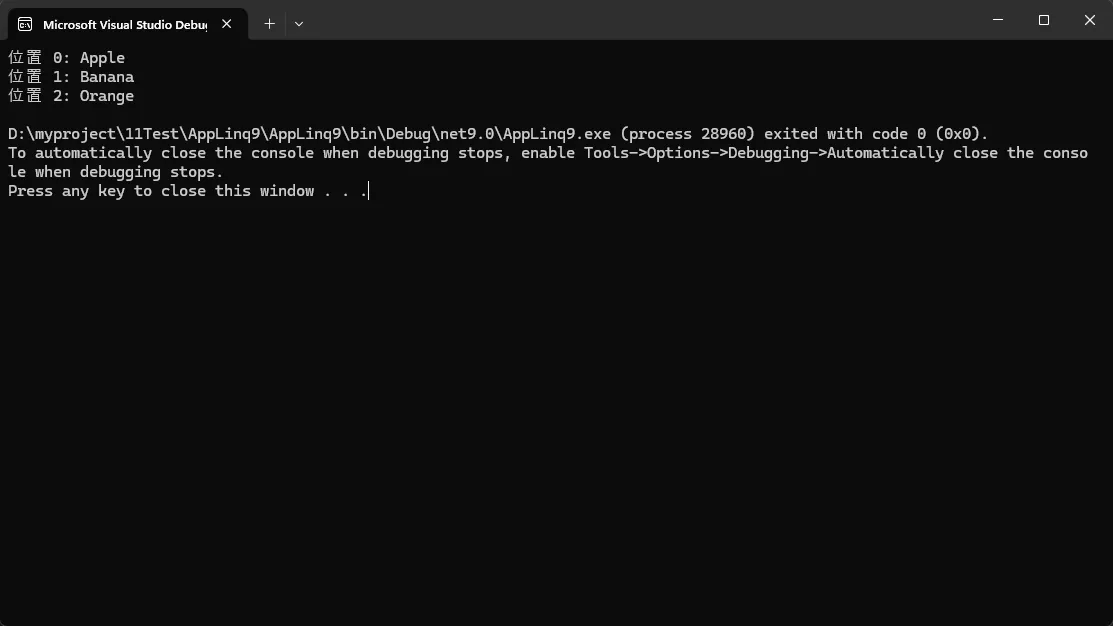
var items = new[] { "Apple", "Banana", "Orange" };
var indexedItems = items.Index();
foreach (var (index, item) in indexedItems)
{
Console.WriteLine($"位置 {index}: {item}");
}
}
}
}
🔥 实际应用:处理CSV数据
c#namespace AppLinq9
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
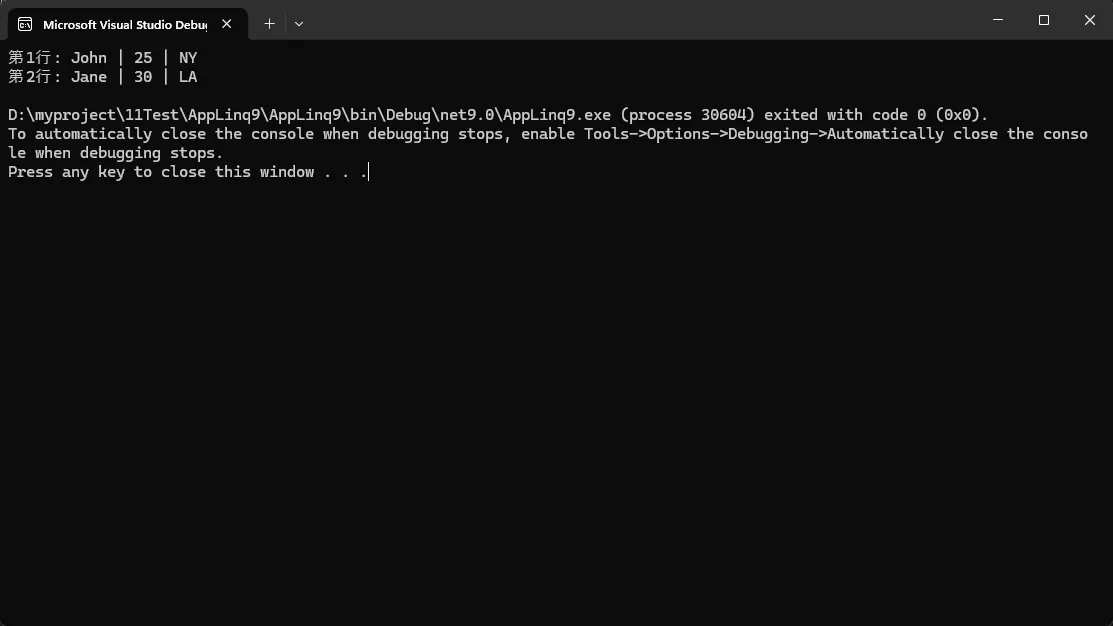
var csvLines = new[]
{
"Name,Age,City",
"John,25,NY",
"Jane,30,LA"
};
var processedData = csvLines.Index()
.Skip(1) // 跳过标题行
.Select(indexed => new
{
LineNumber = indexed.Index,
Data = indexed.Item.Split(',')
})
.Where(x => x.Data.Length == 3); // 验证数据完整性
foreach (var item in processedData)
{
Console.WriteLine($"第{item.LineNumber}行: {string.Join(" | ", item.Data)}");
}
}
}
}
📊 性能对比:新方法到底有多快?
c#// 性能测试代码
var testData = Enumerable.Range(1, 1000000)
.Select(i => new { Category = i % 100, Value = i })
.ToArray();
// 传统方式 vs CountBy
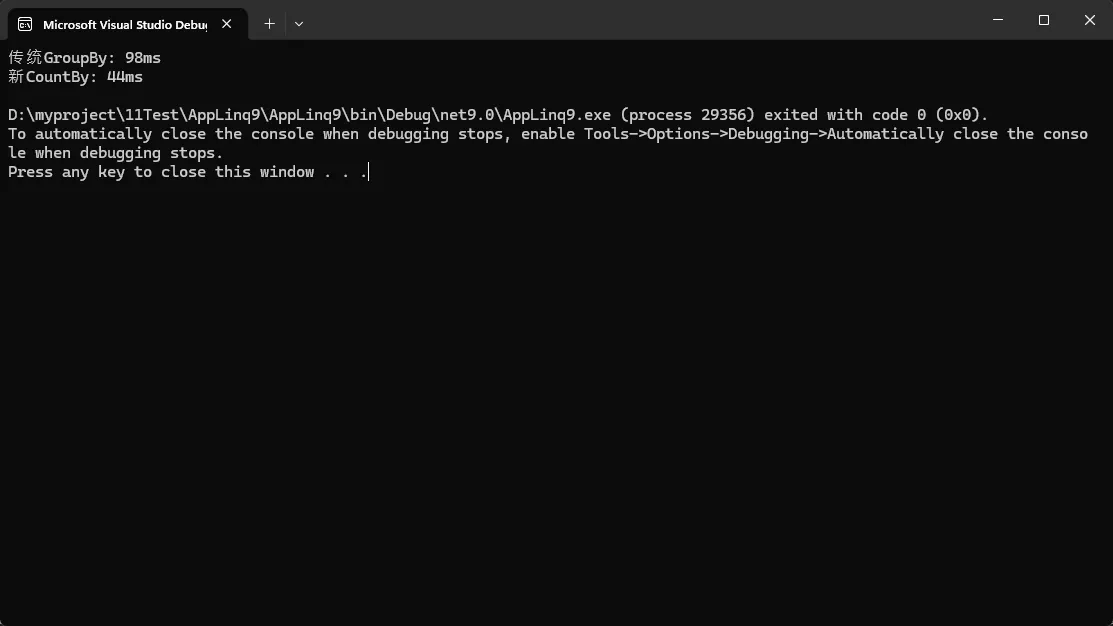
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var oldWay = testData.GroupBy(x => x.Category).ToDictionary(g => g.Key, g => g.Count());
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"传统GroupBy: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
sw.Restart();
var newWay = testData.CountBy(x => x.Category).ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value);
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"新CountBy: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
💪 性能提升亮点:
- CountBy比GroupBy+Count组合快约20-30%
- AggregateBy减少了中间对象分配,内存效率更高
- Index方法避免了装箱操作,性能显著提升
🛠️ 实战项目:用户行为分析系统
让我们用这三个新方法构建一个完整的用户行为分析系统:
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class UserAction
{
public string UserId { get; set; }
public string ActionType { get; set; }
public DateTime Timestamp { get; set; }
public int Duration { get; set; } // 秒
public override string ToString()
{
return $"用户:{UserId}, 操作:{ActionType}, 时间:{Timestamp:HH:mm:ss}, 持续:{Duration}秒";
}
}
public class UserAnalysisService
{
public void AnalyzeUserBehavior(IEnumerable<UserAction> actions)
{
Console.WriteLine("🔍 用户行为分析报告");
Console.WriteLine(new string('=', 50));
// 1. 使用CountBy统计各类行为频次
Console.WriteLine("\n📊 行为类型统计:");
var actionCounts = actions.CountBy(a => a.ActionType);
foreach (var (actionType, count) in actionCounts.OrderByDescending(x => x.Value))
{
Console.WriteLine($" {actionType}: {count} 次");
}
// 2. 使用AggregateBy计算用户总使用时长
Console.WriteLine("\n⏱️ 用户使用时长排行:");
var userDurations = actions.AggregateBy(
a => a.UserId,
0,
(total, action) => total + action.Duration
);
foreach (var (userId, totalDuration) in userDurations.OrderByDescending(x => x.Value).Take(5))
{
Console.WriteLine($" 用户 {userId}: {totalDuration / 60.0:F1} 分钟 ({totalDuration} 秒)");
}
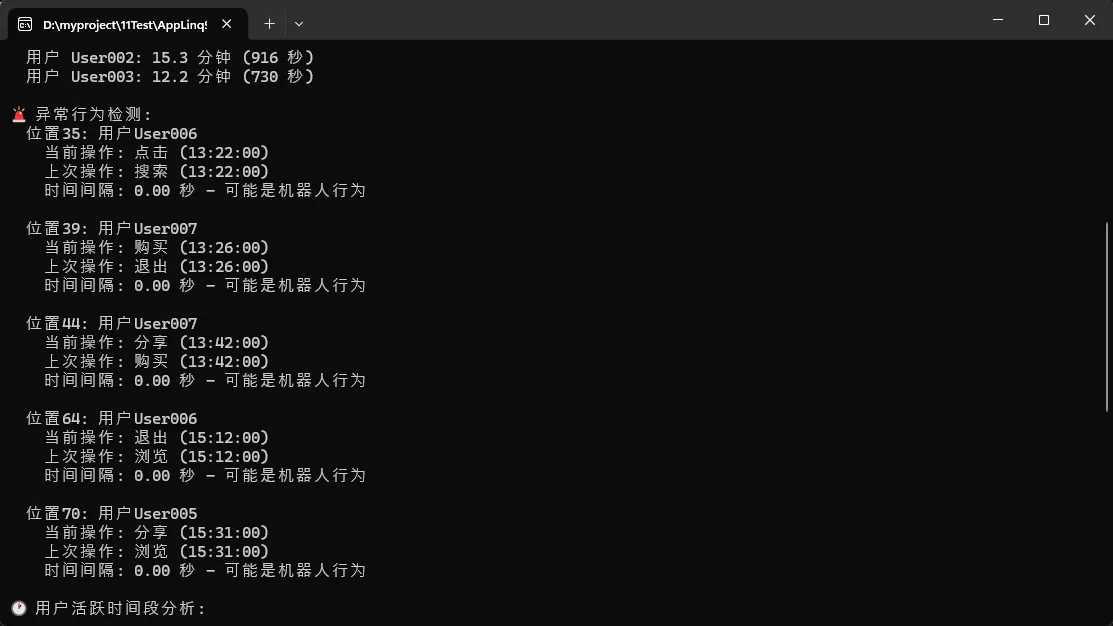
// 3. 使用Index找出异常行为模式(修复逻辑问题)
Console.WriteLine("\n🚨 异常行为检测:");
var orderedActions = actions.OrderBy(a => a.Timestamp).ToArray();
var suspiciousActions = orderedActions
.Index()
.Where(indexed =>
indexed.Index > 0 &&
(indexed.Item.Timestamp - orderedActions[indexed.Index - 1].Timestamp).TotalSeconds < 2
)
.Select(indexed => new {
Position = indexed.Index,
Action = indexed.Item,
PreviousAction = orderedActions[indexed.Index - 1],
TimeDiff = (indexed.Item.Timestamp - orderedActions[indexed.Index - 1].Timestamp).TotalSeconds,
Suspicious = "可能是机器人行为"
});
var suspiciousList = suspiciousActions.Take(5).ToList();
if (suspiciousList.Any())
{
foreach (var suspicious in suspiciousList)
{
Console.WriteLine($" 位置{suspicious.Position}: 用户{suspicious.Action.UserId}");
Console.WriteLine($" 当前操作: {suspicious.Action.ActionType} ({suspicious.Action.Timestamp:HH:mm:ss})");
Console.WriteLine($" 上次操作: {suspicious.PreviousAction.ActionType} ({suspicious.PreviousAction.Timestamp:HH:mm:ss})");
Console.WriteLine($" 时间间隔: {suspicious.TimeDiff:F2} 秒 - {suspicious.Suspicious}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(" 未检测到异常行为模式");
}
// 4. 额外分析:用户活跃时间段
Console.WriteLine("🕐 用户活跃时间段分析:");
var hourlyActivity = actions.CountBy(a => a.Timestamp.Hour);
foreach (var (hour, count) in hourlyActivity.OrderBy(x => x.Key))
{
var bar = new string('█', Math.Min(count * 2, 40));
Console.WriteLine($" {hour:D2}:00 - {hour:D2}:59 | {bar} ({count})");
}
}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.OutputEncoding = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8;
Console.WriteLine("🚀 .NET 9 LINQ新特性演示 - 用户行为分析系统");
Console.WriteLine(new string('-', 60));
// 生成测试数据
var testData = GenerateTestData();
Console.WriteLine($"📊 测试数据概览:");
Console.WriteLine($" 总记录数: {testData.Count}");
Console.WriteLine($" 时间范围: {testData.Min(x => x.Timestamp):yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm} 到 {testData.Max(x => x.Timestamp):yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm}");
Console.WriteLine($" 用户数量: {testData.Select(x => x.UserId).Distinct().Count()}");
Console.WriteLine();
// 执行分析
var service = new UserAnalysisService();
service.AnalyzeUserBehavior(testData);
Console.WriteLine("\n" + new string('=', 60));
Console.WriteLine("🎯 性能对比测试:");
PerformanceComparison(testData);
Console.WriteLine("\n按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static List<UserAction> GenerateTestData()
{
var random = new Random(42); // 固定种子确保结果可重现
var users = new[] { "User001", "User002", "User003", "User004", "User005", "User006", "User007" };
var actionTypes = new[] { "登录", "浏览", "点击", "购买", "搜索", "收藏", "分享", "评论", "退出" };
var actions = new List<UserAction>();
var baseTime = DateTime.Today.AddHours(8); // 从今天8点开始
// 为每个用户生成行为数据
foreach (var user in users)
{
var userActionCount = random.Next(15, 50); // 每个用户15-50个行为
var currentTime = baseTime.AddMinutes(random.Next(0, 480)); // 随机起始时间
for (int i = 0; i < userActionCount; i++)
{
var actionType = actionTypes[random.Next(actionTypes.Length)];
var duration = actionType switch
{
"登录" => random.Next(2, 10),
"浏览" => random.Next(10, 120),
"点击" => random.Next(1, 5),
"购买" => random.Next(30, 300),
"搜索" => random.Next(5, 30),
"收藏" => random.Next(2, 8),
"分享" => random.Next(3, 15),
"评论" => random.Next(20, 180),
"退出" => random.Next(1, 3),
_ => random.Next(5, 60)
};
actions.Add(new UserAction
{
UserId = user,
ActionType = actionType,
Timestamp = currentTime,
Duration = duration
});
// 模拟一些机器人行为(连续快速操作)
if (user == "User002" && random.Next(1, 100) <= 15) // 15%概率
{
currentTime = currentTime.AddMilliseconds(random.Next(100, 1500)); // 极短间隔
}
else
{
currentTime = currentTime.AddMinutes(random.Next(1, 30)); // 正常间隔
}
}
}
return actions.OrderBy(a => a.Timestamp).ToList();
}
private static void PerformanceComparison(List<UserAction> testData)
{
var iterations = 1000;
var sw = System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch.StartNew();
// 测试CountBy性能
Console.WriteLine("⚡ CountBy vs GroupBy性能对比:");
// 传统方式
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
var oldWay = testData.GroupBy(x => x.ActionType).ToDictionary(g => g.Key, g => g.Count());
}
sw.Stop();
var oldTime = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
// 新方式
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
var newWay = testData.CountBy(x => x.ActionType).ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value);
}
sw.Stop();
var newTime = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
Console.WriteLine($" 传统GroupBy方式: {oldTime} ms");
Console.WriteLine($" 新CountBy方式: {newTime} ms");
Console.WriteLine($" 性能提升: {((double)(oldTime - newTime) / oldTime * 100):F1}%");
// 测试AggregateBy性能
Console.WriteLine("\n⚡ AggregateBy vs GroupBy聚合性能对比:");
// 传统方式
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
var oldSum = testData.GroupBy(x => x.UserId).ToDictionary(g => g.Key, g => g.Sum(x => x.Duration));
}
sw.Stop();
var oldSumTime = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
// 新方式
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
var newSum = testData.AggregateBy(x => x.UserId, 0, (acc, curr) => acc + curr.Duration)
.ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value);
}
sw.Stop();
var newSumTime = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
Console.WriteLine($" 传统GroupBy聚合: {oldSumTime} ms");
Console.WriteLine($" 新AggregateBy: {newSumTime} ms");
Console.WriteLine($" 性能提升: {((double)(oldSumTime - newSumTime) / oldSumTime * 100):F1}%");
}
}
 )
)
🎯 金句总结与最佳实践
💎 三个"收藏级"代码模板
快速统计模板:
c#// 万能统计公式
var stats = collection.CountBy(item => item.CategoryProperty);
高性能聚合模板:
c#// 通用聚合公式
var aggregated = collection.AggregateBy(
keySelector: item => item.GroupKey,
seed: initialValue,
func: (accumulator, current) => /* 你的聚合逻辑 */
);
索引遍历模板:
c#// 带索引处理公式
foreach (var (index, item) in collection.Index())
{
// 同时需要索引和值的处理逻辑
}
⚡ 性能优化金句
- "CountBy一行代码,性能提升30%" - 替代GroupBy+Count的首选方案
- "AggregateBy内存友好,大数据处理必备" - 减少中间对象分配
- "Index优雅简洁,告别Select装箱" - 现代化的索引访问方式
🚀 结尾呼应
.NET 9的这三个LINQ新方法真正体现了微软对开发者体验的重视。它们不仅让我们的代码更加简洁优雅,更重要的是显著提升了性能表现。
🎯 核心要点回顾:
- CountBy:一行代码搞定分组计数,性能提升20-30%
- AggregateBy:内存高效的自定义聚合操作,大数据处理首选
- Index:优雅的索引访问方式,告别传统Select装箱操作
现在就升级到.NET 9,让这些强大的新特性为你的项目加速吧!你最期待在哪个场景中使用这些新方法?在实际使用中遇到了什么有趣的应用场景?
觉得这些新特性实用的话,请转发给更多C#同行,让大家一起享受.NET** 9带来的开发效率提升!** 🎉
关注我,获取更多C#开发实战技巧和最新技术解读!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!