目录
你是否遇到过这样的问题:窗体刚显示就闪退?数据还没加载完用户就能操作界面?窗体关闭时数据丢失?这些都与窗体生命周期的理解不当有关。
作为C#开发者,深入理解Winform窗体生命周期不仅能避免90%的界面bug,还能让你的应用更加流畅稳定。本文将通过实战代码,带你彻底掌握Load、Shown、Closing等关键事件的正确使用方式。
🔍 窗体生命周期全景图
📊 生命周期事件执行顺序
c#using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AppWinformLifecycle
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 1. 构造函数 - 最先执行
Debug.WriteLine("1. Constructor");
}
protected override void OnHandleCreated(EventArgs e)
{
// 2. 句柄创建 - 窗体句柄被创建
Debug.WriteLine("2. HandleCreated");
base.OnHandleCreated(e);
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 3. Load事件 - 窗体首次加载
Debug.WriteLine("3. Load Event");
}
protected override void OnShown(EventArgs e)
{
// 5. Shown事件 - 窗体首次显示给用户
Debug.WriteLine("4. Shown Event");
base.OnShown(e);
}
private void Form1_Activated(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 4. Activated事件 - 窗体获得焦点
Debug.WriteLine("5. Activated Event");
}
}
}
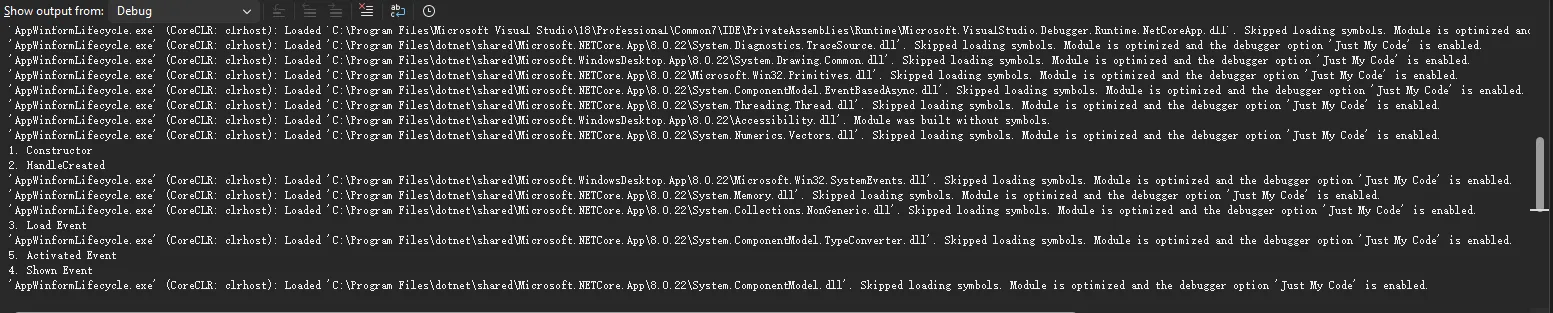
注意:4,5这两个顺序有点意思
💡 核心事件深度解析
🎯 Load事件:数据初始化的黄金时机
最佳实践:在Load事件中进行数据加载、控件初始化等操作。
c#private async void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
// 正确做法:显示加载状态
ShowLoadingIndicator();
// 异步加载数据,避免界面假死
var userData = await LoadUserDataAsync();
var configData = await LoadConfigAsync();
// 初始化UI控件
InitializeDataGridView(userData);
InitializeSettings(configData);
// 设置默认值和状态
SetDefaultValues();
UpdateUIState();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 重要:异常处理
MessageBox.Show($"数据加载失败: {ex.Message}", "错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
finally
{
HideLoadingIndicator();
}
}
// 性能优化技巧:异步数据加载
private async Task<List<User>> LoadUserDataAsync()
{
// 模拟数据库查询
return await Task.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000); // 模拟耗时操作
return GetUsersFromDatabase();
});
}
🌟 Shown事件:用户体验的关键节点
核心特点:窗体完全显示后才触发,适合需要准确窗体尺寸的操作。
c#private void Form1_Shown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// ✅ 适合在Shown中执行的操作
// 1. 窗体位置调整(需要准确尺寸)
CenterFormOnScreen();
// 2. 启动定时器或后台任务
StartPerformanceMonitor();
// 3. 显示欢迎消息或教程
ShowWelcomeMessage();
// 4. 自动聚焦到特定控件
txtUserName.Focus();
}
// 💡 实用技巧:智能窗体居中
private void CenterFormOnScreen()
{
// 获取当前显示器工作区域
Screen currentScreen = Screen.FromControl(this);
Rectangle workingArea = currentScreen.WorkingArea;
// 计算居中位置
int x = (workingArea.Width - this.Width) / 2 + workingArea.X;
int y = (workingArea.Height - this.Height) / 2 + workingArea.Y;
this.Location = new Point(x, y);
}
🛡️ FormClosing事件:数据保护的最后防线
关键作用:可以取消关闭操作,是数据保存的最佳时机。
c#private void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// ✅ 检查是否有未保存的数据
if (HasUnsavedChanges())
{
var result = MessageBox.Show(
"检测到未保存的更改,是否保存后退出?",
"确认退出",
MessageBoxButtons.YesNoCancel,
MessageBoxIcon.Question);
switch (result)
{
case DialogResult.Yes:
if (!SaveData())
{
e.Cancel = true; // 保存失败,取消关闭
return;
}
break;
case DialogResult.Cancel:
e.Cancel = true; // 用户取消,阻止关闭
return;
}
}
// ✅ 清理资源
CleanupResources();
}
// 🔥 最佳实践:优雅的资源清理
private void CleanupResources()
{
try
{
// 停止定时器
performanceTimer?.Stop();
// 释放数据库连接
databaseConnection?.Close();
// 保存用户偏好设置
SaveUserPreferences();
// 写入日志
Logger.Info("应用程序正常退出");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 记录但不阻止关闭
Logger.Error($"资源清理失败: {ex.Message}");
}
}
🎨 Activated/Deactivated事件:焦点管理专家
c#private void Form1_Activated(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// ✅ 窗体获得焦点时的操作
// 1. 恢复实时数据刷新
StartDataRefresh();
// 2. 检查外部文件更改
CheckForFileChanges();
// 3. 更新状态栏
UpdateStatusBar("窗体已激活");
}
private void Form1_Deactivated(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// ✅ 窗体失去焦点时的操作
// 1. 暂停不必要的刷新(节省性能)
StopDataRefresh();
// 2. 自动保存草稿
AutoSaveData();
// 3. 更新状态
UpdateStatusBar("窗体已失活");
}
这两个事件在实际应用中我没有用过
🛠️ 实战应用场景
📱 场景一:带进度条的数据加载窗体
c#using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing;
namespace AppWinformLifecycle
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private ProgressBar progressBar;
private Label statusLabel;
private Button startButton;
private ListBox dataListBox;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeCustomComponents();
}
private void InitializeCustomComponents()
{
// 设置窗体
this.Size = new Size(500, 350);
this.Text = "数据加载进度示例";
this.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
// 状态标签
statusLabel = new Label
{
Text = "准备加载数据...",
Location = new Point(20, 20),
Size = new Size(450, 25),
Font = new Font("Microsoft YaHei", 10)
};
// 进度条
progressBar = new ProgressBar
{
Location = new Point(20, 55),
Size = new Size(450, 25),
Minimum = 0,
Maximum = 100,
Value = 0
};
// 开始按钮
startButton = new Button
{
Text = "开始加载",
Location = new Point(20, 95),
Size = new Size(100, 30),
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
startButton.Click += StartButton_Click;
// 数据显示列表
dataListBox = new ListBox
{
Location = new Point(20, 140),
Size = new Size(450, 150),
Font = new Font("Microsoft YaHei", 9)
};
// 添加控件到窗体
this.Controls.AddRange(new Control[]
{
statusLabel,
progressBar,
startButton,
dataListBox
});
}
private async void StartButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
await DataLoadForm_Load(sender, e);
}
private async Task DataLoadForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 禁用开始按钮,防止重复点击
startButton.Enabled = false;
// 清空之前的数据
dataListBox.Items.Clear();
// 初始化进度显示
progressBar.Value = 0;
statusLabel.Text = "开始加载数据...";
statusLabel.ForeColor = Color.Blue;
try
{
// 分步骤加载数据
await LoadDataWithProgress();
// 完成状态
statusLabel.Text = "数据加载完成!";
statusLabel.ForeColor = Color.Green;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
HandleLoadError(ex);
}
finally
{
// 重新启用按钮
startButton.Enabled = true;
}
}
private async Task LoadDataWithProgress()
{
var steps = new[]
{
("加载用户数据...", (Func<Task>)LoadUsers),
("加载配置信息...", (Func<Task>)LoadConfig),
("初始化界面...", (Func<Task>)InitializeUI)
};
for (int i = 0; i < steps.Length; i++)
{
// 更新状态文本
statusLabel.Text = steps[i].Item1;
// 执行加载步骤
await steps[i].Item2();
// 更新进度条
progressBar.Value = (i + 1) * 100 / steps.Length;
// 刷新UI(虽然使用async/await通常不需要,但为了确保UI响应)
Application.DoEvents();
// 添加小延迟以便观察进度
await Task.Delay(200);
}
}
private async Task LoadUsers()
{
// 模拟加载用户数据
await Task.Delay(1000); // 模拟网络请求或数据库操作
// 添加模拟用户数据到列表
var users = new[] { "张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "钱七" };
foreach (var user in users)
{
dataListBox.Items.Add($"用户: {user}");
await Task.Delay(100); // 模拟逐个加载
Application.DoEvents();
}
}
private async Task LoadConfig()
{
// 模拟加载配置信息
await Task.Delay(800);
var configs = new[]
{
"数据库连接: 已建立",
"缓存设置: 已配置",
"日志级别: INFO",
"主题设置: 默认"
};
foreach (var config in configs)
{
dataListBox.Items.Add($"配置: {config}");
await Task.Delay(80);
Application.DoEvents();
}
}
private async Task InitializeUI()
{
// 模拟初始化UI组件
await Task.Delay(600);
var uiComponents = new[]
{
"主菜单: 已加载",
"工具栏: 已初始化",
"状态栏: 已配置"
};
foreach (var component in uiComponents)
{
dataListBox.Items.Add($"界面: {component}");
await Task.Delay(150);
Application.DoEvents();
}
}
private void HandleLoadError(Exception ex)
{
statusLabel.Text = $"加载失败: {ex.Message}";
statusLabel.ForeColor = Color.Red;
// 重置进度条
progressBar.Value = 0;
// 显示错误对话框
MessageBox.Show(
$"数据加载过程中发生错误:\n\n{ex.Message}",
"加载错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error
);
}
}
}
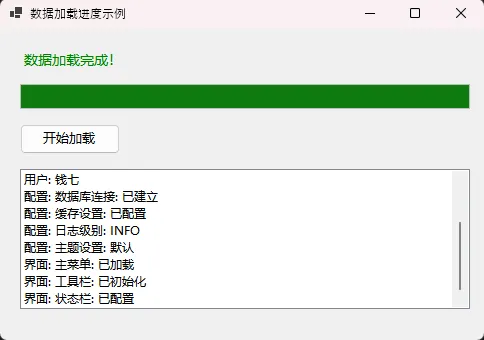
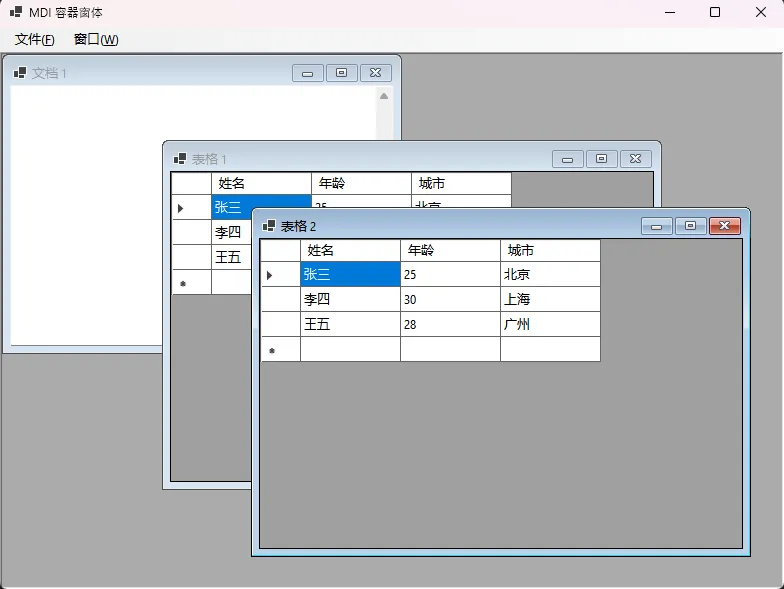
🔒 场景二:MDI容器窗体管理
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AppWinformLifecycle
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private List<Form> childForms = new List<Form>();
private MenuStrip mainMenu;
private ToolStripMenuItem windowMenu;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.Load += Form1_Load;
}
private void Form1_Load(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.IsMdiContainer = true;
InitializeMDI();
}
private void InitializeMDI()
{
// 设置MDI容器窗体
this.Text = "MDI 容器窗体";
this.Size = new Size(800, 600);
this.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
this.WindowState = FormWindowState.Maximized;
// 创建主菜单
CreateMainMenu();
}
private void CreateMainMenu()
{
mainMenu = new MenuStrip();
// 文件菜单
var fileMenu = new ToolStripMenuItem("文件(&F)");
fileMenu.DropDownItems.Add("新建文档", null, (s, e) => CreateChildForm("文档"));
fileMenu.DropDownItems.Add("新建表格", null, (s, e) => CreateChildForm("表格"));
fileMenu.DropDownItems.Add(new ToolStripSeparator());
fileMenu.DropDownItems.Add("退出", null, (s, e) => this.Close());
// 窗口菜单
windowMenu = new ToolStripMenuItem("窗口(&W)");
windowMenu.DropDownItems.Add("层叠", null, (s, e) => this.LayoutMdi(MdiLayout.Cascade));
windowMenu.DropDownItems.Add("水平平铺", null, (s, e) => this.LayoutMdi(MdiLayout.TileHorizontal));
windowMenu.DropDownItems.Add("垂直平铺", null, (s, e) => this.LayoutMdi(MdiLayout.TileVertical));
windowMenu.DropDownItems.Add(new ToolStripSeparator());
windowMenu.DropDownItems.Add("关闭所有窗口", null, CloseAllChildren);
// 添加菜单项
mainMenu.Items.AddRange(new ToolStripMenuItem[] { fileMenu, windowMenu });
// 设置MDI窗口列表(自动在窗口菜单中显示子窗体列表)
this.MainMenuStrip = mainMenu;
this.Controls.Add(mainMenu);
}
private void CreateChildForm(string formType)
{
Form childForm;
switch (formType)
{
case "文档":
childForm = new DocumentForm();
break;
case "表格":
childForm = new DataGridForm();
break;
default:
childForm = new DocumentForm();
break;
}
// 设置为MDI子窗体
childForm.MdiParent = this;
// 添加到子窗体列表
childForms.Add(childForm);
// 订阅子窗体的FormClosed事件
childForm.FormClosed += ChildForm_FormClosed;
// 显示子窗体
childForm.Show();
}
private void ChildForm_FormClosed(object sender, FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
// 从列表中移除已关闭的子窗体
if (sender is Form closedForm)
{
childForms.Remove(closedForm);
}
}
private void CloseAllChildren(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 关闭所有子窗体
var childrenToClose = this.MdiChildren.ToArray();
foreach (Form child in childrenToClose)
{
child.Close();
}
}
private void MDIContainer_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// ✅ 逐个检查子窗体是否可以关闭
foreach (Form childForm in this.MdiChildren)
{
childForm.Close();
if (!childForm.IsDisposed)
{
e.Cancel = true; // 有子窗体无法关闭
MessageBox.Show("无法关闭应用程序,因为有子窗体拒绝关闭。",
"关闭确认", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
}
}
}
// 简单的文档子窗体
public class DocumentForm : Form
{
private static int documentCounter = 1;
private TextBox textBox;
private bool hasUnsavedChanges = false;
public DocumentForm()
{
InitializeComponents();
}
private void InitializeComponents()
{
this.Text = $"文档 {documentCounter++}";
this.Size = new Size(400, 300);
textBox = new TextBox
{
Multiline = true,
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
ScrollBars = ScrollBars.Both
};
textBox.TextChanged += (s, e) =>
{
hasUnsavedChanges = true;
if (!this.Text.EndsWith(" *"))
this.Text += " *";
};
this.Controls.Add(textBox);
}
protected override void OnFormClosing(FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
if (hasUnsavedChanges)
{
var result = MessageBox.Show(
$"文档 '{this.Text}' 已被修改,是否保存?",
"保存确认",
MessageBoxButtons.YesNoCancel,
MessageBoxIcon.Question);
switch (result)
{
case DialogResult.Yes:
// 模拟保存操作
MessageBox.Show("文档已保存!", "保存", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
hasUnsavedChanges = false;
break;
case DialogResult.Cancel:
e.Cancel = true; // 取消关闭
return;
case DialogResult.No:
// 不保存,直接关闭
break;
}
}
base.OnFormClosing(e);
}
}
// 简单的数据表格子窗体
public class DataGridForm : Form
{
private static int gridCounter = 1;
private DataGridView dataGridView;
public DataGridForm()
{
InitializeComponents();
}
private void InitializeComponents()
{
this.Text = $"表格 {gridCounter++}";
this.Size = new Size(500, 350);
dataGridView = new DataGridView
{
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
AutoGenerateColumns = true
};
// 添加示例数据
dataGridView.Columns.Add("Name", "姓名");
dataGridView.Columns.Add("Age", "年龄");
dataGridView.Columns.Add("City", "城市");
dataGridView.Rows.Add("张三", "25", "北京");
dataGridView.Rows.Add("李四", "30", "上海");
dataGridView.Rows.Add("王五", "28", "广州");
this.Controls.Add(dataGridView);
}
}
}
⚠️ 常见坑点与解决方案
🕳️ 坑点一:在Load事件中直接操作控件尺寸
c#// ❌ 错误做法:Load时控件可能还未完全显示
private void Form_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 此时获取到的尺寸可能不准确
int width = this.Width;
ResizeControls(width); // 可能出现布局问题
}
// ✅ 正确做法:在Shown事件中操作
private void Form_Shown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 此时窗体已完全显示,尺寸准确
int width = this.Width;
ResizeControls(width);
}
🕳️ 坑点二:忘记处理异步操作的异常
c#// ❌ 危险做法:异步操作缺少异常处理
private async void Form_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var data = await LoadDataAsync(); // 可能抛出异常
DisplayData(data);
}
// ✅ 安全做法:完善的异常处理
private async void Form_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
var data = await LoadDataAsync();
DisplayData(data);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// 操作被取消
this.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.Error(ex);
ShowErrorMessage(ex.Message);
}
}
🎯 总结与最佳实践
掌握Winform窗体生命周期的三个关键要点:
- 🎪 分工明确:Load负责数据加载,Shown负责UI最终调整,Closing负责资源清理
- ⚡ 性能至上:使用异步操作避免界面假死,合理利用Activated/Deactivated节省资源
- 🛡️ 稳定可靠:完善的异常处理机制,确保用户数据安全和应用稳定性
记住这句话:"好的窗体生命周期管理,是用户体验和应用稳定性的基石"。
💬 互动话题:
- 你在项目中遇到过哪些与窗体生命周期相关的问题?
- 有没有其他实用的窗体事件处理技巧想要分享?
🔗 觉得内容有用请转发给更多C#开发同行,一起提升开发技能!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录