目录
你是否在WPF开发中遇到过这样的困惑:为什么有些属性可以实现数据绑定,有些却不行?为什么自定义控件的属性无法触发界面更新?如果你正在为这些问题感到困扰,那么今天我们就来彻底搞懂WPF中最核心的概念之一——依赖属性。
依赖属性(Dependency Property)是WPF架构的基石,它不仅支持数据绑定、样式、动画等高级功能,更是构建现代化WPF应用不可或缺的技术。掌握了依赖属性,你就掌握了WPF开发的精髓。
🤔 为什么需要依赖属性?
在传统的.NET属性系统中,普通的CLR属性无法满足WPF的高级需求。让我们通过一个实际案例来理解这个问题:
C#// 传统CLR属性的局限性
public class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
这样的普通属性存在以下问题:
- 无法自动通知变更:属性值改变时,UI不会自动更新
- 不支持数据绑定:无法与XAML中的控件建立双向绑定关系
- 缺乏验证机制:无法在属性赋值时进行有效性检查
- 无法参与样式系统:不能通过样式或触发器来改变属性值
💡 依赖属性的核心特性
依赖属性通过以下机制解决了传统属性的痛点:
🎯 特性一:属性值优先级系统
依赖属性建立了一套完整的值优先级体系:
- 动画值(最高优先级)
- 本地值(通过代码直接设置)
- 触发器值
- 样式值
- 继承值
- 默认值(最低优先级)
🎯 特性二:变更通知机制
自动实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口的功能,无需手动编写通知代码。
🎯 特性三:内存优化
只有在属性被实际使用时才分配内存空间,大大减少了内存占用。
🛠️ 实战案例:创建自定义依赖属性
让我们通过一个实际的用户控件来演示如何创建和使用依赖属性:
📋 案例场景:温度显示控件
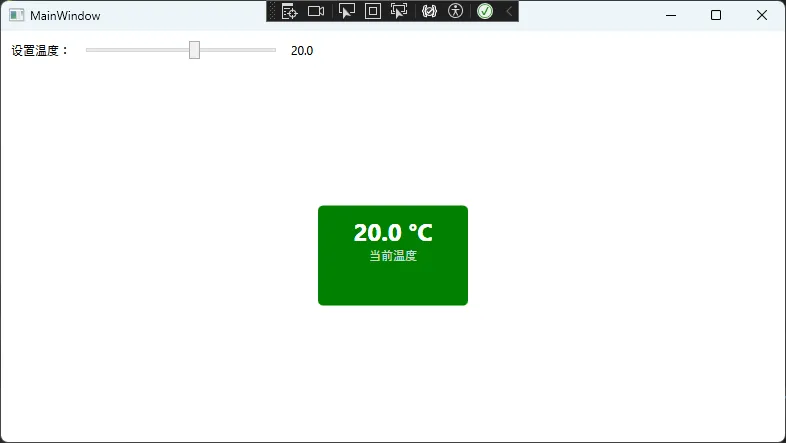
假设我们要创建一个温度显示控件,能够根据温度值自动改变颜色,并支持数据绑定。
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows;
namespace AppDependentProperties
{
public class TemperatureControl : Control
{
static TemperatureControl()
{
// 重写默认样式
DefaultStyleKeyProperty.OverrideMetadata(typeof(TemperatureControl),
new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(typeof(TemperatureControl)));
}
// 定义温度依赖属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty TemperatureProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Temperature",
typeof(double),
typeof(TemperatureControl),
new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(0.0,
FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.AffectsRender |
FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.BindsTwoWayByDefault,
OnTemperatureChanged));
// CLR属性包装器
public double Temperature
{
get { return (double)GetValue(TemperatureProperty); }
set { SetValue(TemperatureProperty, value); }
}
// 属性变更回调方法
private static void OnTemperatureChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (d is TemperatureControl control)
{
control.UpdateTemperatureColor((double)e.NewValue);
}
}
// 根据温度更新颜色
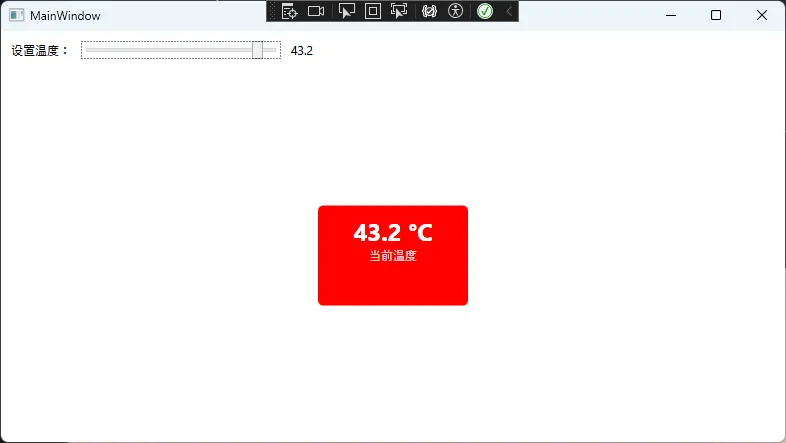
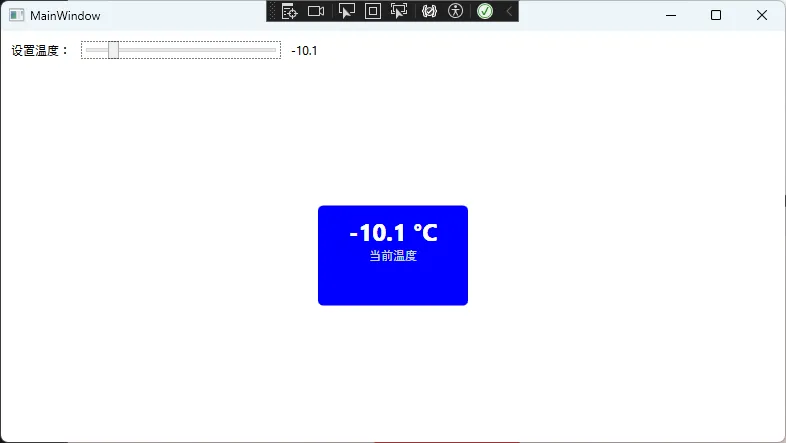
private void UpdateTemperatureColor(double temperature)
{
if (temperature < 0)
Background = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Blue); // 冰点以下
else if (temperature < 25)
Background = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Green); // 舒适温度
else if (temperature < 35)
Background = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Orange); // 温暖
else
Background = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Red); // 高温
}
// 单位依赖属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty UnitProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Unit",
typeof(string),
typeof(TemperatureControl),
new FrameworkPropertyMetadata("°C"));
public string Unit
{
get { return (string)GetValue(UnitProperty); }
set { SetValue(UnitProperty, value); }
}
}
}
🎨 控件模板定义
在Generic.xaml中定义控件的默认样式:
XML<ResourceDictionary
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDependentProperties">
<Style TargetType="{x:Type local:TemperatureControl}">
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type local:TemperatureControl}">
<Border Background="{TemplateBinding Background}"
BorderBrush="{TemplateBinding BorderBrush}"
BorderThickness="{TemplateBinding BorderThickness}"
CornerRadius="5"
Padding="10">
<StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock FontSize="24"
FontWeight="Bold"
Foreground="White"
HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<Run Text="{Binding Temperature,
RelativeSource={RelativeSource TemplatedParent},
StringFormat=F1}"/>
<Run Text="{Binding Unit,
RelativeSource={RelativeSource TemplatedParent}}"/>
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Text="当前温度"
FontSize="12"
Foreground="LightGray"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
</ResourceDictionary>
📱 使用示例
XML<Window x:Class="AppDependentProperties.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDependentProperties"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:WeatherViewModel/>
</Window.DataContext>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<!-- 温度控制面板 -->
<StackPanel Grid.Row="0" Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="10">
<TextBlock Text="设置温度:" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<Slider x:Name="TempSlider"
Minimum="-20" Maximum="50"
Value="{Binding CurrentTemperature}"
Width="200" Margin="10,0"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Value, ElementName=TempSlider, StringFormat=F1}"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
<!-- 温度显示控件 -->
<local:TemperatureControl Grid.Row="1"
Temperature="{Binding CurrentTemperature}"
Unit="°C"
Width="150" Height="100"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</Grid>
</Window>
🔧 ViewModel实现
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppDependentProperties
{
public class WeatherViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private double _currentTemperature = 20.0;
public double CurrentTemperature
{
get => _currentTemperature;
set
{
if (_currentTemperature != value)
{
_currentTemperature = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected virtual void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
}
🚀 高级应用:附加属性实战
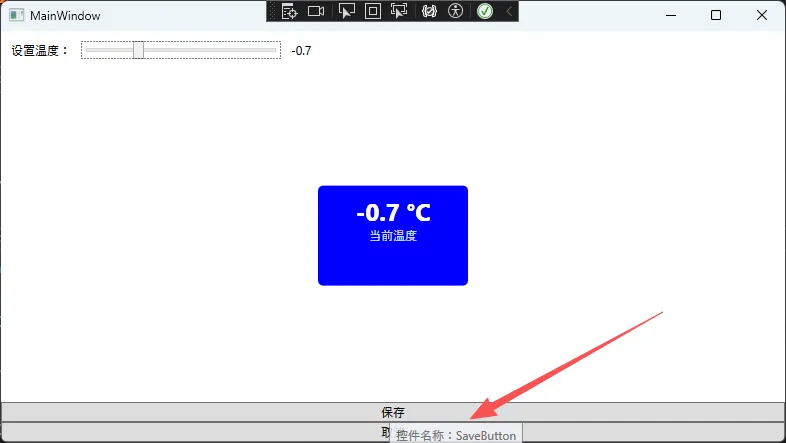
附加属性是依赖属性的一种特殊形式,允许任何对象拥有它们原本没有的属性。最经典的例子是布局面板的附加属性。
💎 案例:自定义提示附加属性
C#public static class ToolTipHelper
{
// 自动提示附加属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty AutoToolTipProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("AutoToolTip",
typeof(bool),
typeof(ToolTipHelper),
new PropertyMetadata(false, OnAutoToolTipChanged));
public static bool GetAutoToolTip(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (bool)obj.GetValue(AutoToolTipProperty);
}
public static void SetAutoToolTip(DependencyObject obj, bool value)
{
obj.SetValue(AutoToolTipProperty, value);
}
private static void OnAutoToolTipChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (d is FrameworkElement element && (bool)e.NewValue)
{
element.Loaded += (sender, args) =>
{
if (element.ToolTip == null && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(element.Name))
{
element.ToolTip = $"控件名称:{element.Name}";
}
};
}
}
}
📄 使用附加属性
XML<StackPanel>
<Button Name="SaveButton"
Content="保存"
local:ToolTipHelper.AutoToolTip="True"/>
<Button Name="CancelButton"
Content="取消"
local:ToolTipHelper.AutoToolTip="True"/>
</StackPanel>
⚠️ 常见陷阱与最佳实践
🔴 陷阱1:忘记CLR属性包装器的限制
C#// ❌ 错误做法:在CLR属性中添加逻辑
public string MyProperty
{
get { return (string)GetValue(MyPropertyProperty); }
set
{
// 不要在这里添加逻辑!XAML可能绕过这个setter
DoSomeValidation(value);
SetValue(MyPropertyProperty, value);
}
}
// ✅ 正确做法:在PropertyChangedCallback中处理
private static void OnMyPropertyChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
// 在这里处理属性变更逻辑
((MyControl)d).DoSomeValidation((string)e.NewValue);
}
🔴 陷阱2:性能优化误区
C#// ❌ 错误:频繁的GetValue调用
private void UpdateUI()
{
if (GetValue(IsActiveProperty) as bool? == true)
{
var text = GetValue(TextProperty) as string;
// ... 更多GetValue调用
}
}
// ✅ 正确:缓存属性值
private void UpdateUI()
{
bool isActive = IsActive; // 使用CLR包装器
if (isActive)
{
string text = Text;
// 使用缓存的值
}
}
🔴 陷阱3:元数据选项的误用
C#// 正确选择元数据选项
public static readonly DependencyProperty MyProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("MyProperty",
typeof(string),
typeof(MyControl),
new FrameworkPropertyMetadata("默认值",
FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.AffectsRender | // 影响渲染
FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.BindsTwoWayByDefault // 默认双向绑定
));
🎯 性能优化秘籍
⚡ 优化1:合理使用CoerceValue
C#// 值约束回调
private static object CoerceTemperature(DependencyObject d, object value)
{
double temp = (double)value;
// 限制温度范围
if (temp < -273.15) return -273.15; // 绝对零度
if (temp > 1000) return 1000; // 合理上限
return temp;
}
public static readonly DependencyProperty TemperatureProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Temperature",
typeof(double),
typeof(TemperatureControl),
new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(0.0, OnTemperatureChanged, CoerceTemperature));
⚡ 优化2:使用ReadOnly依赖属性
C#// 只读依赖属性,提高安全性和性能
private static readonly DependencyPropertyKey IsLoadingPropertyKey =
DependencyProperty.RegisterReadOnly("IsLoading",
typeof(bool),
typeof(MyControl),
new PropertyMetadata(false));
public static readonly DependencyProperty IsLoadingProperty =
IsLoadingPropertyKey.DependencyProperty;
public bool IsLoading
{
get { return (bool)GetValue(IsLoadingProperty); }
protected set { SetValue(IsLoadingPropertyKey, value); }
}
🎉 总结:三个核心要点
通过本文的深入讲解,相信你已经对WPF依赖属性有了全面的理解。让我们总结三个最重要的要点:
🔥 要点一:依赖属性是WPF架构的基础
它不仅解决了传统CLR属性的局限性,更是数据绑定、样式、动画等高级功能的技术基石。掌握依赖属性,就掌握了WPF开发的核心竞争力。
💡 要点二:正确的创建模式至关重要
记住"注册-包装-回调"的三步模式,合理使用元数据选项,避免在CLR包装器中添加业务逻辑,这些最佳实践将让你的代码更加健壮和高效。
⚡ 要点三:性能优化需要深入理解原理
通过合理使用CoerceValue、ReadOnly属性、元数据选项等高级特性,可以显著提升应用程序的性能和用户体验。
💬 互动时间
你在实际项目中是如何使用依赖属性的?遇到过哪些有趣的应用场景或者踩过什么坑?欢迎在评论区分享你的经验,让我们一起讨论更多WPF开发的实战技巧!
🚀 如果这篇文章对你有帮助,请转发给更多需要的同行开发者!
关注我们,获取更多C#开发实战技巧和最新技术资讯!
相关信息
通过网盘分享的文件:AppDependentProperties.zip 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iAOm9hE96AEjMcDZszM_sg?pwd=dw8t 提取码: dw8t --来自百度网盘超级会员v9的分享
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!