最近在Reddit上看到一个引起千万程序员共鸣的帖子:一位仅有2年经验的C#开发者独自维护着一家公司的核心系统,面对百万级数据查询时束手无策。他的困惑让我想起了自己的成长经历——谁没有在LINQ的性能陷阱里跌过跟头呢?
据统计,70%的C#开发者在处理大数据量时都遇到过性能问题,而其中60%的问题源于LINQ使用不当。今天,我将结合实际案例,分享5个立竿见影的LINQ性能优化技巧,让你从此告别查询超时!
🔥 问题分析:为什么你的LINQ查询这么慢?
常见痛点梳理
许多开发者面临的核心问题包括:
- 物化陷阱:不理解
.ToList()的后果 - 过度获取:拉取不需要的数据
- 延迟加载:造成N+1查询问题
- 盲目使用Include:加载无关数据
让我们看看这个真实案例:
C#// ❌ 危险操作 - 会导致内存溢出
var allCustomers = db.Customers.ToList();
var filteredCustomers = allCustomers.Where(c => c.Country == "China");
问题分析:这段代码会将整个Customers表加载到内存中,如果表中有百万条记录,直接导致内存溢出。
💡 解决方案:5个实战优化技巧
🎯 技巧1:善用Select投影,只取所需
核心原则:永远不要获取超过需求的数据
C#namespace AppLinq5
{
// Customer 实体类
public class Customer
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public bool IsActive { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; } // 大文本字段
}
// DTO 类 - 只包含需要的字段
public class CustomerDto
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
}
public class CustomerRepository
{
private readonly List<Customer> _customers;
public CustomerRepository()
{
// 模拟数据
_customers = new List<Customer>
{
new Customer { Id = 1, Name = "张三", Email = "zhang@email.com", Phone = "123456", Address = "北京市", IsActive = true, Description = "很长的描述文本..." },
new Customer { Id = 2, Name = "李四", Email = "li@email.com", Phone = "789012", Address = "上海市", IsActive = true, Description = "另一个很长的描述..." },
new Customer { Id = 3, Name = "王五", Email = "wang@email.com", Phone = "345678", Address = "广州市", IsActive = false, Description = "第三个长描述..." }
};
}
public IQueryable<Customer> GetCustomers()
{
return _customers.AsQueryable();
}
}
public class CustomerService
{
private readonly CustomerRepository _repository;
public CustomerService(CustomerRepository repository)
{
_repository = repository;
}
// ❌ 错误做法 - 查询所有字段
public List<Customer> GetAllCustomersBad()
{
return _repository.GetCustomers()
.Where(c => c.IsActive)
.ToList(); // 返回所有字段,包括不需要的大文本字段
}
// ✅ 正确做法 - 只选择需要的字段
public List<CustomerDto> GetCustomerSummary()
{
return _repository.GetCustomers()
.Where(c => c.IsActive)
.Select(c => new CustomerDto
{
Id = c.Id,
Name = c.Name,
Email = c.Email // 只选择需要的字段
})
.ToList();
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var repository = new CustomerRepository();
var customerService = new CustomerService(repository);
// ✅ 获取客户摘要信息 - 只包含需要的字段
var customerSummaries = customerService.GetCustomerSummary();
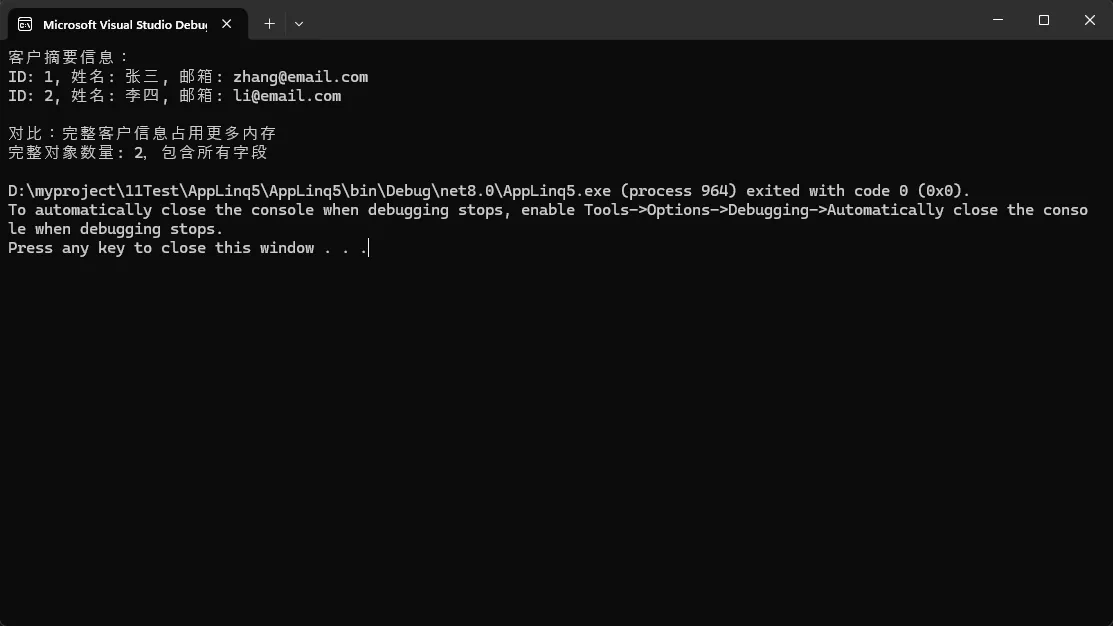
Console.WriteLine("客户摘要信息:");
foreach (var customer in customerSummaries)
{
Console.WriteLine($"ID: {customer.Id}, 姓名: {customer.Name}, 邮箱: {customer.Email}");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n对比:完整客户信息占用更多内存");
var fullCustomers = customerService.GetAllCustomersBad();
Console.WriteLine($"完整对象数量: {fullCustomers.Count},包含所有字段");
}
}
}
你是否遇到过这样的场景:需要定时更新界面数据、实现倒计时功能,或者创建自动保存机制?作为C#开发者,这些需求在WinForms开发中几乎每天都会碰到。今天我们就来深入探讨System.Windows.Forms.Timer这个"小而美"的控件,让你彻底掌握定时任务的开发技巧。
本文将通过实战案例,教你如何用Timer控件解决常见的定时任务问题,避开开发中的常见陷阱,让你的应用更加专业和稳定。
🎯 Timer控件核心原理解析
在深入实战之前,我们先理解Timer的核心机制。WinForms中的Timer并不是"真正"的多线程定时器,而是基于Windows消息循环的组件。
🔧 三大核心属性
- Enabled:控制定时器启停状态(true/false)
- Interval:时间间隔,单位毫秒,最小值通常为15-55ms
- Tag:存储自定义数据的万能属性
⚡ 核心事件与方法
- Tick事件:定时触发的核心事件处理器
- Start()/Stop():编程式启停控制
💡 实战应用1:打造专业数字时钟
这是Timer最经典的应用场景。让我们创建一个高颜值的实时时钟:
C#using Timer = System.Windows.Forms.Timer;
namespace AppWinformTimer
{
public partial class FrmClock : Form
{
private Label timeLabel;
private Timer clockTimer;
public FrmClock()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeUI();
SetupTimer();
}
private void InitializeUI()
{
this.Text = "专业数字时钟";
this.Size = new Size(400, 200);
this.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
timeLabel = new Label
{
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter,
Font = new Font("Microsoft YaHei", 28F, FontStyle.Bold),
ForeColor = Color.DodgerBlue,
BackColor = Color.Black
};
this.Controls.Add(timeLabel);
}
private void SetupTimer()
{
clockTimer = new Timer
{
Interval = 1000 // 1秒更新一次
};
clockTimer.Tick += ClockTimer_Tick;
clockTimer.Start();
// 立即显示当前时间
UpdateTimeDisplay();
}
private void ClockTimer_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UpdateTimeDisplay();
}
private void UpdateTimeDisplay()
{
timeLabel.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
protected override void OnFormClosed(FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
// 🚨 重要:记得释放资源
clockTimer?.Dispose();
base.OnFormClosed(e);
}
}
}

你是否在WPF开发中遇到过这样的困惑:为什么有些属性支持数据绑定,而有些却不行?为什么WPF控件的属性看起来如此"神奇",能够自动响应变化?这背后的秘密就在于WPF的依赖属性系统。
作为WPF的核心特性之一,依赖属性(Dependency Property)与传统的CLR属性有着本质的不同。理解这两者的区别,不仅能帮你解决数据绑定、样式设置等常见问题,更能让你的WPF应用程序性能更优、功能更强大。
本文将通过实战代码和深度分析,带你彻底搞懂依赖属性系统的工作原理与应用场景。
🔍 问题分析:为什么需要依赖属性?
传统CLR属性的局限性
传统的C#属性本质上是对字段的封装,存在以下限制:
- 无法支持数据绑定:WPF的双向绑定机制需要属性具备变化通知能力
- 缺乏值优先级:无法处理样式、模板、继承等多种值来源的优先级
- 内存占用大:每个对象都需要存储所有属性的值
- 缺乏元数据支持:无法提供验证、强制转换等扩展功能
WPF的解决方案:依赖属性系统
依赖属性通过以下机制解决了这些问题:
- 属性系统:统一管理属性值的存储和获取
- 值优先级:支持本地值、样式、模板等多层级值源
- 变化通知:内置PropertyChanged机制
- 内存优化:稀疏存储,只存储被设置的属性值
💡 核心区别深度解析
🔥 1. 定义方式的根本不同
传统CLR属性定义:
C#public class TraditionalControl : Control
{
private string _title;
public string Title
{
get { return _title; }
set
{
_title = value;
// 需要手动触发PropertyChanged
}
}
}
依赖属性定义:
C#public class ModernControl : Control
{
// 1. 注册依赖属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty TitleProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
nameof(Title), // 属性名
typeof(string), // 属性类型
typeof(ModernControl), // 所有者类型
new PropertyMetadata( // 元数据
string.Empty, // 默认值
OnTitleChanged, // 变化回调
CoerceTitle // 值强制转换
));
// 2. 提供CLR包装器
public string Title
{
get { return (string)GetValue(TitleProperty); }
set { SetValue(TitleProperty, value); }
}
// 3. 属性变化回调
private static void OnTitleChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var control = (ModernControl)d;
// 处理属性变化逻辑
control.OnTitleChanged((string)e.OldValue, (string)e.NewValue);
}
// 4. 值强制转换
private static object CoerceTitle(DependencyObject d, object value)
{
// 确保Title不为null
return value ?? string.Empty;
}
protected virtual void OnTitleChanged(string oldValue, string newValue)
{
// 子类可重写此方法
}
}
🚀 2. 数据绑定支持
传统属性的绑定问题:
C#public class StudentViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string _name;
public string Name
{
get { return _name; }
set
{
if (_name != value)
{
_name = value;
// 必须手动实现PropertyChanged
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this,
new PropertyChangedEventArgs(nameof(Name)));
}
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
}
依赖属性的自动绑定:
XML<Window x:Class="AppDependentPropertiesThan.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDependentPropertiesThan"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.Resources>
<Style TargetType="{x:Type local:ModernControl}">
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type local:ModernControl}">
<Border Background="LightBlue"
BorderBrush="DarkBlue"
BorderThickness="2"
CornerRadius="5"
Padding="10">
<TextBlock Text="{TemplateBinding Title}"
FontSize="16"
FontWeight="Bold"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</Border>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
</Window.Resources>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<local:ModernControl Title="{Binding Name}" Grid.Row="0" />
</Grid>
</Window>
在工业4.0浪潮下,设备数字化转型已成为制造业的核心竞争力。想象一下,如果你的工厂设备能像"钢铁侠"的贾维斯一样智能,24小时监控每一个传感器,预测故障,优化维护时间,这将为企业节省多少成本?
今天,我们将用C#从零构建一套完整的工业传感器智能分析系统,涵盖实时数据采集、智能异常检测、预测性维护和AI对话分析。
🎯 为什么选择C#构建工业物联网系统?
💪 C#在工业场景的天然优势
强类型安全:工业数据不容错误,C#的编译时类型检查为数据安全提供了第一道防线。
丰富生态:从底层硬件通信到上层AI分析,.NET生态提供了完整的解决方案。
跨平台部署:支持Windows、Linux部署,适应不同工业环境需求。
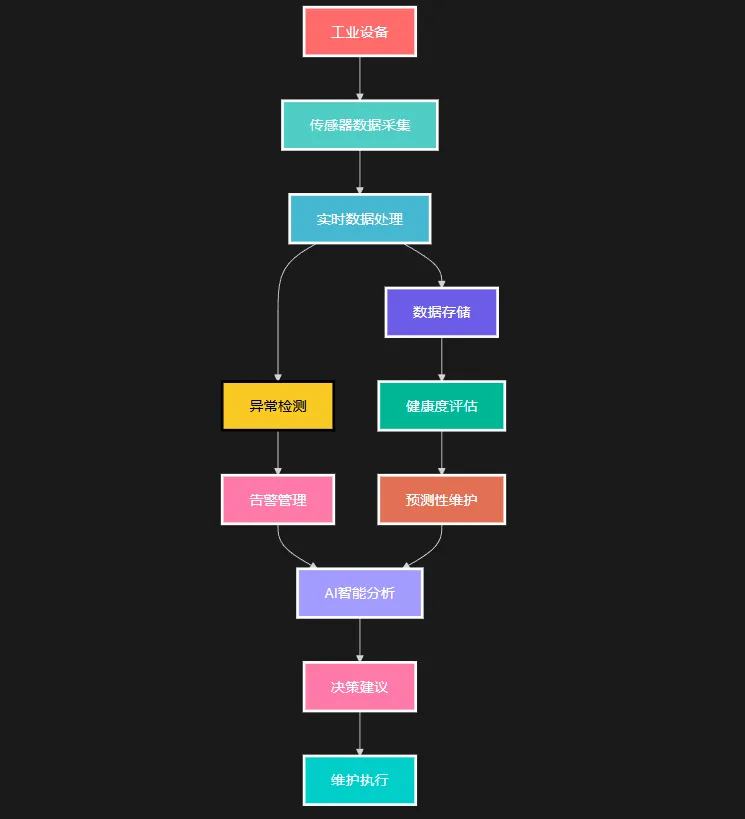
🏗️ 系统架构设计:五层架构保证可扩展性
我们的系统采用经典的分层架构:
Markdown┌─────────────────────────────────────┐ │ AI智能分析层 │ ← Semantic Kernel + OpenAI ├─────────────────────────────────────┤ │ 业务逻辑层 │ ← 告警管理、预测性维护 ├─────────────────────────────────────┤ │ 数据处理层 │ ← 实时分析、异常检测 ├─────────────────────────────────────┤ │ 数据模型层 │ ← 设备、传感器抽象 ├─────────────────────────────────────┤ │ 数据采集层 │ ← 模拟真实传感器数据 └─────────────────────────────────────┘
在工业控制、物联网设备通信中,你是否遇到过这样的场景:向设备发送一个简单的查询指令,却发现返回的数据总是"分批到达"?明明应该收到完整的20字节响应,却只能收到几个零散的数据包?
别急,这不是你的代码有问题!
这是串口通信中最常见的"分包接收"现象。设备可能一次发送10字节,下一次发送剩余的10字节,而我们的程序却不知道什么时候才算接收完成。
今天我们就来彻底解决这个让无数C#开发者头疼的问题!
🤔 问题分析:为什么会分包接收?
根本原因
串口通信是异步的,数据传输会受到以下因素影响:
- 硬件缓冲区大小限制
- 设备处理速度差异
- 网络延迟(对于串口转以太网设备)
- 系统调度
传统方案的痛点
C#// ❌ 错误示例:只能收到第一包数据
serialPort.Write(command, 0, command.Length);
Thread.Sleep(100); // 固定等待时间
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int count = serialPort.Read(buffer, 0, 1024); // 可能只读到部分数据
这种写法的问题:
- 固定等待时间不可靠
- 无法判断数据是否接收完整
- 容易丢失后续数据包
💡 解决方案:四种策略任你选择
基于不同应用场景,我设计了四种接收策略:
🚀 方案一:数据间隔超时判断(⭐推荐)
适用场景:不知道数据长度,但设备发送完毕后会有明显时间间隔
C#public byte[] SendQueryWithGapTimeout(byte[] command, int gapTimeoutMs = 100, int maxWaitMs = 3000)
{
// 清空缓冲区并开始接收
lock (bufferLock)
{
receivedBuffer.Clear();
isWaitingForResponse = true;
lastReceiveTime = DateTime.Now;
}
// 发送指令
serialPort.Write(command, 0, command.Length);
DateTime startTime = DateTime.Now;
while ((DateTime.Now - startTime).TotalMilliseconds < maxWaitMs)
{
Thread.Sleep(10);
lock (bufferLock)
{
// 🔥 关键逻辑:有数据且间隔超时则认为接收完成
if (receivedBuffer.Count > 0 &&
(DateTime.Now - lastReceiveTime).TotalMilliseconds > gapTimeoutMs)
{
isWaitingForResponse = false;
return receivedBuffer.ToArray();
}
}
}
return null;
}