目录
你是否遇到过这样的奇怪现象:0.1 + 0.2 在Python中竟然不等于 0.3?或者在Windows应用开发中,浮点数计算结果总是出现微小的偏差,导致程序逻辑出错?这些看似简单的浮点数问题,实际上涉及到计算机底层的IEEE 754标准和浮点数精度处理机制。
作为Python开发者,特别是在上位机开发和数据处理场景中,深入理解浮点数的工作原理和精度问题至关重要。本文将从IEEE 754标准入手,全面解析Python浮点数的精度问题,并提供实用的解决方案,让你彻底掌握浮点数的正确使用方法。
🔬 问题分析:为什么浮点数计算会出现精度问题?
💻 IEEE 754标准详解
Python中的float类型遵循IEEE 754标准,这是一个国际标准,定义了浮点数在计算机中的存储和运算规则。
Pythonimport sys
import struct
# 查看Python浮点数的基本信息
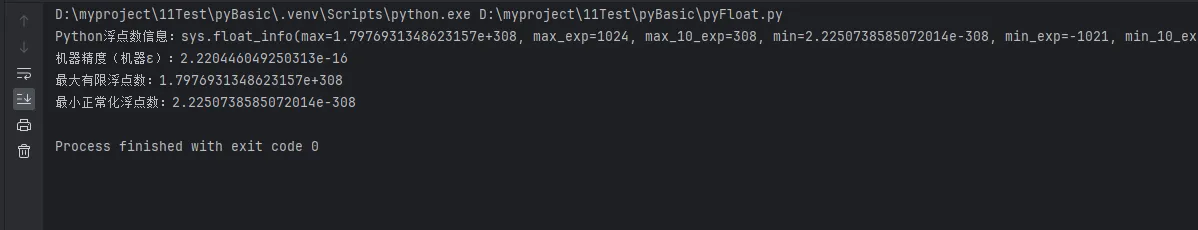
print(f"Python浮点数信息:{sys.float_info}")
print(f"机器精度(机器ε):{sys.float_info.epsilon}")
print(f"最大有限浮点数:{sys.float_info.max}")
print(f"最小正常化浮点数:{sys.float_info.min}")
IEEE 754双精度浮点数(Python默认)采用64位存储:
- 符号位:1位,表示正负
- 指数位:11位,表示数值范围
- 尾数位:52位,决定精度
🎭 精度问题的根本原因
Python# 经典的浮点数精度问题演示
def demonstrate_float_precision():
"""演示浮点数精度问题"""
# 案例1:简单的加法运算
result1 = 0.1 + 0.2
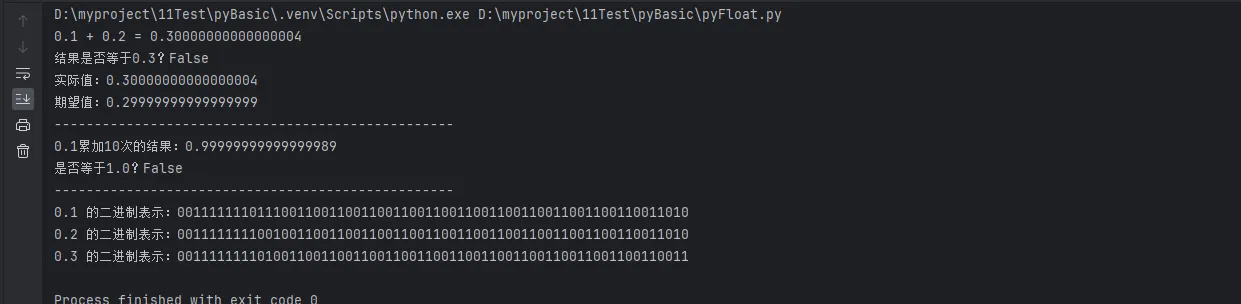
print(f"0.1 + 0.2 = {result1}")
print(f"结果是否等于0.3?{result1 == 0.3}")
print(f"实际值:{result1:.17f}")
print(f"期望值:{0.3:.17f}")
print("-" * 50)
# 案例2:累积误差
total = 0.0
for i in range(10):
total += 0.1
print(f"0.1累加10次的结果:{total:.17f}")
print(f"是否等于1.0?{total == 1.0}")
print("-" * 50)
# 案例3:二进制表示问题
numbers = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3]
for num in numbers:
binary = format(struct.unpack('!Q', struct.pack('!d', num))[0], '064b')
print(f"{num} 的二进制表示:{binary}")
demonstrate_float_precision()
输出结果分析:
🔍 深入理解:十进制与二进制转换
Pythonfrom fractions import Fraction
import decimal
def analyze_decimal_binary_conversion():
"""分析十进制与二进制转换问题"""
# 0.1在计算机中的真实表示
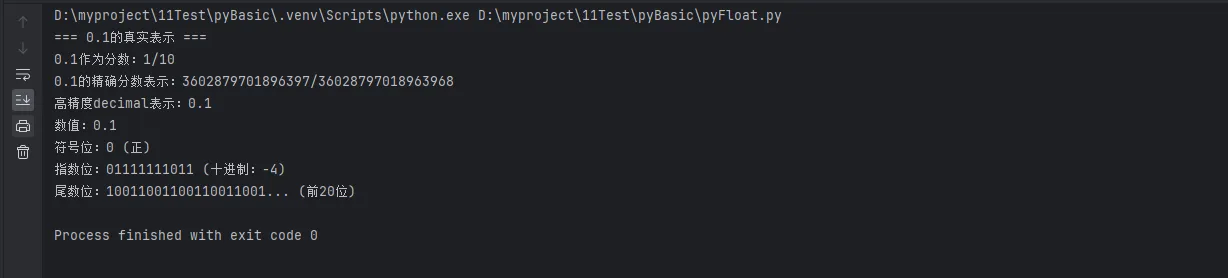
print("=== 0.1的真实表示 ===")
# 使用Fraction显示精确的分数形式
f = Fraction(0.1).limit_denominator()
print(f"0.1作为分数:{f}")
# 显示IEEE 754的实际存储值
exact_fraction = Fraction(0.1)
print(f"0.1的精确分数表示:{exact_fraction}")
# 使用decimal模块获取精确值
decimal.getcontext().prec = 50 # 设置高精度
d = decimal.Decimal('0.1')
print(f"高精度decimal表示:{d}")
# 转换为二进制查看
def float_to_binary_detailed(num):
"""详细显示浮点数的二进制分解"""
packed = struct.pack('!d', num)
bits = ''.join(f'{byte:08b}' for byte in packed)
sign = bits[0]
exponent = bits[1:12]
mantissa = bits[12:]
print(f"数值:{num}")
print(f"符号位:{sign} ({'负' if sign == '1' else '正'})")
print(f"指数位:{exponent} (十进制:{int(exponent, 2) - 1023})")
print(f"尾数位:{mantissa[:20]}... (前20位)")
float_to_binary_detailed(0.1)
analyze_decimal_binary_conversion()
🛠️ 解决方案:正确处理浮点数精度
🎯 方案1:使用math.isclose()进行浮点数比较
Pythonimport sys
import struct
import math
class FloatComparison:
"""浮点数比较工具类"""
def __init__(self, rel_tol=1e-09, abs_tol=0.0):
"""
初始化比较参数
rel_tol: 相对容差(默认1e-09)
abs_tol: 绝对容差(默认0.0)
"""
self.rel_tol = rel_tol
self.abs_tol = abs_tol
def is_equal(self, a, b, custom_rel_tol=None, custom_abs_tol=None):
"""安全的浮点数相等比较"""
rel_tol = custom_rel_tol if custom_rel_tol is not None else self.rel_tol
abs_tol = custom_abs_tol if custom_abs_tol is not None else self.abs_tol
return math.isclose(a, b, rel_tol=rel_tol, abs_tol=abs_tol)
def is_zero(self, value, tolerance=1e-10):
"""判断是否接近零"""
return abs(value) < tolerance
def round_to_significant_digits(self, value, digits):
"""保留指定有效数字"""
if value == 0:
return 0
return round(value, digits - int(math.floor(math.log10(abs(value)))) - 1)
# 实际应用示例
def practical_float_comparison():
"""实际应用中的浮点数比较"""
comparator = FloatComparison()
# 测试用例1:基本运算比较
result = 0.1 + 0.2
expected = 0.3
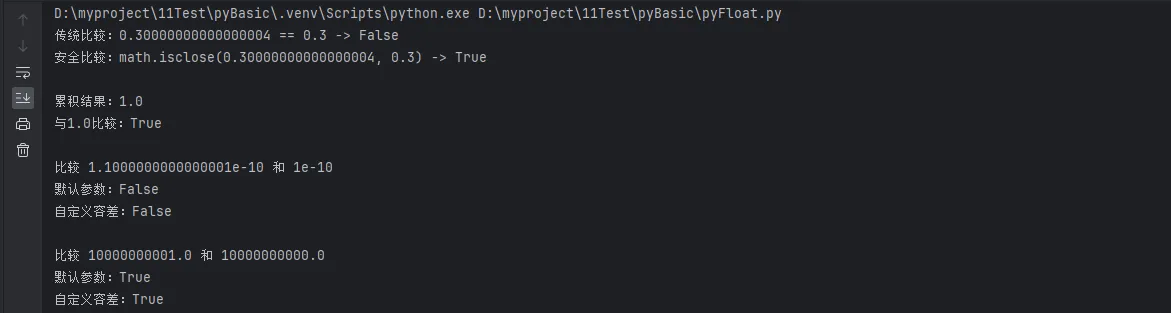
print(f"传统比较:{result} == {expected} -> {result == expected}")
print(f"安全比较:math.isclose({result}, {expected}) -> {comparator.is_equal(result, expected)}")
print()
# 测试用例2:累积误差场景
total = sum(0.1 for _ in range(10))
print(f"累积结果:{total}")
print(f"与1.0比较:{comparator.is_equal(total, 1.0)}")
print()
# 测试用例3:科学计算场景
scientific_values = [
(1e-10 + 1e-11, 1e-10, 1e-12), # 很小的数值
(1e10 + 1, 1e10, 1e-5), # 很大的数值
]
for a, b, tolerance in scientific_values:
print(f"比较 {a} 和 {b}")
print(f"默认参数:{math.isclose(a, b)}")
print(f"自定义容差:{comparator.is_equal(a, b, custom_abs_tol=tolerance)}")
print()
practical_float_comparison()
🔧 方案2:decimal模块实现高精度计算
Pythonfrom decimal import Decimal, getcontext, ROUND_HALF_UP
import time
class PreciseCalculator:
"""高精度计算器"""
def __init__(self, precision=28):
"""设置计算精度"""
getcontext().prec = precision
self.precision = precision
def add(self, a, b):
"""精确加法"""
return Decimal(str(a)) + Decimal(str(b))
def subtract(self, a, b):
"""精确减法"""
return Decimal(str(a)) - Decimal(str(b))
def multiply(self, a, b):
"""精确乘法"""
return Decimal(str(a)) * Decimal(str(b))
def divide(self, a, b):
"""精确除法"""
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("除数不能为零")
return Decimal(str(a)) / Decimal(str(b))
def financial_round(self, value, decimal_places=2):
"""金融级四舍五入"""
decimal_value = Decimal(str(value))
return decimal_value.quantize(
Decimal('0.' + '0' * decimal_places),
rounding=ROUND_HALF_UP
)
def performance_test(self, iterations=100000):
"""性能测试:float vs decimal"""
# float运算测试
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(iterations):
result = 0.1 + 0.2 + 0.3
float_time = time.time() - start_time
# decimal运算测试
start_time = time.time()
d1, d2, d3 = Decimal('0.1'), Decimal('0.2'), Decimal('0.3')
for i in range(iterations):
result = d1 + d2 + d3
decimal_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"=== 性能测试结果 ({iterations}次运算) ===")
print(f"float运算时间:{float_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"decimal运算时间:{decimal_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"性能比率:decimal/float = {decimal_time/float_time:.2f}")
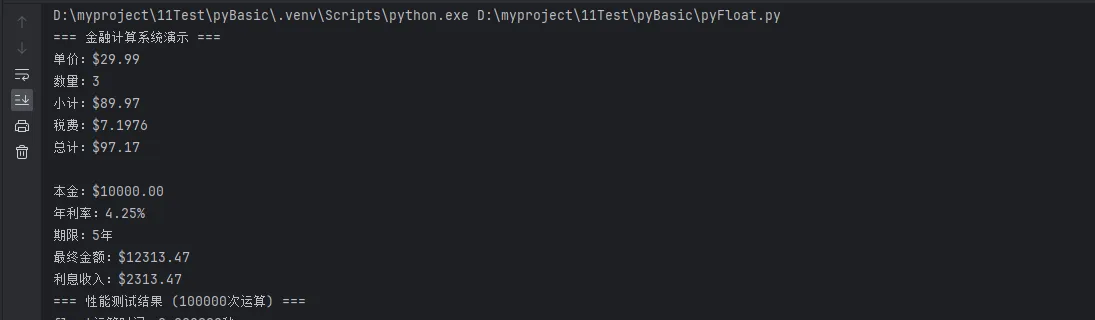
# 实战应用:金融计算系统
def financial_calculation_demo():
"""金融计算演示"""
calc = PreciseCalculator(precision=10)
print("=== 金融计算系统演示 ===")
# 场景1:价格计算
unit_price = "29.99"
quantity = "3"
tax_rate = "0.08"
subtotal = calc.multiply(unit_price, quantity)
tax = calc.multiply(subtotal, tax_rate)
total = calc.add(subtotal, tax)
print(f"单价:${unit_price}")
print(f"数量:{quantity}")
print(f"小计:${subtotal}")
print(f"税费:${tax}")
print(f"总计:${calc.financial_round(total)}")
print()
# 场景2:利息计算
principal = "10000.00"
annual_rate = "0.0425"
years = "5"
# 复利计算:A = P(1 + r)^t
base = calc.add("1", annual_rate)
power_result = Decimal(str(base)) ** int(years)
final_amount = calc.multiply(principal, str(power_result))
interest = calc.subtract(final_amount, principal)
print(f"本金:${principal}")
print(f"年利率:{float(annual_rate)*100}%")
print(f"期限:{years}年")
print(f"最终金额:${calc.financial_round(final_amount)}")
print(f"利息收入:${calc.financial_round(interest)}")
# 性能测试
calc.performance_test()
financial_calculation_demo()
⚡ 方案3:自定义浮点数处理工具
Pythonimport math
from typing import Union, Optional
class SmartFloat:
"""智能浮点数处理类"""
def __init__(self, value: Union[float, int, str], precision: int = 15):
"""
初始化智能浮点数
value: 数值
precision: 显示精度
"""
self.value = float(value)
self.precision = precision
def __str__(self):
"""字符串表示"""
return f"{self.value:.{self.precision}g}"
def __repr__(self):
"""调试表示"""
return f"SmartFloat({self.value}, precision={self.precision})"
def __add__(self, other):
"""加法运算"""
if isinstance(other, SmartFloat):
return SmartFloat(self.value + other.value, self.precision)
return SmartFloat(self.value + float(other), self.precision)
def __eq__(self, other):
"""相等比较"""
if isinstance(other, SmartFloat):
return math.isclose(self.value, other.value)
return math.isclose(self.value, float(other))
def __lt__(self, other):
"""小于比较"""
other_val = other.value if isinstance(other, SmartFloat) else float(other)
return self.value < other_val and not math.isclose(self.value, other_val)
def close_to(self, other, rel_tol=1e-09, abs_tol=0.0):
"""自定义精度比较"""
other_val = other.value if isinstance(other, SmartFloat) else float(other)
return math.isclose(self.value, other_val, rel_tol=rel_tol, abs_tol=abs_tol)
@classmethod
def from_fraction(cls, numerator: int, denominator: int, precision: int = 15):
"""从分数创建"""
return cls(numerator / denominator, precision)
def to_rational_approximation(self, max_denominator: int = 1000000):
"""转换为有理数近似"""
from fractions import Fraction
return Fraction(self.value).limit_denominator(max_denominator)
# Windows上位机开发中的实际应用
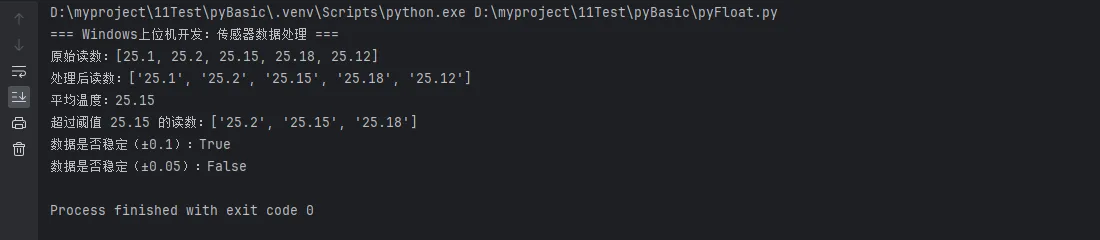
def windows_application_demo():
"""Windows应用开发中的浮点数处理"""
print("=== Windows上位机开发:传感器数据处理 ===")
# 模拟传感器读数(带有精度误差)
temperature_readings = [25.1, 25.2, 25.15, 25.18, 25.12]
# 使用SmartFloat处理
smart_readings = [SmartFloat(reading) for reading in temperature_readings]
# 计算平均值
total = SmartFloat(0)
for reading in smart_readings:
total = total + reading
average = SmartFloat(total.value / len(smart_readings))
print(f"原始读数:{temperature_readings}")
print(f"处理后读数:{[str(r) for r in smart_readings]}")
print(f"平均温度:{average}")
# 阈值检测
threshold = SmartFloat(25.15)
over_threshold = [r for r in smart_readings if not (r < threshold)]
print(f"超过阈值 {threshold} 的读数:{[str(r) for r in over_threshold]}")
# 数据稳定性检查
def is_stable(readings, tolerance=0.1):
"""检查数据是否稳定"""
if len(readings) < 2:
return True
for i in range(1, len(readings)):
if not readings[i].close_to(readings[0], abs_tol=tolerance):
return False
return True
print(f"数据是否稳定(±0.1):{is_stable(smart_readings, 0.1)}")
print(f"数据是否稳定(±0.05):{is_stable(smart_readings, 0.05)}")
windows_application_demo()
💡 代码实战:构建完整的浮点数处理库
Pythonimport math
import sys
from typing import List, Tuple
from decimal import Decimal, getcontext
class FloatPrecisionManager:
"""浮点数精度管理器 - 完整解决方案"""
def __init__(self):
"""初始化管理器"""
self.default_rel_tol = 1e-09
self.default_abs_tol = 0.0
getcontext().prec = 28
def safe_compare(self, a: float, b: float,
rel_tol: float = None, abs_tol: float = None) -> bool:
"""安全的浮点数比较"""
rel_tol = rel_tol or self.default_rel_tol
abs_tol = abs_tol or self.default_abs_tol
return math.isclose(a, b, rel_tol=rel_tol, abs_tol=abs_tol)
def safe_sum(self, numbers: List[float]) -> float:
"""安全的浮点数求和(减少累积误差)"""
# 使用Kahan求和算法
total = 0.0
compensation = 0.0
for num in numbers:
y = num - compensation
temp = total + y
compensation = (temp - total) - y
total = temp
return total
def format_scientific(self, value: float, significant_digits: int = 6) -> str:
"""科学记数法格式化"""
if value == 0:
return "0.0"
# 计算指数
exponent = int(math.floor(math.log10(abs(value))))
mantissa = value / (10 ** exponent)
# 格式化尾数
mantissa_str = f"{mantissa:.{significant_digits-1}f}"
return f"{mantissa_str}e{exponent:+d}"
def analyze_precision_loss(self, operation: str,
operands: List[float]) -> dict:
"""分析精度损失"""
result = {
'operation': operation,
'operands': operands,
'float_result': None,
'decimal_result': None,
'precision_loss': None,
'relative_error': None
}
try:
# 使用float计算
if operation == 'add':
result['float_result'] = sum(operands)
elif operation == 'multiply':
float_result = 1.0
for op in operands:
float_result *= op
result['float_result'] = float_result
# 使用Decimal计算(作为"真值"参考)
decimal_operands = [Decimal(str(op)) for op in operands]
if operation == 'add':
result['decimal_result'] = sum(decimal_operands)
elif operation == 'multiply':
decimal_result = Decimal('1')
for op in decimal_operands:
decimal_result *= op
result['decimal_result'] = decimal_result
# 计算精度损失
float_val = result['float_result']
decimal_val = float(result['decimal_result'])
result['precision_loss'] = abs(float_val - decimal_val)
if decimal_val != 0:
result['relative_error'] = abs(float_val - decimal_val) / abs(decimal_val)
except Exception as e:
result['error'] = str(e)
return result
def benchmark_operations(self, iterations: int = 100000) -> dict:
"""基准测试各种浮点数操作"""
import time
test_data = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5] * (iterations // 5)
results = {}
# 测试普通float求和
start_time = time.perf_counter()
float_sum = sum(test_data)
results['float_sum_time'] = time.perf_counter() - start_time
results['float_sum_result'] = float_sum
# 测试Kahan求和
start_time = time.perf_counter()
kahan_sum = self.safe_sum(test_data)
results['kahan_sum_time'] = time.perf_counter() - start_time
results['kahan_sum_result'] = kahan_sum
# 测试Decimal求和
start_time = time.perf_counter()
decimal_data = [Decimal(str(x)) for x in test_data]
decimal_sum = sum(decimal_data)
results['decimal_sum_time'] = time.perf_counter() - start_time
results['decimal_sum_result'] = float(decimal_sum)
return results
# 综合示例:Python开发中的最佳实践
def comprehensive_example():
"""综合示例:展示所有技术的实际应用"""
manager = FloatPrecisionManager()
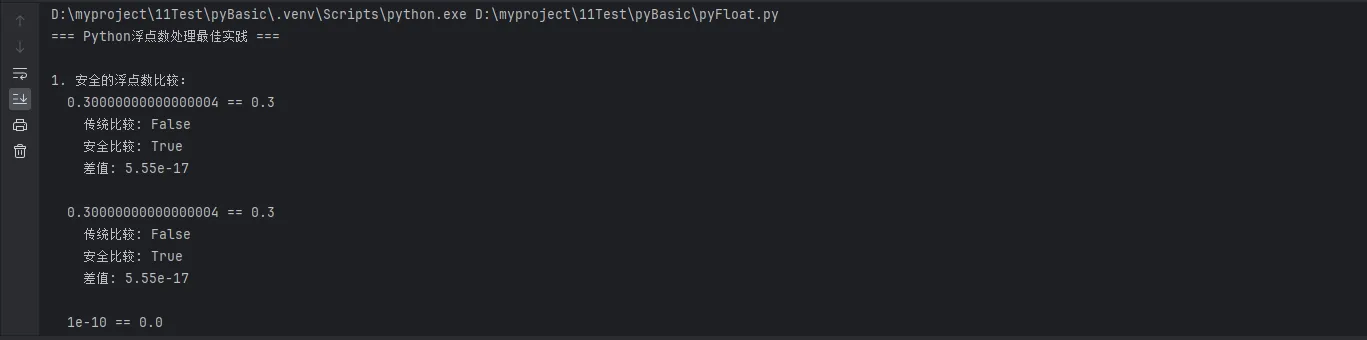
print("=== Python浮点数处理最佳实践 ===\n")
# 1. 基本比较操作
print("1. 安全的浮点数比较:")
test_pairs = [
(0.1 + 0.2, 0.3),
(0.1 * 3, 0.3),
(1e-10, 0.0),
(math.pi, 22/7)
]
for a, b in test_pairs:
unsafe_equal = (a == b)
safe_equal = manager.safe_compare(a, b)
print(f" {a} == {b}")
print(f" 传统比较: {unsafe_equal}")
print(f" 安全比较: {safe_equal}")
print(f" 差值: {abs(a-b):.2e}")
print()
# 2. 精度损失分析
print("2. 精度损失分析:")
test_operations = [
('add', [0.1, 0.2, 0.3]),
('multiply', [0.1, 0.1, 0.1]),
('add', [1e-16] * 1000) # 累积误差测试
]
for op, operands in test_operations:
analysis = manager.analyze_precision_loss(op, operands)
print(f" 操作: {op}({operands[:3]}{'...' if len(operands) > 3 else ''})")
print(f" Float结果: {analysis['float_result']}")
print(f" Decimal结果: {analysis['decimal_result']}")
print(f" 精度损失: {analysis['precision_loss']:.2e}")
if analysis['relative_error']:
print(f" 相对误差: {analysis['relative_error']:.2e}")
print()
# 3. 性能基准测试
print("3. 性能基准测试:")
benchmark = manager.benchmark_operations(50000)
print(f" 数据规模: 50000个浮点数")
print(f" Float求和: {benchmark['float_sum_result']:.10f} "
f"(耗时: {benchmark['float_sum_time']:.6f}s)")
print(f" Kahan求和: {benchmark['kahan_sum_result']:.10f} "
f"(耗时: {benchmark['kahan_sum_time']:.6f}s)")
print(f" Decimal求和: {benchmark['decimal_sum_result']:.10f} "
f"(耗时: {benchmark['decimal_sum_time']:.6f}s)")
# 4. 实际应用建议
print("\n4. 实际应用建议:")
recommendations = [
"💡 日常计算:使用 math.isclose() 进行浮点数比较",
"💰 金融计算:使用 decimal 模块确保精度",
"🔬 科学计算:根据精度要求选择合适的数据类型",
"⚡ 性能优先:大量计算时考虑使用 numpy 的优化算法",
"🐛 调试技巧:使用 sys.float_info 了解浮点数限制"
]
for rec in recommendations:
print(f" {rec}")
comprehensive_example()
🎯 总结与最佳实践
通过本文的深入探讨,我们全面了解了Python浮点数的核心知识点。让我们总结三个关键要点:
核心要点回顾:
- 🔬 IEEE 754标准理解:浮点数精度问题源于二进制表示的局限性,不是Python的缺陷,而是计算机科学的基本特征。掌握这一点是正确使用浮点数的基础。
- 🛠️ 精度处理方案:针对不同场景选择合适的解决方案 -
math.isclose()适用于一般比较,decimal模块适合金融计算,自定义工具类满足特殊需求。 - 💡 实战应用技巧:在Windows上位机开发和数据处理中,建立完善的浮点数处理机制不仅能避免计算错误,还能提升代码的健壮性和可维护性。
掌握这些Python开发技巧,将让你在编程实践中更加得心应手,特别是在处理精确计算和数值分析任务时。继续关注我们的技术分享,获取更多实用的Python编程技巧和上位机开发最佳实践!
📚 延伸学习建议:深入学习NumPy数组计算、SciPy科学计算库,以及在工业控制系统中的数值稳定性设计模式。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录