目录
高级串口通信技术在工业自动化、嵌入式系统、医疗设备以及智能仪器等领域中占据着非常重要的地位。随着现代应用对数据传输的实时性、准确性和安全性要求的不断提高,传统的串口通信方式逐渐暴露出其在事件响应速度和数据处理效率方面的不足。因此,在 C# 环境中充分利用 SerialPort 类库,通过事件驱动、异步多线程 I/O,以及高效的数据包解析技术,构建一个高性能、稳定可靠的串口通信系统显得尤为关键。
串口数据读写
串口通信的第一步在于如何高效地进行数据的读与写。数据的发送与接收不仅影响整个通信系统的响应速度,同时也决定了数据传输的稳定性与完整性。下面我们从发送、接收和缓冲区管理以及数据编码处理三个方面展开讨论。
发送字符串数据
在 C# 中,通过 SerialPort 类的 Write 或 WriteLine 方法可以直接发送字符串数据。
例如,使用 WriteLine 方法发送命令:
C#// 发送字符串数据
serialPort.WriteLine("AT+COMMAND");
这种方法适用于简单的文本指令,但对于复杂数据包的传输,还需考虑数据的编码、校验和响应处理。
接收数据与缓冲区管理
在数据接收过程中,SerialPort 类提供了多种读取方法,如 ReadExisting、ReadLine、ReadByte 及 Read。这些方法各有优缺点:
-
ReadExisting
一次性读取当前缓冲区中的所有数据,但可能会受到缓冲区溢出或数据粘包问题的影响。
-
ReadLine
按行读取数据,适用于以换行符结束的字符串,对于实时数据处理可能会导致延时。
-
缓冲区管理
- 缓冲区大小调整:适当调整 SerialPort 的接收缓冲区大小,有助于防止数据丢失或缓冲区溢出。
- 清空缓存:使用
DiscardInBuffer和DiscardOutBuffer方法,可有效清除由于旧数据导致的干扰。
下表对几种常用读取方法进行了比较:
| 读取方法 | 适用场景 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ReadExisting | 简单连续数据流 | 实现简单,调用便捷 | 可能造成数据粘包,无法精确控制结束标志 |
| ReadLine | 按行定义的数据协议 | 能自动识别结束符 | 对于没有换行符的数据,可能会造成延时 |
| Read | 固定长度或分包数据 | 可自定义读取长度与方式 | 数据处理需自行预处理,避免遗漏或余量数据 |
数据编码与处理
传输数据过程中必须保证数据格式的正确性,常用的编码方式包括 ASCII、UTF-8、Unicode 等。使用 Encoding 类可以确保数据在发送和接收过程中不会出现乱码。例如,发送 UTF-8 编码的数据如下:
C#// 发送 UTF-8 编码的字符串
byte[] buffer = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("数据传输测试");
serialPort.Write(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
在数据接收处,同样需要采用匹配的编码格式进行解码:
C#// 读取并解码数据
byte[] readBuffer = new byte[serialPort.BytesToRead];
serialPort.Read(readBuffer, 0, readBuffer.Length);
string receivedData = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(readBuffer);
通过使用相匹配的编码方式,可以有效防止跨平台和多语言环境中的字符编码错误,从而确保数据完整无误。
事件驱动的串口通信
传统的串口通信多依赖于 DataReceived 事件的触发机制,但这种方法在高数据量或复杂异步操作场合下容易引发线程安全问题和数据处理延迟。近年来,使用异步读写方法(如 BeginRead/EndRead 以及 ReadAsync)已逐渐成为提升串口通信效率的重要手段。
DataReceived 与 ErrorReceived 事件解析
SerialPort 类中,DataReceived 事件常用于通知应用程序有新数据到达。然而,这种事件驱动方式存在以下问题:
- 线程安全问题:DataReceived 事件在后台线程中被调用,直接对 UI 或共享资源进行操作可能会引发线程安全异常,需要额外的 Invoke 调用进行线程切换。
- 数据粘包问题:操作系统并不会为每一个字节单独触发事件,可能会在数据量较大时一次性触发,导致数据解析时出现边界错误。
- 错误报告不及时:错误(如校验错误、帧错误)可能不会在 DataReceived 事件中及时报告,使用底层 BaseStream 读取过程中则可以更直接地处理异常。
因此,许多专家(如 Ben Voigt)建议在复杂场景下放弃直接使用 DataReceived,而采用异步 I/O 方法来提升数据处理效率和系统可靠性。
异步读写方法的应用
使用异步读写方法可以大大降低串口通信的延迟并减少线程阻塞。典型的实现方式是使用 BeginRead/EndRead 接口。
图 1:异步读取数据流程图
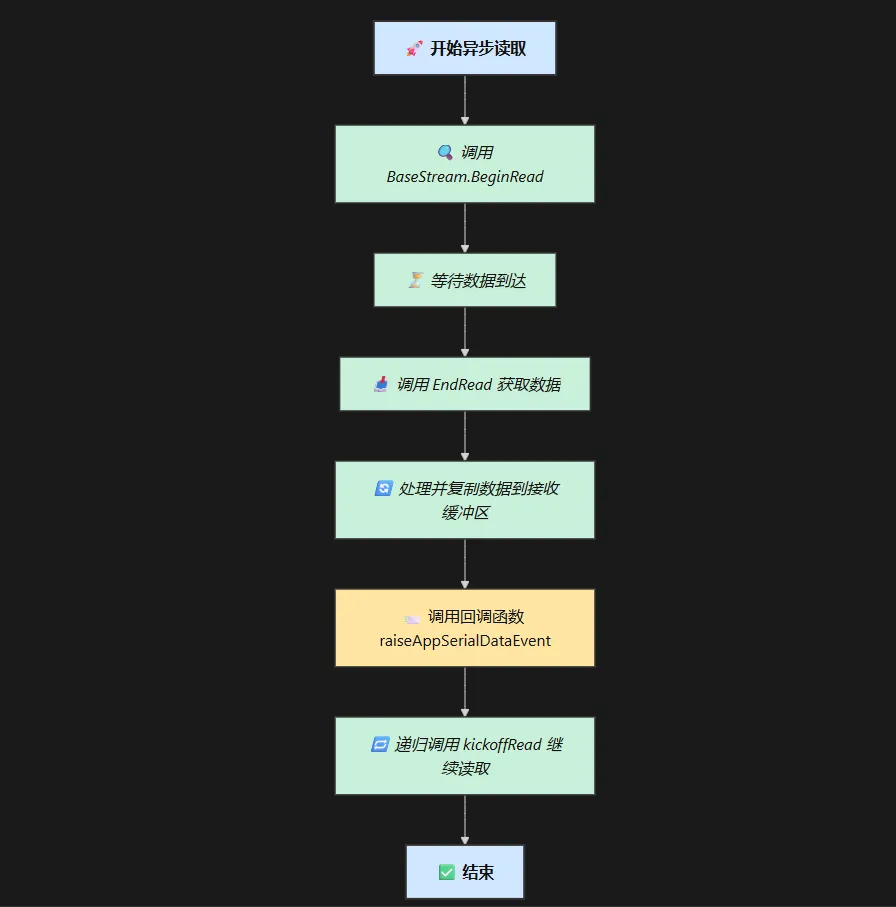
在异步写操作中,WriteAsync 方法可以代替传统的 Write 方法,以避免因数据量过大时的阻塞问题。通过异步 I/O,可以实现更高效的串口读写操作,提升系统整体性能。
线程同步与安全性讨论
在事件驱动的异步应用中,另一个重要问题在于多个线程对串口资源的访问可能引起竞争状态。为此,我们通常采取以下几种措施:
- 使用锁机制:通过
lock关键字确保关键代码段不会被多个线程同时访问,从而保证数据的完整性和一致性。 - 使用同步队列:特别是在需要跨线程传递数据点时,可以用线程安全的队列或者
Queue.Synchronized包装器。 - 避免直接修改共享变量:如 Alan Zucconi 在处理 Arduino 与 Unity 数据通信时建议,通过同步队列传递消息而不是直接操作共享数据,从而降低线程间的耦合度。
串口数据解析技术
在实际应用中,接收到的数据往往包含复杂的数据包,需要精确解析各个字段的信息。数据包解析的关键在于能够正确识别包头、提取命令和数据内容,同时还需要防止分包、粘包等问题。下面我们详细探讨几种常用解析技术。
二进制数据解析及数据转换
针对二进制数据包的解析,通常需要对收到的字节数组进行逐步分析。常见的数据包格式可能包含以下部分:
- 包头 (SOH):标识数据包开始的字符
- 数据长度:标记后续数据的长度,例如两个 32 位整数表示命令和数据的长度
- 命令和数据内容:分别用不同的编码格式存储字符串或二进制数据
- 校验和:用于检测数据包完整性
解析过程中,可以使用 BitConverter 类对字节数组进行转换。比如,下面的示例展示了如何解析一个简单数据包,其中包含命令长度和数据长度信息(参见 Euan's Blog 的说明,chunk_id=84-97):
C#private ParseResult TryParsePacket(ReadOnlySpan<byte> buffer,
out int consumedBytes, out string command, out string data)
{
consumedBytes = 0;
command = string.Empty;
data = string.Empty;
int indexOfSoh = buffer.IndexOf(Packet.Soh);
if (indexOfSoh == -1)
{
consumedBytes = buffer.Length;
return ParseResult.Error;
}
if (indexOfSoh > 0)
{
consumedBytes = indexOfSoh;
return ParseResult.Error;
}
buffer = buffer.Slice(1);
if (buffer.Length < sizeof(int) * 2)
return ParseResult.Partial;
int commandLength = BinaryPrimitives.ReadInt32LittleEndian(buffer);
int dataLength = BinaryPrimitives.ReadInt32LittleEndian(buffer.Slice(sizeof(int)));
buffer = buffer.Slice(sizeof(int) * 2);
if (buffer.Length < commandLength + dataLength)
return ParseResult.Partial;
try
{
command = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer.Slice(0, commandLength));
data = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer.Slice(commandLength, dataLength));
consumedBytes = 1 + sizeof(int) * 2 + commandLength + dataLength;
return ParseResult.Complete;
}
catch
{
consumedBytes = 1;
return ParseResult.Error;
}
}
#endregion
使用这种方法尽管能正确提取数据,但在高性能场景下,不可避免会出现过多的数组切割和内存拷贝。为了解决这一问题,可以利用 .NET 中的新特性 Span,以避免不必要的内存分配和复制操作。
CRC 校验与错误检测
在通信过程中,数据传输过程中可能会发生数据损坏或丢失。CRC 校验技术可以有效检测数据包中的错误。
CRC 主要通过对数据包中各个字节执行多项式运算,得到校验值,再与数据包内携带的校验和进行对比,判断数据是否正确。
以下是一个简化版的 CRC 计算示例(具体实现因需求而异,在实际开发中可依据业务协议定制):
C#public static ushort CalculateCRC(byte[] data, int offset, int length)
{
ushort crc = 0xFFFF;
for (int i = offset; i < offset + length; i++)
{
crc ^= data[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
crc = (ushort)((crc & 0x0001) != 0 ? (crc >> 1) ^ 0xA001 : crc >> 1);
}
}
return crc;
}
利用 CRC 校验能够大幅降低数据传输错误导致的问题,是确保数据通信可靠性的重要技术手段。
数据包拆包与粘包处理
在实际通信中,尤其是使用流式异步 I/O 方式时,常常会遇到数据包拆分或粘连的问题,即一次读取可能只包含部分数据包,或者一次读取包含多个数据包。为了解决这一问题,常用的思路包括:
-
状态机解析法
根据数据包中的固定标志(如 SOH),状态机能够逐步确认数据包的起始位置、头部长度以及整体包长度,从而实现数据拆包。例如,解析流程可以分为:
- 搜索 SOH 字节
- 判断剩余数据是否足够构成完整头部
- 读取命令和数据长度
- 判断剩余数据是否足够构成完整数据包
- 正常提取数据包内容,否则保留部分数据等待下一次接收
-
使用 Span 进行优化
如前所述,通过 Span,可以方便地对接收缓冲区进行切片操作,既提高了内存利用率,又简化了拆包逻辑。
完整代码
C#using System.Buffers.Binary;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.IO.Ports;
using System.Text;
namespace AppSerialAsync
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private SerialPort serialPort;
private readonly ConcurrentQueue<byte[]> dataQueue = new();
private readonly object lockObject = new();
private byte[] receiveBuffer = new byte[4096];
private int bufferPosition = 0;
private bool isReading = false;
public enum ParseResult
{
Complete,
Partial,
Error
}
public static class Packet
{
public const byte Soh = 0x01; // 包头
}
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeSerialPort();
LoadAvailablePorts();
}
#region Serial Port Initialization
private void InitializeSerialPort()
{
serialPort = new SerialPort
{
BaudRate = 9600,
DataBits = 8,
Parity = Parity.None,
StopBits = StopBits.One,
Handshake = Handshake.None,
ReceivedBytesThreshold = 1,
ReadTimeout = 500,
WriteTimeout = 500,
ReadBufferSize = 4096,
WriteBufferSize = 2048
};
}
private void LoadAvailablePorts()
{
cmbPorts.Items.Clear();
foreach (string port in SerialPort.GetPortNames())
{
cmbPorts.Items.Add(port);
}
if (cmbPorts.Items.Count > 0)
cmbPorts.SelectedIndex = 0;
}
#endregion
#region Connection Handling
private async void btnConnect_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (!serialPort.IsOpen)
{
if (cmbPorts.SelectedItem == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("请选择串口端口!", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
return;
}
serialPort.PortName = cmbPorts.SelectedItem.ToString();
serialPort.BaudRate = int.Parse(cmbBaudRate.Text);
serialPort.Open();
serialPort.DiscardInBuffer();
serialPort.DiscardOutBuffer();
await StartAsyncReading();
btnConnect.Text = "断开连接";
btnConnect.BackColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red;
UpdateConnectionStatus("已连接", System.Drawing.Color.Green);
LogMessage($"串口 {serialPort.PortName} 连接成功,波特率: {serialPort.BaudRate}");
}
else
{
StopAsyncReading();
serialPort.Close();
btnConnect.Text = "连接串口";
btnConnect.BackColor = System.Drawing.SystemColors.Control;
UpdateConnectionStatus("未连接", System.Drawing.Color.Red);
LogMessage("串口连接已断开");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"串口操作失败: {ex.Message}", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
LogMessage($"错误: {ex.Message}");
}
}
#endregion
#region Async Reading
private async Task StartAsyncReading()
{
if (isReading) return;
isReading = true;
bufferPosition = 0;
await Task.Run(BeginAsyncRead);
}
private void BeginAsyncRead()
{
if (!serialPort.IsOpen || !isReading) return;
try
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
serialPort.BaseStream.BeginRead(buffer, 0, buffer.Length, ar =>
{
try
{
int bytesRead = serialPort.BaseStream.EndRead(ar);
if (bytesRead > 0)
{
byte[] receivedData = new byte[bytesRead];
Array.Copy(buffer, 0, receivedData, 0, bytesRead);
ProcessReceivedData(receivedData);
}
if (isReading && serialPort.IsOpen)
{
BeginAsyncRead();
}
}
catch (IOException ioEx)
{
BeginInvoke(new Action(() => LogMessage($"IO异常: {ioEx.Message}")));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
BeginInvoke(new Action(() => LogMessage($"读取异常: {ex.Message}")));
}
}, null);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
BeginInvoke(new Action(() => LogMessage($"开始异步读取失败: {ex.Message}")));
}
}
private void StopAsyncReading()
{
isReading = false;
}
#endregion
#region Data Processing
private void ProcessReceivedData(byte[] newData)
{
lock (lockObject)
{
if (bufferPosition + newData.Length > receiveBuffer.Length)
{
Array.Resize(ref receiveBuffer, receiveBuffer.Length * 2);
}
Array.Copy(newData, 0, receiveBuffer, bufferPosition, newData.Length);
bufferPosition += newData.Length;
ParseDataPackets();
BeginInvoke(new Action(() =>
{
string hexData = BitConverter.ToString(newData).Replace("-", " ");
LogMessage($"接收原始数据: {hexData}");
lblRxCount.Text = $"接收: {int.Parse(lblRxCount.Text.Split(':')[1].Trim()) + newData.Length}";
}));
BeginInvoke(new Action(() =>
{
string hexBuffer = BitConverter.ToString(receiveBuffer, 0, bufferPosition).Replace("-", " ");
LogMessage($"当前缓冲区: {hexBuffer} 长度: {bufferPosition}");
}));
}
}
private void ParseDataPackets()
{
while (bufferPosition > 0)
{
ReadOnlySpan<byte> spanData = receiveBuffer.AsSpan(0, bufferPosition);
var result = TryParsePacket(spanData, out int consumedBytes, out string command, out string data);
if (result == ParseResult.Complete)
{
BeginInvoke(new Action(() =>
{
LogMessage($"解析数据包 - 命令: {command}, 数据: {data}");
txtReceived.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] 命令: {command}, 数据: {data}\r\n");
txtReceived.ScrollToCaret();
}));
Array.Copy(receiveBuffer, consumedBytes, receiveBuffer, 0, bufferPosition - consumedBytes);
bufferPosition -= consumedBytes;
}
else if (result == ParseResult.Partial)
{
break;
}
else
{
Array.Copy(receiveBuffer, 1, receiveBuffer, 0, bufferPosition - 1);
bufferPosition--;
}
}
}
private ParseResult TryParsePacket(ReadOnlySpan<byte> buffer, out int consumedBytes, out string command, out string data)
{
consumedBytes = 0;
command = string.Empty;
data = string.Empty;
int indexOfSoh = buffer.IndexOf(Packet.Soh);
if (indexOfSoh == -1)
{
consumedBytes = buffer.Length;
return ParseResult.Error;
}
if (indexOfSoh > 0)
{
consumedBytes = indexOfSoh;
return ParseResult.Error;
}
buffer = buffer.Slice(1);
if (buffer.Length < sizeof(int) * 2)
return ParseResult.Partial;
int commandLength = BinaryPrimitives.ReadInt32LittleEndian(buffer);
int dataLength = BinaryPrimitives.ReadInt32LittleEndian(buffer.Slice(sizeof(int)));
buffer = buffer.Slice(sizeof(int) * 2);
if (buffer.Length < commandLength + dataLength)
return ParseResult.Partial;
try
{
command = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer.Slice(0, commandLength));
data = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer.Slice(commandLength, dataLength));
consumedBytes = 1 + sizeof(int) * 2 + commandLength + dataLength;
return ParseResult.Complete;
}
catch
{
consumedBytes = 1;
return ParseResult.Error;
}
}
#endregion
#region Data Sending
private async void btnSend_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!serialPort.IsOpen)
{
MessageBox.Show("请先连接串口!", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
try
{
string dataToSend = txtSend.Text;
if (rbSendText.Checked)
{
await SendTextData(dataToSend);
}
else if (rbSendPacket.Checked)
{
await SendDataPacket("CMD", dataToSend);
}
else
{
await SendHexData(dataToSend);
}
byte[] sentData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(dataToSend);
lblTxCount.Text = $"发送: {int.Parse(lblTxCount.Text.Split(':')[1].Trim()) + sentData.Length}";
LogMessage($"发送数据: {dataToSend}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"发送数据失败: {ex.Message}", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
LogMessage($"发送错误: {ex.Message}");
}
}
private async Task SendTextData(string text)
{
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(text);
await serialPort.BaseStream.WriteAsync(data, 0, data.Length);
}
private async Task SendDataPacket(string command, string data)
{
byte[] commandBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(command);
byte[] dataBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(data);
byte[] packet = new byte[1 + sizeof(int) * 2 + commandBytes.Length + dataBytes.Length];
int offset = 0;
packet[offset++] = Packet.Soh;
BinaryPrimitives.WriteInt32LittleEndian(packet.AsSpan(offset), commandBytes.Length);
offset += sizeof(int);
BinaryPrimitives.WriteInt32LittleEndian(packet.AsSpan(offset), dataBytes.Length);
offset += sizeof(int);
Array.Copy(commandBytes, 0, packet, offset, commandBytes.Length);
offset += commandBytes.Length;
Array.Copy(dataBytes, 0, packet, offset, dataBytes.Length);
await serialPort.BaseStream.WriteAsync(packet, 0, packet.Length);
}
private async Task SendHexData(string hexString)
{
try
{
hexString = hexString.Replace(" ", "").Replace("-", "");
byte[] data = new byte[hexString.Length / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)
{
data[i] = Convert.ToByte(hexString.Substring(i * 2, 2), 16);
}
await serialPort.BaseStream.WriteAsync(data, 0, data.Length);
}
catch (FormatException)
{
throw new ArgumentException("无效的十六进制格式");
}
}
#endregion
#region UI & Logging
private void btnClearReceived_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) => txtReceived.Clear();
private void btnClearLog_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) => txtLog.Clear();
private void btnRefreshPorts_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LoadAvailablePorts();
LogMessage("端口列表已刷新");
}
private void UpdateConnectionStatus(string status, System.Drawing.Color color)
{
if (InvokeRequired)
{
BeginInvoke(new Action(() => UpdateConnectionStatus(status, color)));
return;
}
lblStatus.Text = $"状态: {status}";
lblStatus.ForeColor = color;
}
private void LogMessage(string message)
{
if (InvokeRequired)
{
BeginInvoke(new Action(() => LogMessage(message)));
return;
}
txtLog.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] {message}\r\n");
txtLog.ScrollToCaret();
}
#endregion
#region Utility
public static ushort CalculateCRC(byte[] data, int offset, int length)
{
ushort crc = 0xFFFF;
for (int i = offset; i < offset + length; i++)
{
crc ^= data[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
crc = (ushort)((crc & 0x0001) != 0 ? (crc >> 1) ^ 0xA001 : crc >> 1);
}
}
return crc;
}
protected override void OnFormClosing(FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
if (serialPort != null && serialPort.IsOpen)
{
StopAsyncReading();
serialPort.Close();
}
base.OnFormClosing(e);
}
#endregion
}
}
结论
随着对数据传输速度和处理准确性要求的不断提高,高级串口通信技术已经成为工业和嵌入式系统中不可或缺的一部分。
通过本文的详细讨论和实例讲解,希望能够为广大开发者提供有价值的参考和指导,使其在实际工程中能够应对各种串口数据传输和解析问题,并最终构建出一个高效、稳定、可靠的串口通信系统。
相关信息
通过网盘分享的文件:AppSerialAsync.zip 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ykhRZlJRLN8oQeyt1-_d9g?pwd=syrt 提取码: syrt --来自百度网盘超级会员v9的分享
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!