目录
🔥 C#内存管理双雄:GC.Collect vs GC.SuppressFinalize 深度解析
你是否在C#开发中遇到过内存泄漏问题?是否困惑于何时使用GC.Collect(),何时使用GC.SuppressFinalize()?作为.NET开发者,掌握垃圾回收机制的核心方法至关重要。今天我们深入剖析这两个关键方法,通过实战代码示例,帮你彻底理解它们的区别和最佳使用场景。本文将解决你在内存管理中遇到的实际问题,让你的应用性能更上一层楼!
🎯 问题分析:内存管理的常见痛点
在C#开发中,开发者经常面临以下困扰:
- 何时手动触发垃圾回收? 很多开发者误认为频繁调用
GC.Collect()能提升性能 - 如何正确实现Dispose模式? 不知道为什么要调用
GC.SuppressFinalize(this) - 内存泄漏难以定位 非托管资源没有被正确释放
这些问题的根源在于对.NET垃圾回收机制理解不深,让我们逐一击破!
💡 核心概念解析
🔍 GC.Collect() - 强制垃圾回收
GC.Collect()是一个强制触发垃圾回收的方法,但99%的情况下你不应该使用它。
核心作用:
- 立即启动垃圾回收过程
- 回收所有代的内存(0代、1代、2代)
- 暂停应用程序执行
🛡️ GC.SuppressFinalize() - 抑制终结器调用
GC.SuppressFinalize()告诉垃圾回收器:这个对象已经被正确清理,不需要调用终结器了。
核心作用:
- 提升性能,避免不必要的终结器调用
- 配合IDisposable模式使用
- 防止对象进入终结队列
🚀 实战解决方案
方案一:正确的资源释放模式
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppGCCollect
{
public class FileManager : IDisposable
{
private FileStream _fileStream;
private bool _disposed = false;
public FileManager(string filePath)
{
_fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create);
}
// 公共的Dispose方法
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
// 🔥 关键:告诉GC不要调用终结器
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
// 受保护的Dispose方法
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!_disposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
// 释放托管资源
_fileStream?.Dispose();
}
// 释放非托管资源(如果有的话)
_disposed = true;
}
}
// 终结器(析构函数)
~FileManager()
{
Dispose(false);
}
}
}
// 调用
using var fileManager = new FileManager("example.txt");
应用场景: 处理文件、数据库连接、网络流等需要显式释放的资源
性能提升: 避免对象进入终结队列,减少GC压力
方案二:内存密集型操作的GC优化
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppGCCollect
{
public class DataProcessor
{
public void ProcessLargeDataSet()
{
// 处理大量数据前检查内存状态
long memoryBefore = GC.GetTotalMemory(false);
Console.WriteLine($"处理前内存: {memoryBefore / 1024 / 1024} MB");
// 处理大量临时对象
ProcessData();
// ⚠️ 特殊情况:只在真正需要时才调用
if (ShouldForceGC())
{
GC.Collect();
GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers();
GC.Collect(); // 二次回收确保彻底清理
}
long memoryAfter = GC.GetTotalMemory(true);
Console.WriteLine($"处理后内存: {memoryAfter / 1024 / 1024} MB");
}
private bool ShouldForceGC()
{
// 🎯 只在以下情况考虑手动GC:
// 1. 刚完成大量内存分配
// 2. 即将进入空闲期
// 3. 需要精确的内存测量
return GC.GetTotalMemory(false) > 100 * 1024 * 1024; // 超过100MB
}
private void ProcessData()
{
// 模拟大量数据处理
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
var largeArray = new byte[1024 * 1024]; // 1MB数组
// 处理数据...
}
}
}
}
应用场景: 科学计算、图像处理、大数据分析等内存密集型应用
注意事项: 只在确实需要时使用,过度使用会降低性能
方案三:高性能的对象池实现
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppGCCollect
{
public class ObjectPool<T> : IDisposable where T : class, new()
{
private readonly ConcurrentQueue<T> _objects = new();
private readonly Func<T> _objectGenerator;
private bool _disposed = false;
public ObjectPool(Func<T> objectGenerator = null)
{
_objectGenerator = objectGenerator ?? (() => new T());
}
public T GetObject()
{
if (_objects.TryDequeue(out T item))
{
return item;
}
return _objectGenerator();
}
public void ReturnObject(T item)
{
if (item != null && !_disposed)
{
_objects.Enqueue(item);
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (!_disposed)
{
// 清理池中的对象
while (_objects.TryDequeue(out T item))
{
if (item is IDisposable disposable)
{
disposable.Dispose();
}
}
_disposed = true;
// 🔥 关键:抑制终结器
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
public class PoolExample
{
ObjectPool<StringBuilder> pool = new ObjectPool<StringBuilder>();
public PoolExample(ObjectPool<StringBuilder> pool)
{
this.pool = pool;
}
public string ProcessStrings(string[] inputs)
{
var sb = pool.GetObject();
try
{
foreach (var input in inputs)
{
sb.AppendLine(input.ToUpper());
}
return sb.ToString();
}
finally
{
sb.Clear(); // 重置状态
pool.ReturnObject(sb);
}
}
}
}
// 调用
using var pool = new ObjectPool<StringBuilder>(() => new StringBuilder(1024));
var example = new PoolExample(pool);
string[] inputs = { "Hello", "from", "the", "other", "side" };
string result = example.ProcessStrings(inputs);
应用场景: 高并发Web应用、游戏开发、实时系统
性能优势: 减少对象分配,降低GC压力
方案四:内存监控和诊断工具
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppGCCollect
{
public static class MemoryDiagnostics
{
public static void PrintMemoryInfo(string operation = "")
{
var gc0 = GC.CollectionCount(0);
var gc1 = GC.CollectionCount(1);
var gc2 = GC.CollectionCount(2);
var memory = GC.GetTotalMemory(false);
Console.WriteLine($"=== {operation} 内存状态 ===");
Console.WriteLine($"内存使用: {memory / 1024.0 / 1024.0:F2} MB");
Console.WriteLine($"GC次数 - Gen0: {gc0}, Gen1: {gc1}, Gen2: {gc2}");
Console.WriteLine($"是否有待处理的终结器: {GC.GetTotalMemory(false) != GC.GetTotalMemory(true)}");
}
public static void MonitorGCActivity(Action action, string description)
{
PrintMemoryInfo($"执行前 - {description}");
var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
action();
stopwatch.Stop();
PrintMemoryInfo($"执行后 - {description}");
Console.WriteLine($"执行时间: {stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms\n");
}
// 🎯 实用的内存压力测试
public static void MemoryPressureTest()
{
MonitorGCActivity(() =>
{
var objects = new List<byte[]>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
objects.Add(new byte[1024 * 1024]); // 1MB
}
// 对象超出作用域,等待GC回收
}, "大量内存分配测试");
}
}
}
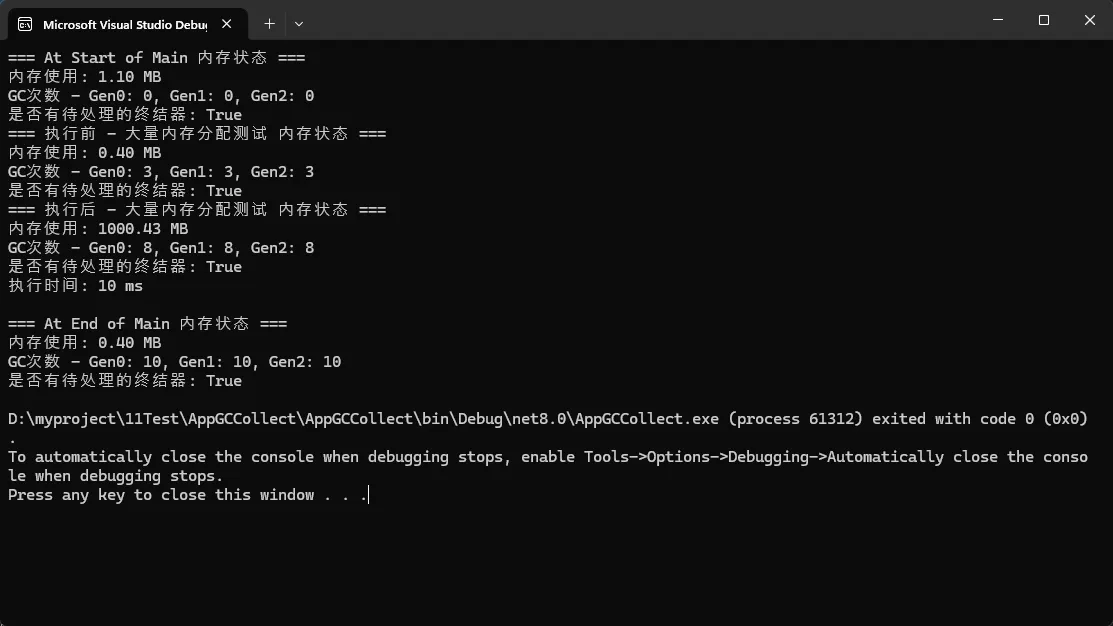
应用场景: 性能调优、内存泄漏诊断、系统监控
实用价值: 快速定位内存问题,验证优化效果
⚠️ 常见陷阱与解决方案
陷阱1:滥用GC.Collect()
c#// ❌ 错误做法
public void BadExample()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
ProcessData();
GC.Collect(); // 严重影响性能!
}
}
// ✅ 正确做法
public void GoodExample()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
ProcessData();
}
// 让GC自动管理,或在确实需要时才调用
}
陷阱2:忘记调用SuppressFinalize
c#// ❌ 错误的Dispose实现
public void Dispose()
{
_resource?.Dispose();
// 忘记调用SuppressFinalize,对象仍会进入终结队列
}
// ✅ 正确的Dispose实现
public void Dispose()
{
_resource?.Dispose();
GC.SuppressFinalize(this); // 🔥 关键步骤
}
🎯 最佳实践总结
基于实战经验,这里是三个核心要点:
- GC.SuppressFinalize是必需品 - 在实现IDisposable时必须调用,这能显著提升性能并避免内存泄漏[ref:14,16]
- GC.Collect是危险品 - 99%的情况下不要使用,让.NET的GC自动管理内存。只在特定场景(如内存测试、空闲期优化)才考虑使用[ref:15,18]
- 监控胜过猜测 - 使用内存诊断工具实际测量,而不是凭感觉优化内存管理[ref:18]
掌握这两个方法的正确使用方式,你的C#应用将在内存管理方面更加高效和稳定。记住:合理的资源管理设计比手动优化更重要!
💬 互动话题:
- 你在项目中遇到过哪些内存管理的棘手问题?
- 是否使用过其他内存优化技巧?欢迎在评论区分享经验!
觉得这篇文章对你有帮助?点赞收藏并转发给更多同行,让我们一起提升C#开发技能!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录