目录
你是否遇到过这样的场景:客户要求在Windows窗体上实现自定义绘图效果,比如绘制统计图表、自定义控件外观,或者实现图片的特殊处理?传统的控件已经无法满足需求,这时候你就需要掌握GDI+ 这个强大的图形绘制技术了。
作为.NET Framework的重要组成部分,GDI+(Graphics Device Interface Plus)为WinForm开发者提供了丰富的2D图形绘制能力。从简单的线条绘制到复杂的图像处理,GDI+都能轻松胜任。本文将从零开始,带你掌握GDI+的核心概念和实战技巧,让你的WinForm应用更加生动精彩!
💡 什么是GDI+?为什么要学它?
🔍 问题分析
很多C#开发者在面临以下场景时会感到困扰:
- 自定义控件外观:系统控件样式单一,无法满足UI设计需求
- 动态图表绘制:需要根据数据实时生成图表和统计图
- 图像处理需求:对图片进行缩放、裁剪、滤镜等操作
- 游戏开发基础:简单2D游戏的图形渲染
传统的控件拖拽式开发已经无法满足这些个性化需求,这时候掌握GDI+就显得尤为重要。
🎨 GDI+核心优势
GDI+ 是微软为.NET平台专门设计的图形API,相比传统GDI具有以下优势:
- 面向对象设计:更符合C#编程习惯
- 抗锯齿支持:图形更加平滑美观
- 丰富的绘制功能:支持渐变、纹理、Alpha混合
- 图像格式支持:原生支持PNG、JPEG、GIF等多种格式
🚀 GDI+基础概念详解
📐 Graphics类:绘图的核心
Graphics类是GDI+的核心,它代表了一个绘图表面。获取Graphics对象的三种常见方式:
c#// 在Paint事件中获取
private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
Graphics g = e.Graphics;
// 在这里进行绘制操作
}
c#// 通过控件创建
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
// 使用完后记得释放资源
g.Dispose();
c#// 通过图像创建(用于离线绘制)
Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap(800, 600);
Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(bitmap);
// 绘制完成后保存图像
bitmap.Save("output.png");
g.Dispose();
bitmap.Dispose();
⚠️ 重要提醒:Graphics对象是稀缺的系统资源,使用完毕后一定要调用Dispose()方法释放,或者使用using语句自动释放。
🖌️ Pen和Brush:绘图的画笔
Pen(钢笔) 用于绘制线条和形状边框:
c#private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
var g = e.Graphics;
// 创建不同样式的画笔
Pen redPen = new Pen(Color.Red, 2); // 红色,宽度2
Pen dashedPen = new Pen(Color.Blue, 1);
dashedPen.DashStyle = DashStyle.Dash; // 设置虚线样式
// 绘制矩形边框
g.DrawRectangle(redPen, 10, 10, 100, 50);
// 记得释放资源
redPen.Dispose();
dashedPen.Dispose();
}

Brush(画刷) 用于填充封闭区域:
c#private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
var g = e.Graphics;
// 实心画刷
SolidBrush solidBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.LightBlue);
// 渐变画刷
LinearGradientBrush gradientBrush = new LinearGradientBrush(
new Point(0, 0), new Point(100, 100),
Color.Red, Color.Blue);
// 填充矩形
g.FillRectangle(solidBrush, 10, 10, 100, 50);
g.FillRectangle(gradientBrush, 120, 10, 100, 50);
// 释放资源
solidBrush.Dispose();
gradientBrush.Dispose();
}

🎯 实战案例1:绘制动态数据图表
📊 需求场景
为销售管理系统绘制动态柱状图,根据实时数据展示各月份销售额。
c#using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;
namespace AppWinformDraw
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private int[] salesData = { 120, 150, 180, 200, 170, 220 };
private string[] months = { "1月", "2月", "3月", "4月", "5月", "6月" };
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.SetStyle(ControlStyles.AllPaintingInWmPaint |
ControlStyles.UserPaint |
ControlStyles.DoubleBuffer, true);
}
private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
Graphics g = e.Graphics;
g.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.AntiAlias; // 开启抗锯齿
// 绘制坐标轴
DrawAxes(g);
// 绘制柱状图
DrawBars(g);
// 绘制标题
DrawTitle(g);
}
private void DrawAxes(Graphics g)
{
using (Pen axisPen = new Pen(Color.Black, 2))
{
// X轴
g.DrawLine(axisPen, 50, 300, 450, 300);
// Y轴
g.DrawLine(axisPen, 50, 50, 50, 300);
}
}
private void DrawBars(Graphics g)
{
int maxValue = salesData.Max();
int barWidth = 50;
int spacing = 10;
using (SolidBrush barBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.SkyBlue))
using (SolidBrush textBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Black))
using (Font font = new Font("Arial", 10))
{
for (int i = 0; i < salesData.Length; i++)
{
int x = 70 + i * (barWidth + spacing);
int barHeight = (int)(salesData[i] * 200.0 / maxValue);
int y = 300 - barHeight;
// 绘制柱子
g.FillRectangle(barBrush, x, y, barWidth, barHeight);
// 绘制数值标签
string valueText = salesData[i].ToString();
SizeF textSize = g.MeasureString(valueText, font);
g.DrawString(valueText, font, textBrush,
x + (barWidth - textSize.Width) / 2, y - 20);
// 绘制月份标签
SizeF monthSize = g.MeasureString(months[i], font);
g.DrawString(months[i], font, textBrush,
x + (barWidth - monthSize.Width) / 2, 310);
}
}
}
private void DrawTitle(Graphics g)
{
using (Font titleFont = new Font("微软雅黑", 16, FontStyle.Bold))
using (SolidBrush titleBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.DarkBlue))
{
string title = "销售业绩统计图";
SizeF titleSize = g.MeasureString(title, titleFont);
float x = (this.Width - titleSize.Width) / 2;
g.DrawString(title, titleFont, titleBrush, x, 20);
}
}
}
}
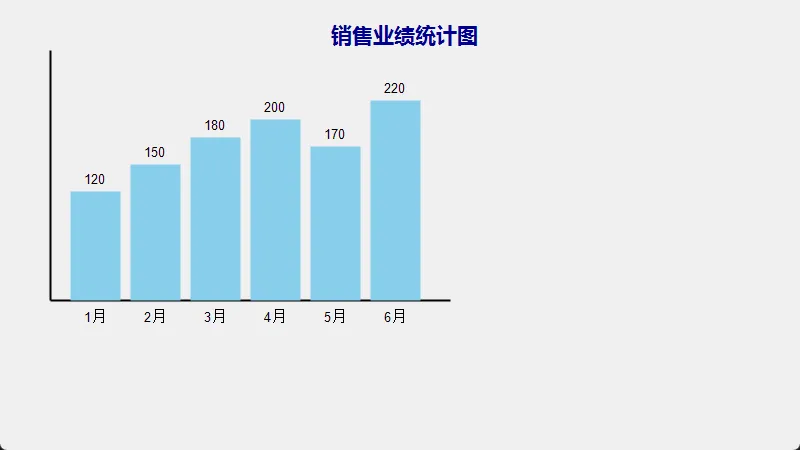
🎨 代码亮点解析
- 双缓冲技术:通过
SetStyle开启双缓冲,避免绘制时的闪烁 - 抗锯齿:使用
SmoothingMode.AntiAlias让图形更加平滑 - 资源管理:使用
using语句自动释放GDI+资源 - 动态计算:根据数据动态计算柱子高度和位置
- 注意,实际业务中,一般不会自己手动绘制,有对应的三方控件实现。
🎯 实战案例2:自定义按钮控件
🎨 需求场景
创建一个具有圆角、渐变背景和鼠标悬停效果的自定义按钮。
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppWinformDraw
{
public class CustomButton : Control
{
private bool isMouseOver = false;
private bool isPressed = false;
public CustomButton()
{
this.SetStyle(ControlStyles.AllPaintingInWmPaint |
ControlStyles.UserPaint |
ControlStyles.ResizeRedraw |
ControlStyles.SupportsTransparentBackColor, true);
this.Size = new Size(100, 35);
this.BackColor = Color.Transparent;
}
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e)
{
Graphics g = e.Graphics;
g.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.AntiAlias;
// 绘制按钮背景
DrawBackground(g);
// 绘制按钮文本
DrawText(g);
// 绘制边框
DrawBorder(g);
}
private void DrawBackground(Graphics g)
{
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, Width - 1, Height - 1);
using (GraphicsPath path = GetRoundRectPath(rect, 8))
{
Color startColor, endColor;
if (isPressed)
{
startColor = Color.FromArgb(100, 100, 100);
endColor = Color.FromArgb(150, 150, 150);
}
else if (isMouseOver)
{
startColor = Color.FromArgb(70, 130, 180);
endColor = Color.FromArgb(100, 149, 237);
}
else
{
startColor = Color.FromArgb(65, 105, 225);
endColor = Color.FromArgb(30, 144, 255);
}
using (LinearGradientBrush brush = new LinearGradientBrush(
rect, startColor, endColor, LinearGradientMode.Vertical))
{
g.FillPath(brush, path);
}
}
}
private void DrawText(Graphics g)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(Text))
{
using (SolidBrush brush = new SolidBrush(ForeColor))
{
StringFormat sf = new StringFormat();
sf.Alignment = StringAlignment.Center;
sf.LineAlignment = StringAlignment.Center;
Rectangle textRect = new Rectangle(0, 0, Width, Height);
g.DrawString(Text, Font, brush, textRect, sf);
}
}
}
private void DrawBorder(Graphics g)
{
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, Width - 1, Height - 1);
using (GraphicsPath path = GetRoundRectPath(rect, 8))
using (Pen pen = new Pen(Color.FromArgb(40, 40, 40), 1))
{
g.DrawPath(pen, path);
}
}
private GraphicsPath GetRoundRectPath(Rectangle rect, int radius)
{
GraphicsPath path = new GraphicsPath();
int diameter = radius * 2;
// 左上角
path.AddArc(rect.X, rect.Y, diameter, diameter, 180, 90);
// 右上角
path.AddArc(rect.Right - diameter, rect.Y, diameter, diameter, 270, 90);
// 右下角
path.AddArc(rect.Right - diameter, rect.Bottom - diameter, diameter, diameter, 0, 90);
// 左下角
path.AddArc(rect.X, rect.Bottom - diameter, diameter, diameter, 90, 90);
path.CloseAllFigures();
return path;
}
protected override void OnMouseEnter(EventArgs e)
{
isMouseOver = true;
Invalidate();
base.OnMouseEnter(e);
}
protected override void OnMouseLeave(EventArgs e)
{
isMouseOver = false;
isPressed = false;
Invalidate();
base.OnMouseLeave(e);
}
protected override void OnMouseDown(MouseEventArgs e)
{
isPressed = true;
Invalidate();
base.OnMouseDown(e);
}
protected override void OnMouseUp(MouseEventArgs e)
{
isPressed = false;
Invalidate();
base.OnMouseUp(e);
}
}
}
🎨 技术要点
- GraphicsPath:用于创建复杂的几何形状,实现圆角效果
- 状态管理:通过鼠标事件管理按钮的不同视觉状态
- 渐变效果:使用LinearGradientBrush创建专业的渐变背景
- 性能优化:只在状态改变时调用Invalidate()重绘
🎯 实战案例3:图像处理工具
🖼️ 需求场景
实现图像的缩放、旋转和滤镜效果处理。
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppWinformDraw
{
public class ImageProcessor
{
public static Bitmap ResizeImage(Image originalImage, int newWidth, int newHeight)
{
Bitmap resizedImage = new Bitmap(newWidth, newHeight);
using (Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(resizedImage))
{
// 设置高质量绘制模式
g.InterpolationMode = InterpolationMode.HighQualityBicubic;
g.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.HighQuality;
g.PixelOffsetMode = PixelOffsetMode.HighQuality;
g.CompositingQuality = CompositingQuality.HighQuality;
// 绘制缩放后的图像
g.DrawImage(originalImage, 0, 0, newWidth, newHeight);
}
return resizedImage;
}
public static Bitmap RotateImage(Image originalImage, float angle)
{
double radians = angle * Math.PI / 180;
double cos = Math.Abs(Math.Cos(radians));
double sin = Math.Abs(Math.Sin(radians));
int newWidth = (int)(originalImage.Width * cos + originalImage.Height * sin);
int newHeight = (int)(originalImage.Width * sin + originalImage.Height * cos);
Bitmap rotatedImage = new Bitmap(newWidth, newHeight);
using (Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(rotatedImage))
{
g.InterpolationMode = InterpolationMode.HighQualityBicubic;
g.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.HighQuality;
g.TranslateTransform(newWidth / 2f, newHeight / 2f);
g.RotateTransform(angle);
g.DrawImage(originalImage,
-originalImage.Width / 2f,
-originalImage.Height / 2f);
}
return rotatedImage;
}
public static Bitmap ApplyGrayscaleFilter(Image originalImage)
{
Bitmap grayscaleImage = new Bitmap(originalImage.Width, originalImage.Height);
// 创建颜色矩阵实现灰度转换
ColorMatrix colorMatrix = new ColorMatrix(new float[][]
{
new float[] {0.299f, 0.299f, 0.299f, 0, 0},
new float[] {0.587f, 0.587f, 0.587f, 0, 0},
new float[] {0.114f, 0.114f, 0.114f, 0, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, 0, 0, 1}
});
ImageAttributes attributes = new ImageAttributes();
attributes.SetColorMatrix(colorMatrix);
using (Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(grayscaleImage))
{
g.DrawImage(originalImage,
new Rectangle(0, 0, originalImage.Width, originalImage.Height),
0, 0, originalImage.Width, originalImage.Height,
GraphicsUnit.Pixel, attributes);
}
return grayscaleImage;
}
public static Bitmap AddWatermark(Image originalImage, string watermarkText)
{
Bitmap watermarkedImage = new Bitmap(originalImage);
using (Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(watermarkedImage))
{
g.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.AntiAlias;
using (Font watermarkFont = new Font("Arial", 20, FontStyle.Bold))
using (SolidBrush watermarkBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.FromArgb(128, Color.White)))
{
// 计算水印位置(右下角)
SizeF textSize = g.MeasureString(watermarkText, watermarkFont);
float x = originalImage.Width - textSize.Width - 10;
float y = originalImage.Height - textSize.Height - 10;
// 绘制水印文本
g.DrawString(watermarkText, watermarkFont, watermarkBrush, x, y);
}
}
return watermarkedImage;
}
}
}

⚠️ 常见坑点与最佳实践
🔧 性能优化要点
- 及时释放资源
c#// ❌ 错误做法 - 忘记释放资源
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
g.DrawString("Hello", this.Font, Brushes.Black, 0, 0);
// 忘记调用 g.Dispose()
// ✅ 正确做法 - 使用using语句
using (Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics())
{
g.DrawString("Hello", this.Font, Brushes.Black, 0, 0);
} // 自动释放资源
- 避免在循环中创建对象
c#// ❌ 错误做法
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Pen pen = new Pen(Color.Red); // 每次循环都创建新对象
g.DrawLine(pen, 0, i, 100, i);
pen.Dispose();
}
// ✅ 正确做法
using (Pen pen = new Pen(Color.Red))
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
g.DrawLine(pen, 0, i, 100, i); // 重复使用同一个对象
}
}
- 合理使用缓存
c#// 缓存经常使用的画刷和画笔
private static readonly SolidBrush CachedBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Blue);
private static readonly Pen CachedPen = new Pen(Color.Red, 2);
🎯 核心要点总结
通过本文的学习,我们掌握了GDI+的三个核心要点:
- 基础概念掌握:理解Graphics、Pen、Brush等核心类的作用和用法,这是所有绘图操作的基础
- 实战应用能力:学会绘制图表、自定义控件、图像处理等实用技能,满足实际项目需求
- 性能优化意识:掌握资源管理、对象复用等最佳实践,避免内存泄漏和性能问题
GDI+为WinForm开发者打开了图形编程的大门。无论是企业级应用的数据可视化,还是个性化界面的定制开发,掌握这些技能都会让你的作品脱颖而出。记住:好的用户体验往往来自于这些看似细微的视觉细节!
💬 互动讨论:你在项目中遇到过哪些有趣的绘图需求?或者在使用GDI+时踩过什么坑?欢迎在评论区分享你的经验!
🔥 觉得文章对你有帮助?请点赞收藏并转发给更多C#开发同行,让我们一起提升开发技能!
注
通过网盘分享的文件:AppWinformDraw.zip 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Gw9HPC4erU9DDwgNyJWWng?pwd=ibm6 提取码: ibm6 --来自百度网盘超级会员v9的分享
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!