目录
作为一名有着多年WinForm开发经验的C#程序员,当你第一次接触WPF时,是否被依赖属性这个概念搞得一头雾水?别担心,你不是一个人在战斗!
从WinForm的简单属性到WPF的依赖属性,这不仅仅是语法的改变,更是开发思维的转换。依赖属性是WPF数据绑定、样式、动画等核心功能的基础,掌握它的注册机制,就像拿到了WPF世界的通行证。
本文将从WinForm开发者的视角,用最接地气的方式带你搞定依赖属性注册,让你的WPF转型之路更加顺畅!
🤔 为什么WinForm属性不够用了?
WinForm vs WPF:属性机制的根本差异
在WinForm中,我们习惯了这样的属性定义:
C#// WinForm中的普通属性
public partial class MyControl : UserControl
{
private string _myText;
public string MyText
{
get { return _myText; }
set
{
_myText = value;
// 手动刷新界面
this.Invalidate();
}
}
}
但在WPF中,这种方式存在几个致命问题:
- 无法支持数据绑定
- 不支持样式设置
- 无法参与动画系统
- 缺乏属性值继承机制
WPF的依赖属性就是为了解决这些问题而生的!
🎯 依赖属性注册的三种实战场景
📌 场景一:基础依赖属性注册
最常见的场景就是为自定义控件添加可绑定的属性。
C#using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace AppDependencyProperty
{
public class CustomButton : Button
{
// 依赖属性注册
public static readonly DependencyProperty CustomTextProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
"CustomText",
typeof(string),
typeof(CustomButton),
new PropertyMetadata("默认文本", OnCustomTextChanged));
// CLR包装器
public string CustomText
{
get { return (string)GetValue(CustomTextProperty); }
set { SetValue(CustomTextProperty, value); }
}
// 属性变化回调
private static void OnCustomTextChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var control = (CustomButton)d;
control.Content = e.NewValue; // 直接更新按钮内容
}
public CustomButton()
{
// 设置初始内容
this.Content = this.CustomText;
}
}
}
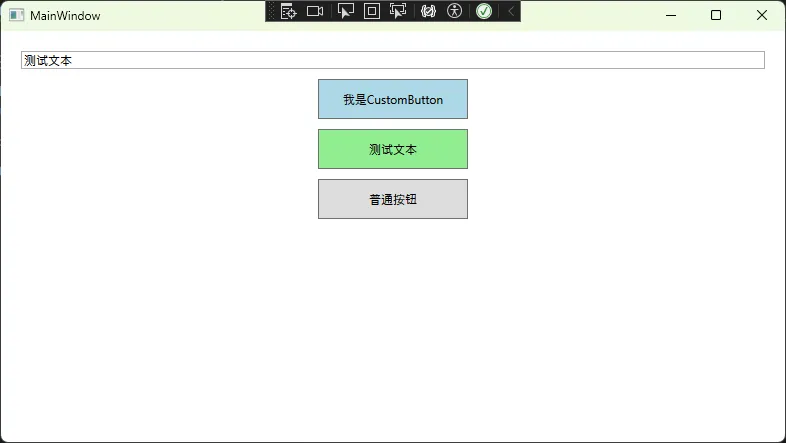
XML<Window x:Class="AppDependencyProperty.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDependencyProperty"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<!-- 原有的TextBox -->
<TextBox x:Name="textBox" Text="测试文本" Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<!-- 使用自定义的CustomButton -->
<local:CustomButton CustomText="我是CustomButton"
Width="150" Height="40"
Margin="0,0,0,10"
Background="LightBlue"/>
<!-- 绑定到TextBox的CustomButton -->
<local:CustomButton CustomText="{Binding ElementName=textBox, Path=Text}"
Width="150" Height="40"
Margin="0,0,0,10"
Background="LightGreen"/>
<!-- 原有的普通按钮 -->
<Button Content="普通按钮" Width="150" Height="40"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
🚨 新手常踩的坑:
- 忘记添加
static readonly修饰符 - 属性名和注册名不一致
- 回调方法不是静态的
📌 场景二:带验证的依赖属性
实际项目中,我们经常需要对属性值进行验证:
C#using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace AppDependencyProperty
{
public partial class RangeSlider : UserControl
{
#region 依赖属性定义
// MinValue属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty MinValueProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
"MinValue",
typeof(double),
typeof(RangeSlider),
new PropertyMetadata(0.0, OnMinValueChanged, CoerceMinValue),
ValidateMinValue);
// MaxValue属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty MaxValueProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
"MaxValue",
typeof(double),
typeof(RangeSlider),
new PropertyMetadata(100.0, OnMaxValueChanged, CoerceMaxValue),
ValidateMaxValue);
// CurrentValue属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty CurrentValueProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
"CurrentValue",
typeof(double),
typeof(RangeSlider),
new PropertyMetadata(50.0, OnCurrentValueChanged, CoerceCurrentValue));
#endregion
#region CLR属性包装器
public double MinValue
{
get { return (double)GetValue(MinValueProperty); }
set { SetValue(MinValueProperty, value); }
}
public double MaxValue
{
get { return (double)GetValue(MaxValueProperty); }
set { SetValue(MaxValueProperty, value); }
}
public double CurrentValue
{
get { return (double)GetValue(CurrentValueProperty); }
set { SetValue(CurrentValueProperty, value); }
}
#endregion
#region 验证回调
private static bool ValidateMinValue(object value)
{
double doubleValue = (double)value;
return !double.IsNaN(doubleValue) && !double.IsInfinity(doubleValue);
}
private static bool ValidateMaxValue(object value)
{
double doubleValue = (double)value;
return !double.IsNaN(doubleValue) && !double.IsInfinity(doubleValue);
}
#endregion
#region 强制回调
private static object CoerceMinValue(DependencyObject d, object baseValue)
{
var slider = d as RangeSlider;
double value = (double)baseValue;
// 确保MinValue不超过MaxValue
if (slider != null && value > slider.MaxValue)
{
return slider.MaxValue;
}
return Math.Max(0, value); // 最小值不能小于0
}
private static object CoerceMaxValue(DependencyObject d, object baseValue)
{
var slider = d as RangeSlider;
double value = (double)baseValue;
// 确保MaxValue不小于MinValue
if (slider != null && value < slider.MinValue)
{
return slider.MinValue;
}
return value;
}
private static object CoerceCurrentValue(DependencyObject d, object baseValue)
{
var slider = d as RangeSlider;
double value = (double)baseValue;
if (slider != null)
{
// 确保CurrentValue在MinValue和MaxValue之间
return Math.Max(slider.MinValue, Math.Min(slider.MaxValue, value));
}
return value;
}
#endregion
#region 属性变化回调
private static void OnMinValueChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var slider = d as RangeSlider;
slider?.UpdateSliderRange();
// 重新强制CurrentValue以确保在有效范围内
slider?.CoerceValue(CurrentValueProperty);
}
private static void OnMaxValueChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var slider = d as RangeSlider;
slider?.UpdateSliderRange();
// 重新强制CurrentValue以确保在有效范围内
slider?.CoerceValue(CurrentValueProperty);
}
private static void OnCurrentValueChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var slider = d as RangeSlider;
slider?.UpdateCurrentValue();
}
#endregion
#region 构造函数和初始化
public RangeSlider()
{
InitializeComponent();
UpdateSliderRange();
}
#endregion
#region 私有方法
private void UpdateSliderRange()
{
// 更新UI显示
if (mainSlider != null)
{
mainSlider.Minimum = MinValue;
mainSlider.Maximum = MaxValue;
}
UpdateDisplayText();
Console.WriteLine($"范围更新: {MinValue:F1} - {MaxValue:F1}");
}
private void UpdateCurrentValue()
{
if (mainSlider != null)
{
mainSlider.Value = CurrentValue;
}
UpdateDisplayText();
}
private void UpdateDisplayText()
{
if (displayText != null)
{
displayText.Text = $"范围: {MinValue:F1} - {MaxValue:F1}, 当前值: {CurrentValue:F1}";
}
}
#endregion
#region 事件处理
private void MainSlider_ValueChanged(object sender, RoutedPropertyChangedEventArgs<double> e)
{
// 更新CurrentValue属性
CurrentValue = e.NewValue;
}
#endregion
}
}
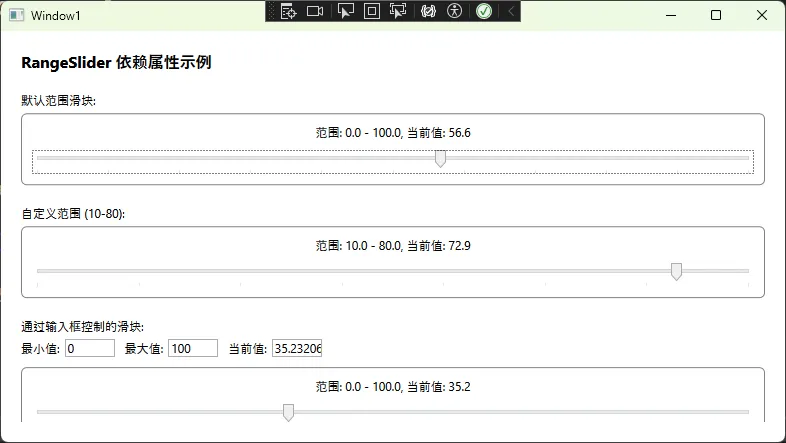
XML<UserControl x:Class="AppDependencyProperty.RangeSlider"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDependencyProperty"
mc:Ignorable="d"
d:DesignHeight="450" d:DesignWidth="800">
<Border BorderBrush="Gray" BorderThickness="1" CornerRadius="5" Padding="10">
<StackPanel>
<!-- 显示文本 -->
<TextBlock x:Name="displayText"
Text="范围: 0.0 - 100.0, 当前值: 50.0"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<!-- 主滑块 -->
<Slider x:Name="mainSlider"
Minimum="0"
Maximum="100"
Value="50"
ValueChanged="MainSlider_ValueChanged"
TickPlacement="BottomRight"
TickFrequency="10"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</UserControl>
📌 场景三:附加属性注册(最容易忽视但很强大)
附加属性让你可以为任何对象添加属性,这在布局和行为设计中极其有用:
C#using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace AppDependencyProperty
{
public static class GridHelper
{
#region AutoRow 附加属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty AutoRowProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached(
"AutoRow",
typeof(bool),
typeof(GridHelper),
new PropertyMetadata(false, OnAutoRowChanged));
public static bool GetAutoRow(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (bool)obj.GetValue(AutoRowProperty);
}
public static void SetAutoRow(DependencyObject obj, bool value)
{
obj.SetValue(AutoRowProperty, value);
}
private static void OnAutoRowChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (d is Grid grid && (bool)e.NewValue)
{
// 如果Grid已经加载,立即分配
if (grid.IsLoaded)
{
AutoAssignRows(grid);
}
else
{
// 等待Grid加载后再分配
grid.Loaded += (s, args) => AutoAssignRows(grid);
}
}
}
private static void AutoAssignRows(Grid grid)
{
// 自动创建足够的行定义
while (grid.RowDefinitions.Count < grid.Children.Count)
{
grid.RowDefinitions.Add(new RowDefinition { Height = GridLength.Auto });
}
// 为Grid的子元素自动分配行号
for (int i = 0; i < grid.Children.Count; i++)
{
Grid.SetRow(grid.Children[i], i);
}
}
#endregion
#region AutoColumn 附加属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty AutoColumnProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached(
"AutoColumn",
typeof(bool),
typeof(GridHelper),
new PropertyMetadata(false, OnAutoColumnChanged));
public static bool GetAutoColumn(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (bool)obj.GetValue(AutoColumnProperty);
}
public static void SetAutoColumn(DependencyObject obj, bool value)
{
obj.SetValue(AutoColumnProperty, value);
}
private static void OnAutoColumnChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (d is Grid grid && (bool)e.NewValue)
{
if (grid.IsLoaded)
{
AutoAssignColumns(grid);
}
else
{
grid.Loaded += (s, args) => AutoAssignColumns(grid);
}
}
}
private static void AutoAssignColumns(Grid grid)
{
// 自动创建足够的列定义
while (grid.ColumnDefinitions.Count < grid.Children.Count)
{
grid.ColumnDefinitions.Add(new ColumnDefinition { Width = GridLength.Auto });
}
// 为Grid的子元素自动分配列号
for (int i = 0; i < grid.Children.Count; i++)
{
Grid.SetColumn(grid.Children[i], i);
}
}
#endregion
#region ShowGridLines 附加属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty ShowGridLinesProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached(
"ShowGridLines",
typeof(bool),
typeof(GridHelper),
new PropertyMetadata(false, OnShowGridLinesChanged));
public static bool GetShowGridLines(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (bool)obj.GetValue(ShowGridLinesProperty);
}
public static void SetShowGridLines(DependencyObject obj, bool value)
{
obj.SetValue(ShowGridLinesProperty, value);
}
private static void OnShowGridLinesChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (d is Grid grid)
{
grid.ShowGridLines = (bool)e.NewValue;
}
}
#endregion
#region 手动刷新方法
/// <summary>
/// 手动刷新Grid布局
/// </summary>
public static void RefreshLayout(Grid grid)
{
if (GetAutoRow(grid))
{
AutoAssignRows(grid);
}
if (GetAutoColumn(grid))
{
AutoAssignColumns(grid);
}
}
#endregion
}
}
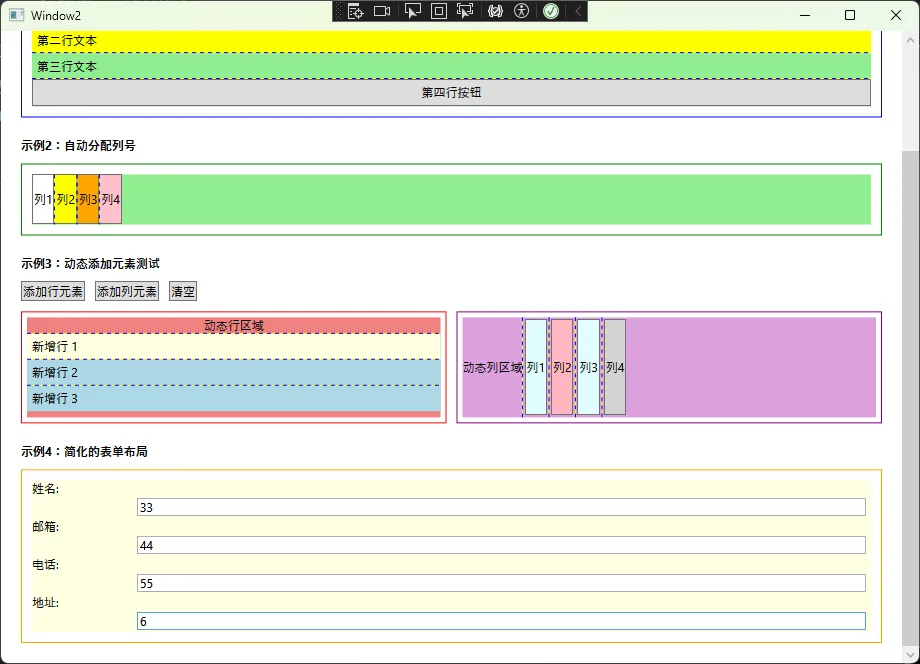
XAML中的使用:
XML<Window x:Class="AppDependencyProperty.Window2"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDependencyProperty"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window2" Height="450" Width="800">
<ScrollViewer>
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<TextBlock Text="GridHelper 附加属性示例"
FontSize="18" FontWeight="Bold"
Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<!-- 示例1:自动行号 -->
<TextBlock Text="示例1:自动分配行号" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<Border BorderBrush="Blue" BorderThickness="1" Padding="10" Margin="0,0,0,20">
<Grid local:GridHelper.AutoRow="True"
local:GridHelper.ShowGridLines="True"
Background="LightBlue">
<TextBlock Text="第一行文本" Background="White" Padding="5"/>
<TextBlock Text="第二行文本" Background="Yellow" Padding="5"/>
<TextBlock Text="第三行文本" Background="LightGreen" Padding="5"/>
<Button Content="第四行按钮" Padding="5"/>
</Grid>
</Border>
<!-- 示例2:自动列号 -->
<TextBlock Text="示例2:自动分配列号" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<Border BorderBrush="Green" BorderThickness="1" Padding="10" Margin="0,0,0,20">
<Grid local:GridHelper.AutoColumn="True"
local:GridHelper.ShowGridLines="True"
Background="LightGreen"
Height="50">
<Button Content="列1" Background="White"/>
<Button Content="列2" Background="Yellow"/>
<Button Content="列3" Background="Orange"/>
<Button Content="列4" Background="Pink"/>
</Grid>
</Border>
<!-- 示例3:动态添加元素 -->
<TextBlock Text="示例3:动态添加元素测试" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="0,0,0,10">
<Button x:Name="addRowButton" Content="添加行元素" Click="AddRowElement_Click" Margin="0,0,10,0"/>
<Button x:Name="addColumnButton" Content="添加列元素" Click="AddColumnElement_Click" Margin="0,0,10,0"/>
<Button x:Name="clearButton" Content="清空" Click="Clear_Click"/>
</StackPanel>
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<!-- 动态行Grid -->
<Border Grid.Column="0" BorderBrush="Red" BorderThickness="1" Padding="5" Margin="0,0,5,0">
<Grid x:Name="dynamicRowGrid"
local:GridHelper.AutoRow="True"
local:GridHelper.ShowGridLines="True"
Background="LightCoral"
MinHeight="100">
<TextBlock Text="动态行区域" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</Grid>
</Border>
<!-- 动态列Grid -->
<Border Grid.Column="1" BorderBrush="Purple" BorderThickness="1" Padding="5" Margin="5,0,0,0">
<Grid x:Name="dynamicColumnGrid"
local:GridHelper.AutoColumn="True"
local:GridHelper.ShowGridLines="True"
Background="Plum"
Height="100">
<TextBlock Text="动态列区域" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</Grid>
</Border>
</Grid>
<!-- 示例4:表单布局 -->
<TextBlock Text="示例4:简化的表单布局" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,20,0,10"/>
<Border BorderBrush="Orange" BorderThickness="1" Padding="10">
<Grid local:GridHelper.AutoRow="True" Background="LightYellow">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="100"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<!-- 不需要手动设置Grid.Row,会自动分配 -->
<TextBlock Text="姓名:" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="5,2"/>
<TextBlock Text="邮箱:" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="5,2"/>
<TextBlock Text="电话:" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="5,2"/>
<TextBlock Text="地址:" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="5,2"/>
</Grid>
</Border>
</StackPanel>
</ScrollViewer>
</Window>
🚨 避开这些常见陷阱
1. 线程安全问题
C#// ❌ 错误:在非UI线程中直接设置依赖属性
private void BackgroundWorker_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
MyProperty = "新值"; // 可能抛出异常
}
// ✅ 正确:使用Dispatcher
private void BackgroundWorker_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
Dispatcher.Invoke(() => MyProperty = "新值");
}
2. 内存泄漏风险
C#// ❌ 错误:静态回调中持有实例引用
private static void OnPropertyChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var control = d as MyControl;
someStaticList.Add(control); // 可能导致内存泄漏
}
// ✅ 正确:使用弱引用或及时清理
private static void OnPropertyChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var control = d as MyControl;
control?.HandlePropertyChange(); // 不保存引用
}
🎯 总结:从WinForm到WPF的华丽转身
通过本文的学习,你已经掌握了依赖属性注册的核心技能:
🔑 三个关键要点:
- 理解本质:依赖属性不是简单的属性升级,而是WPF数据绑定和UI系统的基石
- 掌握模式:Register、RegisterAttached、RegisterReadOnly三种注册方式各有用武之地
- 注重细节:验证回调、强制回调、线程安全等细节决定了代码质量
💪 实战建议:
- 先从简单的依赖属性开始练手
- 逐步添加验证和回调逻辑
- 多研究WPF内置控件的依赖属性实现
从WinForm到WPF的转型路上,依赖属性是你必须跨越的第一道门槛。一旦掌握,你会发现WPF开发的世界如此精彩!
🤝 互动时间:
- 你在从WinForm转WPF的过程中,遇到过哪些让你印象深刻的问题?
- 除了本文提到的场景,你还在哪些地方用到了依赖属性?
觉得这篇文章对你的WPF学习有帮助吗?请转发给更多正在转型路上的同行,让我们一起在C#开发的道路上越走越远! 🚀
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录