目录
你是否在WPF开发中遇到过这样的困惑:为什么有些属性支持数据绑定,而有些却不行?为什么WPF控件的属性看起来如此"神奇",能够自动响应变化?这背后的秘密就在于WPF的依赖属性系统。
作为WPF的核心特性之一,依赖属性(Dependency Property)与传统的CLR属性有着本质的不同。理解这两者的区别,不仅能帮你解决数据绑定、样式设置等常见问题,更能让你的WPF应用程序性能更优、功能更强大。
本文将通过实战代码和深度分析,带你彻底搞懂依赖属性系统的工作原理与应用场景。
🔍 问题分析:为什么需要依赖属性?
传统CLR属性的局限性
传统的C#属性本质上是对字段的封装,存在以下限制:
- 无法支持数据绑定:WPF的双向绑定机制需要属性具备变化通知能力
- 缺乏值优先级:无法处理样式、模板、继承等多种值来源的优先级
- 内存占用大:每个对象都需要存储所有属性的值
- 缺乏元数据支持:无法提供验证、强制转换等扩展功能
WPF的解决方案:依赖属性系统
依赖属性通过以下机制解决了这些问题:
- 属性系统:统一管理属性值的存储和获取
- 值优先级:支持本地值、样式、模板等多层级值源
- 变化通知:内置PropertyChanged机制
- 内存优化:稀疏存储,只存储被设置的属性值
💡 核心区别深度解析
🔥 1. 定义方式的根本不同
传统CLR属性定义:
C#public class TraditionalControl : Control
{
private string _title;
public string Title
{
get { return _title; }
set
{
_title = value;
// 需要手动触发PropertyChanged
}
}
}
依赖属性定义:
C#public class ModernControl : Control
{
// 1. 注册依赖属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty TitleProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
nameof(Title), // 属性名
typeof(string), // 属性类型
typeof(ModernControl), // 所有者类型
new PropertyMetadata( // 元数据
string.Empty, // 默认值
OnTitleChanged, // 变化回调
CoerceTitle // 值强制转换
));
// 2. 提供CLR包装器
public string Title
{
get { return (string)GetValue(TitleProperty); }
set { SetValue(TitleProperty, value); }
}
// 3. 属性变化回调
private static void OnTitleChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var control = (ModernControl)d;
// 处理属性变化逻辑
control.OnTitleChanged((string)e.OldValue, (string)e.NewValue);
}
// 4. 值强制转换
private static object CoerceTitle(DependencyObject d, object value)
{
// 确保Title不为null
return value ?? string.Empty;
}
protected virtual void OnTitleChanged(string oldValue, string newValue)
{
// 子类可重写此方法
}
}
🚀 2. 数据绑定支持
传统属性的绑定问题:
C#public class StudentViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string _name;
public string Name
{
get { return _name; }
set
{
if (_name != value)
{
_name = value;
// 必须手动实现PropertyChanged
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this,
new PropertyChangedEventArgs(nameof(Name)));
}
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
}
依赖属性的自动绑定:
XML<Window x:Class="AppDependentPropertiesThan.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDependentPropertiesThan"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.Resources>
<Style TargetType="{x:Type local:ModernControl}">
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type local:ModernControl}">
<Border Background="LightBlue"
BorderBrush="DarkBlue"
BorderThickness="2"
CornerRadius="5"
Padding="10">
<TextBlock Text="{TemplateBinding Title}"
FontSize="16"
FontWeight="Bold"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</Border>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
</Window.Resources>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<local:ModernControl Title="{Binding Name}" Grid.Row="0" />
</Grid>
</Window>
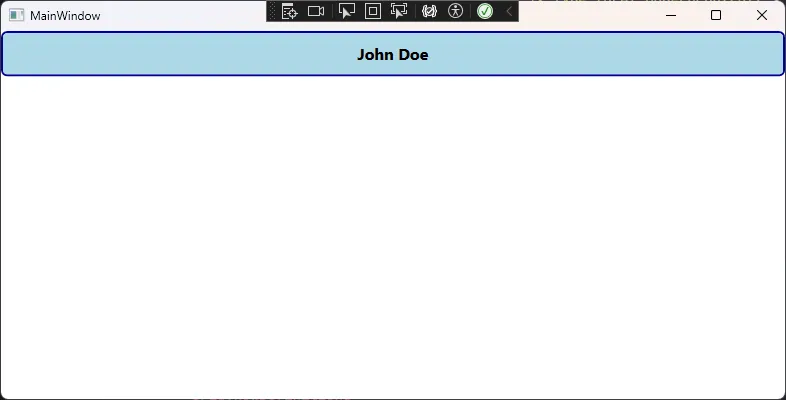
🎨 3. 样式和模板支持
依赖属性的样式支持:
XML<Style TargetType="{x:Type local:ModernControl}">
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type local:ModernControl}">
<Border Background="LightBlue"
BorderBrush="DarkBlue"
BorderThickness="2"
CornerRadius="5"
Padding="10">
<TextBlock Text="{TemplateBinding Title}"
FontSize="16"
FontWeight="Bold"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</Border>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
值优先级演示:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppDependentPropertiesThan
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for Window1.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class Window1 : Window
{
private ModernControl demoControl;
public Window1()
{
InitializeComponent();
StartValuePriorityDemo();
}
private void StartValuePriorityDemo()
{
Debug.WriteLine("=== 依赖属性值优先级演示 ===");
// 清除之前的控件
ControlContainer.Children.Clear();
// 创建新的控件实例
demoControl = new ModernControl();
ControlContainer.Children.Add(demoControl);
// 1. 默认值(优先级最低)
Debug.WriteLine($"1. 默认值: '{demoControl.Title}'");
// 等待一下,让UI更新
Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(new Action(() =>
{
// 2. 应用样式后的值
Debug.WriteLine($"2. 应用样式后: '{demoControl.Title}'");
// 3. 设置本地值(优先级最高)
demoControl.Title = "本地设置的标题";
Debug.WriteLine($"3. 设置本地值后: '{demoControl.Title}'");
// 4. 检查值的来源
var valueSource = DependencyPropertyHelper.GetValueSource(demoControl, ModernControl.TitleProperty);
Debug.WriteLine($"4. 当前值来源: {valueSource.BaseValueSource}");
}), System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.Loaded);
}
private void RestartDemo_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
StartValuePriorityDemo();
}
private void SetLocalValue_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (demoControl != null)
{
demoControl.Title = $"新的本地值 - {DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}";
var valueSource = DependencyPropertyHelper.GetValueSource(demoControl, ModernControl.TitleProperty);
Debug.WriteLine($"设置本地值后 - 值: '{demoControl.Title}', 来源: {valueSource.BaseValueSource}");
}
}
private void ClearLocalValue_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (demoControl != null)
{
// 清除本地值
demoControl.ClearValue(ModernControl.TitleProperty);
var valueSource = DependencyPropertyHelper.GetValueSource(demoControl, ModernControl.TitleProperty);
Debug.WriteLine($"清除本地值后 - 值: '{demoControl.Title}', 来源: {valueSource.BaseValueSource}");
}
}
}
}
⚡ 4. 内存优化机制
传统属性的内存使用:
C#public class TraditionalButton : Control
{
// 每个实例都会分配这些字段的内存
private string _text;
private Brush _background;
private double _fontSize;
private FontWeight _fontWeight;
// ... 更多属性字段
// 即使使用默认值,内存依然被占用
}
依赖属性的稀疏存储:
C#public class OptimizedButton : Control
{
// 只有静态的依赖属性标识符
public static readonly DependencyProperty TextProperty = ...;
public static readonly DependencyProperty BackgroundProperty = ...;
// 实际值存储在DependencyObject的内部字典中
// 只有被显式设置的属性才占用内存
public void DemonstrateMemoryOptimization()
{
var button1 = new OptimizedButton();
var button2 = new OptimizedButton();
// button1和button2共享默认值,不占用额外内存
// 只有当设置了不同的值时,才会分配存储空间
button1.SetValue(TextProperty, "点击我");
// 现在button1才为Text属性分配了内存
}
}
🛠️ 实战应用场景
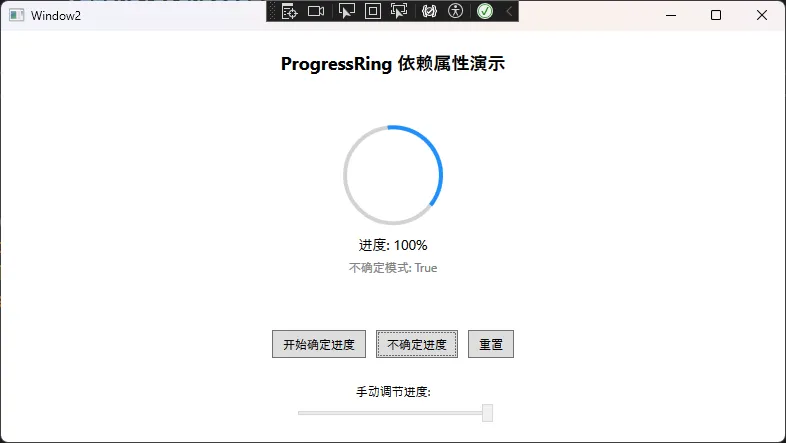
🎯 场景1:自定义控件开发
C#public class ProgressRing : Control
{
static ProgressRing()
{
DefaultStyleKeyProperty.OverrideMetadata(
typeof(ProgressRing),
new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(typeof(ProgressRing)));
}
#region 依赖属性定义
// Progress属性 - 支持动画
public static readonly DependencyProperty ProgressProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
nameof(Progress),
typeof(double),
typeof(ProgressRing),
new PropertyMetadata(0.0, OnProgressChanged, CoerceProgress));
public double Progress
{
get { return (double)GetValue(ProgressProperty); }
set { SetValue(ProgressProperty, value); }
}
private static object CoerceProgress(DependencyObject d, object value)
{
double progress = (double)value;
return Math.Max(0, Math.Min(100, progress)); // 限制在0-100之间
}
private static void OnProgressChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var ring = (ProgressRing)d;
ring.UpdateVisualState();
}
// IsIndeterminate属性 - 控制是否显示不确定进度
public static readonly DependencyProperty IsIndeterminateProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
nameof(IsIndeterminate),
typeof(bool),
typeof(ProgressRing),
new PropertyMetadata(false, OnIsIndeterminateChanged));
public bool IsIndeterminate
{
get { return (bool)GetValue(IsIndeterminateProperty); }
set { SetValue(IsIndeterminateProperty, value); }
}
private static void OnIsIndeterminateChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var ring = (ProgressRing)d;
ring.UpdateVisualState();
}
#endregion
private void UpdateVisualState()
{
if (IsIndeterminate)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(this, "Indeterminate", true);
}
else
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(this, "Determinate", true);
// 更新进度显示
}
}
}
XAML使用:
XML<local:ProgressRing Progress="{Binding LoadingProgress}"
IsIndeterminate="{Binding IsLoading}" />
🔄 场景2:附加属性实现
C#public static class TextHelper
{
// 附加属性:为任意控件添加水印功能
public static readonly DependencyProperty WatermarkProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached(
"Watermark",
typeof(string),
typeof(TextHelper),
new PropertyMetadata(null, OnWatermarkChanged));
public static string GetWatermark(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (string)obj.GetValue(WatermarkProperty);
}
public static void SetWatermark(DependencyObject obj, string value)
{
obj.SetValue(WatermarkProperty, value);
}
private static void OnWatermarkChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (d is TextBox textBox)
{
if (e.NewValue != null)
{
textBox.GotFocus += OnTextBoxGotFocus;
textBox.LostFocus += OnTextBoxLostFocus;
UpdateWatermark(textBox);
}
else
{
textBox.GotFocus -= OnTextBoxGotFocus;
textBox.LostFocus -= OnTextBoxLostFocus;
}
}
}
private static void OnTextBoxGotFocus(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
UpdateWatermark((TextBox)sender);
}
private static void OnTextBoxLostFocus(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
UpdateWatermark((TextBox)sender);
}
private static void UpdateWatermark(TextBox textBox)
{
var watermark = GetWatermark(textBox);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(textBox.Text) && !textBox.IsFocused)
{
textBox.Text = watermark;
textBox.Foreground = Brushes.Gray;
}
else if (textBox.Text == watermark && textBox.IsFocused)
{
textBox.Text = string.Empty;
textBox.Foreground = Brushes.Black;
}
}
}
XAML使用:
XML<TextBox local:TextHelper.Watermark="请输入用户名" />
<TextBox local:TextHelper.Watermark="请输入密码" />
🎭 场景3:动画和数据绑定结合
C#public class AnimatedButton : Button
{
// 支持动画的自定义属性
public static readonly DependencyProperty AnimationProgressProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
nameof(AnimationProgress),
typeof(double),
typeof(AnimatedButton),
new PropertyMetadata(0.0, OnAnimationProgressChanged));
public double AnimationProgress
{
get { return (double)GetValue(AnimationProgressProperty); }
set { SetValue(AnimationProgressProperty, value); }
}
private static void OnAnimationProgressChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var button = (AnimatedButton)d;
// 根据进度更新按钮外观
button.UpdateAppearance((double)e.NewValue);
}
private void UpdateAppearance(double progress)
{
// 根据动画进度调整按钮外观
var transform = new ScaleTransform(1 + progress * 0.1, 1 + progress * 0.1);
this.RenderTransform = transform;
var opacity = 0.5 + progress * 0.5;
this.Opacity = opacity;
}
protected override void OnMouseEnter(MouseEventArgs e)
{
base.OnMouseEnter(e);
// 创建动画
var animation = new DoubleAnimation
{
From = 0,
To = 1,
Duration = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(200),
EasingFunction = new QuadraticEase()
};
this.BeginAnimation(AnimationProgressProperty, animation);
}
protected override void OnMouseLeave(MouseEventArgs e)
{
base.OnMouseLeave(e);
var animation = new DoubleAnimation
{
From = 1,
To = 0,
Duration = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(200),
EasingFunction = new QuadraticEase()
};
this.BeginAnimation(AnimationProgressProperty, animation);
}
}
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒
🚨 1. CLR包装器的局限性
C#// ❌ 错误:在CLR包装器中添加额外逻辑
public string BadTitle
{
get { return (string)GetValue(TitleProperty); }
set
{
// 这里的验证逻辑在XAML绑定时会被绕过!
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
throw new ArgumentException("Title cannot be empty");
SetValue(TitleProperty, value);
}
}
// ✅ 正确:在依赖属性的回调中处理逻辑
public static readonly DependencyProperty GoodTitleProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register(
nameof(GoodTitle),
typeof(string),
typeof(MyControl),
new PropertyMetadata(string.Empty, null, CoerceTitle));
private static object CoerceTitle(DependencyObject d, object value)
{
// 这里的逻辑不会被绕过
if (value == null || string.IsNullOrEmpty(value.ToString()))
return "默认标题";
return value;
}
🚨 2. 性能陷阱
C#// ❌ 错误:频繁调用GetValue/SetValue
private void BadPerformanceMethod()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
// 每次都要通过依赖属性系统查找
var title = (string)GetValue(TitleProperty);
SetValue(TitleProperty, title + i);
}
}
// ✅ 正确:合理使用本地缓存
private void GoodPerformanceMethod()
{
var originalTitle = (string)GetValue(TitleProperty);
var newTitle = originalTitle;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
newTitle += i;
}
// 只在最后设置一次
SetValue(TitleProperty, newTitle);
}
🚨 3. 内存泄漏风险
C#// ❌ 错误:事件处理器可能造成内存泄漏
private static void OnBadPropertyChanged(DependencyObject d,
DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
var control = (MyControl)d;
// 如果这里订阅了外部事件,需要在控件销毁时取消订阅
SomeStaticEvent += control.HandleEvent;
}
// ✅ 正确:实现适当的清理机制
protected override void OnUnloaded(RoutedEventArgs e)
{
base.OnUnloaded(e);
// 清理事件订阅
SomeStaticEvent -= HandleEvent;
}
🎯 总结核心要点
通过深入分析WPF依赖属性系统,我们发现了三个关键优势:
- 🚀 强大的绑定能力:依赖属性天生支持数据绑定、样式设置和动画,让WPF应用具备了强大的UI响应能力,这是传统CLR属性无法比拟的。
- ⚡ 优化的内存管理:通过稀疏存储和值优先级系统,依赖属性能够显著减少内存占用,特别是在创建大量控件实例时,性能优势更加明显。
- 🎨 丰富的扩展机制:元数据系统提供的回调函数、值强制转换和验证机制,让属性具备了强大的扩展能力,是构建复杂WPF应用的基石。
掌握依赖属性不仅能解决数据绑定问题,更能让你的WPF开发更加高效、优雅。记住:选择依赖属性用于UI相关功能,选择传统属性用于纯业务逻辑,这是WPF开发的黄金法则。
💭 互动讨论
- 你在项目中遇到过哪些依赖属性的使用难题?
- 有没有发现依赖属性的其他实用技巧想要分享?
🔥 收藏级代码模板已为你整理好,建议保存备用!觉得有用请转发给更多同行,让我们一起提升WPF开发技能!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录