目录
在日常的Python开发工作中,XML文件处理是一个绕不开的话题。无论是配置文件读取、数据交换,还是Web服务调用,XML都扮演着重要角色。很多开发者在面对XML处理时总是感到困惑:应该选择哪个库?如何高效地读取和修改XML?如何避免常见的编码和格式问题?
本文将深入解析Python内置的xml.dom.minidom模块,通过丰富的实战案例,帮你掌握XML处理的核心技能。从基础的文件读写到复杂的数据结构操作,让你在实际项目中游刃有余地处理各种XML场景。
🔍 问题分析:为什么选择xml.dom.minidom?
内置优势,无需额外安装
与第三方库如lxml、BeautifulSoup相比,xml.dom.minidom是Python标准库的一部分,在任何Python环境中都可以直接使用,特别适合企业级项目和上位机开发场景。
DOM树结构,直观易懂
minidom采用DOM(Document Object Model)方式解析XML,将整个文档加载到内存中形成树状结构,便于理解和操作。
轻量级设计,性能稳定
对于中小型XML文件(通常小于100MB),minidom提供了足够的性能和稳定性,是工业控制和数据采集项目的理想选择。
💡 解决方案:核心API与最佳实践
🎯 核心导入和基本概念
Pythonfrom xml.dom.minidom import parse, parseString, Document
import xml.dom.minidom as minidom
关键对象类型:
Document:整个XML文档Element:XML元素节点Text:文本内容节点Attr:属性节点
🛠️ 代码实战:从基础到进阶
🔥 实战案例1:读取XML配置文件
假设我们有一个设备配置文件config.xml:
XML<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<system>
<database>
<host>192.168.1.100</host>
<port>5432</port>
<username>admin</username>
<password>123456</password>
</database>
<devices>
<device id="001" type="sensor">
<name>温度传感器</name>
<location>车间A</location>
<status>online</status>
</device>
<device id="002" type="actuator">
<name>电机控制器</name>
<location>车间B</location>
<status>offline</status>
</device>
</devices>
</system>
完整读取解决方案:
Pythonimport xml.dom.minidom as minidom
from typing import Dict, List, Any
class XMLConfigReader:
def __init__(self, xml_file: str):
self.dom = minidom.parse(xml_file)
self.root = self.dom.documentElement
def get_database_config(self) -> Dict[str, str]:
"""获取数据库配置信息"""
db_node = self.root.getElementsByTagName('database')[0]
config = {}
for child in db_node.childNodes:
if child.nodeType == child.ELEMENT_NODE:
config[child.nodeName] = child.firstChild.data.strip()
return config
def get_devices_info(self) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""获取所有设备信息"""
devices = []
device_nodes = self.root.getElementsByTagName('device')
for device in device_nodes:
device_info = {
'id': device.getAttribute('id'),
'type': device.getAttribute('type')
}
# 获取子元素信息
for child in device.childNodes:
if child.nodeType == child.ELEMENT_NODE:
device_info[child.nodeName] = child.firstChild.data.strip()
devices.append(device_info)
return devices
def close(self):
"""释放DOM对象"""
self.dom.unlink()
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
reader = XMLConfigReader('config.xml')
# 读取数据库配置
db_config = reader.get_database_config()
print("数据库配置:")
for key, value in db_config.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
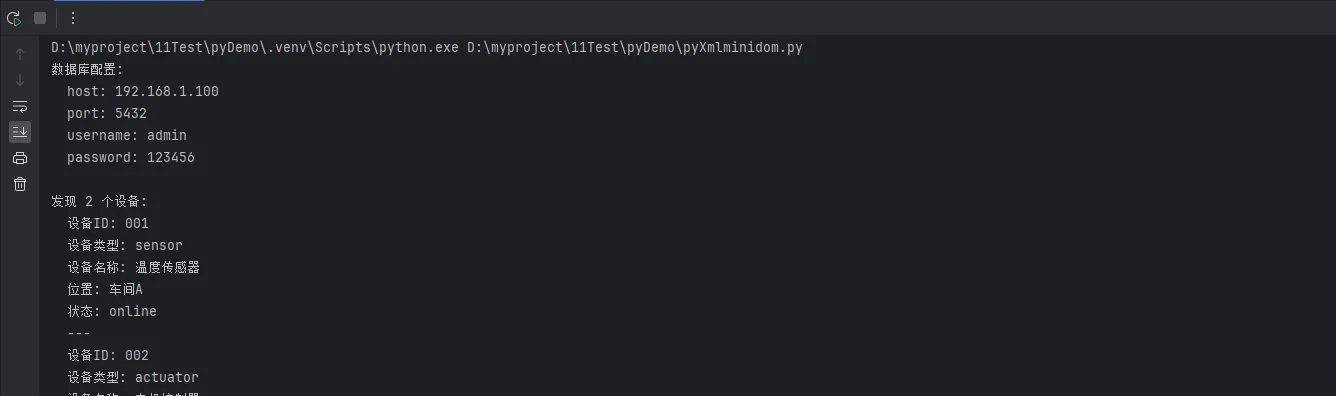
# 读取设备信息
devices = reader.get_devices_info()
print(f"\n发现 {len(devices)} 个设备:")
for device in devices:
print(f" 设备ID: {device['id']}")
print(f" 设备类型: {device['type']}")
print(f" 设备名称: {device['name']}")
print(f" 位置: {device['location']}")
print(f" 状态: {device['status']}")
print(" ---")
finally:
reader.close()
🎨 实战案例2:动态创建和修改XML文件
在上位机开发中,经常需要动态生成设备状态报告或操作日志:
Pythonimport xml.dom.minidom as minidom
from datetime import datetime
from typing import List, Dict
class XMLReportGenerator:
def __init__(self):
self.doc = minidom.Document()
self.root = self.doc.createElement('report')
self.root.setAttribute('generated', datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
self.doc.appendChild(self.root)
def add_device_status(self, device_id: str, device_name: str,
status: str, parameters: Dict[str, str]):
"""添加设备状态信息"""
device_node = self.doc.createElement('device')
device_node.setAttribute('id', device_id)
device_node.setAttribute('status', status)
# 设备名称
name_node = self.doc.createElement('name')
name_node.appendChild(self.doc.createTextNode(device_name))
device_node.appendChild(name_node)
# 参数信息
params_node = self.doc.createElement('parameters')
for key, value in parameters.items():
param_node = self.doc.createElement('parameter')
param_node.setAttribute('name', key)
param_node.appendChild(self.doc.createTextNode(str(value)))
params_node.appendChild(param_node)
device_node.appendChild(params_node)
# 时间戳
timestamp_node = self.doc.createElement('timestamp')
timestamp_node.appendChild(
self.doc.createTextNode(datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
)
device_node.appendChild(timestamp_node)
self.root.appendChild(device_node)
def add_alarm_record(self, alarm_type: str, message: str, level: str = 'warning'):
"""添加报警记录"""
alarm_node = self.doc.createElement('alarm')
alarm_node.setAttribute('type', alarm_type)
alarm_node.setAttribute('level', level)
msg_node = self.doc.createElement('message')
msg_node.appendChild(self.doc.createTextNode(message))
alarm_node.appendChild(msg_node)
time_node = self.doc.createElement('occurrence_time')
time_node.appendChild(
self.doc.createTextNode(datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
)
alarm_node.appendChild(time_node)
self.root.appendChild(alarm_node)
def save_to_file(self, filename: str):
"""保存到文件,格式化输出"""
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.doc.writexml(f, indent='', addindent=' ', newl='\n', encoding='utf-8')
def get_pretty_xml(self) -> str:
"""获取格式化的XML字符串"""
rough_string = self.doc.toprettyxml(indent=" ", encoding='utf-8')
return rough_string.decode('utf-8')
# 实际应用示例
def generate_device_report():
"""生成设备状态报告"""
generator = XMLReportGenerator()
# 模拟设备数据
devices_data = [
{
'id': '001',
'name': '温度传感器A',
'status': 'normal',
'parameters': {
'temperature': '25.6',
'humidity': '45.2',
'battery_level': '89'
}
},
{
'id': '002',
'name': '压力传感器B',
'status': 'warning',
'parameters': {
'pressure': '1.05',
'vibration': '0.02',
'temperature': '78.5'
}
}
]
# 添加设备状态
for device in devices_data:
generator.add_device_status(
device['id'],
device['name'],
device['status'],
device['parameters']
)
# 添加报警信息
generator.add_alarm_record('temperature_high', '设备002温度超过安全阈值', 'critical')
generator.add_alarm_record('battery_low', '设备001电池电量不足', 'warning')
# 保存报告
filename = f"device_report_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')}.xml"
generator.save_to_file(filename)
print(f"设备状态报告已生成: {filename}")
print("报告内容预览:")
print(generator.get_pretty_xml())
# 执行生成报告
generate_device_report()

⚡ 实战案例3:XML文件内容修改和更新
在实际项目中,经常需要更新配置文件或修改现有数据:
Pythonimport xml.dom.minidom as minidom
import os
from typing import Optional
class XMLEditor:
def __init__(self, xml_file: str):
self.xml_file = xml_file
self.dom = minidom.parse(xml_file)
self.root = self.dom.documentElement
self.modified = False
def update_device_status(self, device_id: str, new_status: str) -> bool:
"""更新指定设备的状态"""
devices = self.root.getElementsByTagName('device')
for device in devices:
if device.getAttribute('id') == device_id:
status_nodes = device.getElementsByTagName('status')
if status_nodes:
# 更新现有状态节点
status_nodes[0].firstChild.data = new_status
self.modified = True
return True
else:
# 创建新的状态节点
status_node = self.dom.createElement('status')
status_node.appendChild(self.dom.createTextNode(new_status))
device.appendChild(status_node)
self.modified = True
return True
return False
def add_new_device(self, device_id: str, device_type: str,
name: str, location: str, status: str = 'offline'):
"""添加新设备"""
devices_node = self.root.getElementsByTagName('devices')[0]
# 创建新设备节点
device_node = self.dom.createElement('device')
device_node.setAttribute('id', device_id)
device_node.setAttribute('type', device_type)
# 添加设备详细信息
elements = {
'name': name,
'location': location,
'status': status
}
for tag_name, value in elements.items():
element = self.dom.createElement(tag_name)
element.appendChild(self.dom.createTextNode(value))
device_node.appendChild(element)
devices_node.appendChild(device_node)
self.modified = True
def remove_device(self, device_id: str) -> bool:
"""删除指定设备"""
devices = self.root.getElementsByTagName('device')
for device in devices:
if device.getAttribute('id') == device_id:
device.parentNode.removeChild(device)
device.unlink() # 释放内存
self.modified = True
return True
return False
def update_database_config(self, **config):
"""更新数据库配置"""
db_node = self.root.getElementsByTagName('database')[0]
for key, value in config.items():
nodes = db_node.getElementsByTagName(key)
if nodes:
# 更新现有配置
nodes[0].firstChild.data = str(value)
self.modified = True
else:
# 添加新配置项
new_node = self.dom.createElement(key)
new_node.appendChild(self.dom.createTextNode(str(value)))
db_node.appendChild(new_node)
self.modified = True
def save_changes(self, backup: bool = True):
"""保存修改,可选择是否备份原文件"""
if not self.modified:
print("没有修改需要保存")
return
if backup and os.path.exists(self.xml_file):
backup_file = f"{self.xml_file}.backup"
os.rename(self.xml_file, backup_file)
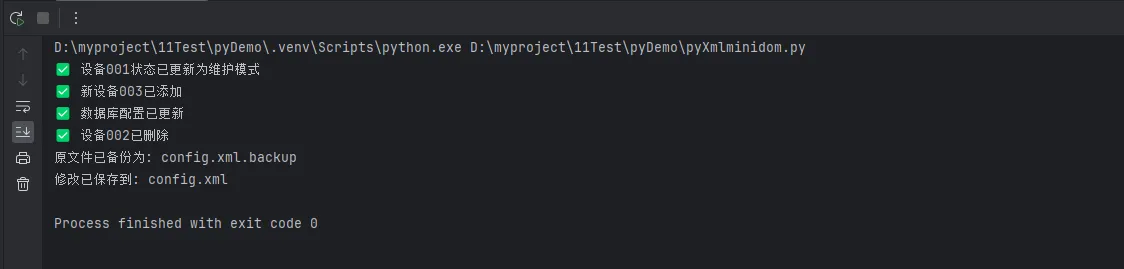
print(f"原文件已备份为: {backup_file}")
with open(self.xml_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.dom.writexml(f, indent='', addindent=' ', newl='\n', encoding='utf-8')
print(f"修改已保存到: {self.xml_file}")
self.modified = False
def close(self):
"""释放DOM对象"""
self.dom.unlink()
# 使用示例
def demonstrate_xml_editing():
"""演示XML编辑功能"""
editor = XMLEditor('config.xml')
try:
# 更新设备状态
if editor.update_device_status('001', 'maintenance'):
print("✅ 设备001状态已更新为维护模式")
# 添加新设备
editor.add_new_device('003', 'controller', '新控制器', '车间C', 'testing')
print("✅ 新设备003已添加")
# 更新数据库配置
editor.update_database_config(
host='192.168.1.101',
backup_enabled='true'
)
print("✅ 数据库配置已更新")
# 删除设备
if editor.remove_device('002'):
print("✅ 设备002已删除")
# 保存所有修改
editor.save_changes(backup=True)
finally:
editor.close()
# 执行演示
demonstrate_xml_editing()
🔧 进阶技巧:错误处理和性能优化
Pythonimport xml.dom.minidom as minidom
import xml.parsers.expat
from contextlib import contextmanager
import logging
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@contextmanager
def safe_xml_operation(xml_file: str):
"""安全的XML操作上下文管理器"""
dom = None
try:
dom = minidom.parse(xml_file)
yield dom
except xml.parsers.expat.ExpatError as e:
logger.error(f"XML解析错误: {e}")
raise ValueError(f"无效的XML文件格式: {xml_file}")
except FileNotFoundError:
logger.error(f"文件未找到: {xml_file}")
raise
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"处理XML时发生错误: {e}")
raise
finally:
if dom:
dom.unlink()
def validate_xml_structure(xml_file: str, required_elements: list) -> bool:
"""验证XML文件结构"""
try:
with safe_xml_operation(xml_file) as dom:
root = dom.documentElement
for element in required_elements:
nodes = root.getElementsByTagName(element)
if not nodes:
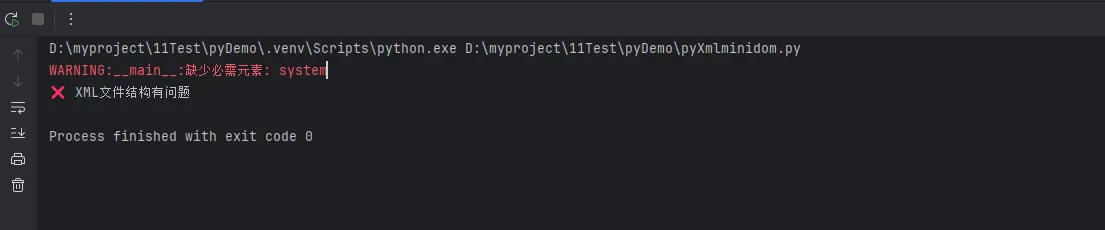
logger.warning(f"缺少必需元素: {element}")
return False
logger.info("XML结构验证通过")
return True
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"XML结构验证失败: {e}")
return False
# 性能优化示例
class OptimizedXMLProcessor:
"""优化的XML处理器"""
def __init__(self):
self._element_cache = {}
def get_cached_elements(self, dom, tag_name: str):
"""缓存元素查询结果"""
if tag_name not in self._element_cache:
self._element_cache[tag_name] = dom.getElementsByTagName(tag_name)
return self._element_cache[tag_name]
def clear_cache(self):
"""清除缓存"""
self._element_cache.clear()
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 验证XML结构
required_elements = ['system', 'database', 'devices']
if validate_xml_structure('config.xml', required_elements):
print("✅ XML文件结构正确")
else:
print("❌ XML文件结构有问题")
📊 实用工具函数集合
Pythondef xml_to_dict(element):
"""将XML元素转换为字典"""
result = {}
# 处理属性
if element.attributes:
result['@attributes'] = {}
for i in range(element.attributes.length):
attr = element.attributes.item(i)
result['@attributes'][attr.name] = attr.value
# 处理子元素
children = [child for child in element.childNodes
if child.nodeType == child.ELEMENT_NODE]
if children:
child_dict = {}
for child in children:
child_result = xml_to_dict(child)
if child.nodeName in child_dict:
# 处理同名元素,转换为列表
if not isinstance(child_dict[child.nodeName], list):
child_dict[child.nodeName] = [child_dict[child.nodeName]]
child_dict[child.nodeName].append(child_result)
else:
child_dict[child.nodeName] = child_result
result.update(child_dict)
else:
# 叶子节点,获取文本内容
text_content = ''.join([child.data for child in element.childNodes
if child.nodeType == child.TEXT_NODE]).strip()
if text_content:
result = text_content
return result
def pretty_print_xml(dom_node, indent: int = 0):
"""美化打印XML结构"""
indent_str = " " * indent
if dom_node.nodeType == dom_node.ELEMENT_NODE:
print(f"{indent_str}<{dom_node.nodeName}>")
# 打印属性
if dom_node.attributes:
for i in range(dom_node.attributes.length):
attr = dom_node.attributes.item(i)
print(f"{indent_str} @{attr.name} = {attr.value}")
# 递归打印子节点
for child in dom_node.childNodes:
if child.nodeType == child.ELEMENT_NODE:
pretty_print_xml(child, indent + 1)
elif child.nodeType == child.TEXT_NODE and child.data.strip():
print(f"{indent_str} 文本: {child.data.strip()}")
# 示例用法
if __name__ == "__main__":
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
xml_string = """<root>
<child1 attr1="value1">Text1</child1>
<child2 attr2="value2">
<subchild>SubText</subchild>
</child2>
<child1 attr3="value3">Text2</child1>
</root>"""
dom = parseString(xml_string)
xml_dict = xml_to_dict(dom.documentElement)
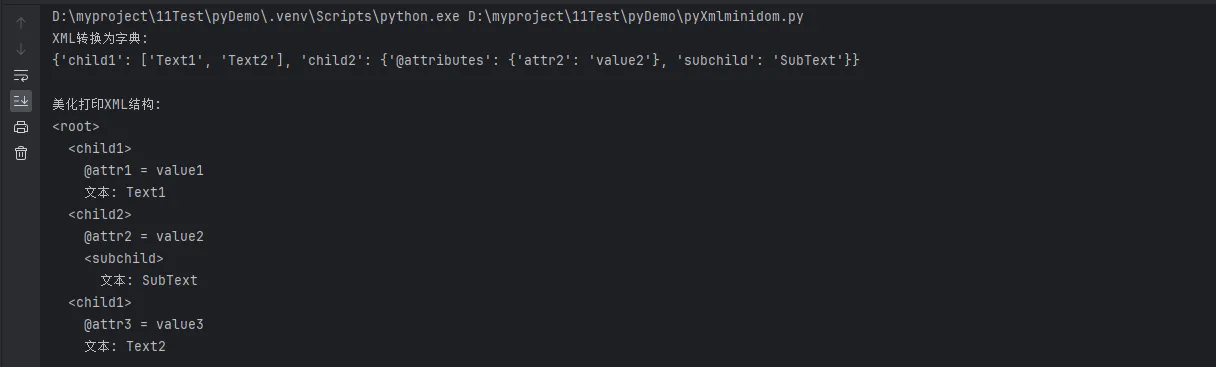
print("XML转换为字典:")
print(xml_dict)
print("\n美化打印XML结构:")
pretty_print_xml(dom.documentElement)
print("\nXML转换为字典:")
print(xml_dict)
🎯 核心要点总结
通过本文的深入解析和实战演练,我们掌握了xml.dom.minidom的核心应用技能:
第一个关键点:结构化读取 - 掌握了DOM树的遍历方法,能够高效提取XML中的配置信息和数据内容,这是处理配置文件和数据交换的基础技能。
第二个关键点:动态创建和修改 - 学会了程序化生成XML文档和实时更新现有内容,这在报告生成、日志记录和配置管理中极为实用。
第三个关键点:工程化最佳实践 - 通过错误处理、性能优化和上下文管理,确保了代码在生产环境中的稳定性和可维护性。
xml.dom.minidom虽然不是最快的XML处理库,但其简洁的API和稳定的表现使其成为Python开发者处理中小型XML文件的理想选择。在上位机开发、数据采集和企业级应用中,这些技能将助你事半功倍。
记住,好的代码不仅仅是能运行,更要具备良好的异常处理和资源管理机制。继续实践这些技术要点,你将在XML处理领域游刃有余!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!