目录
作为一名C#开发者,当你初次接触Java时,是否会有种"似曾相识却又处处不同"的感觉?特别是在类与对象的声明方式上,两种语言看似相近,实则暗藏玄机。
今天就来深入对比Java与C#在类与对象声明和访问修饰符方面的核心差异,帮你快速避开转型路上的常见陷阱,让代码写得更地道、更高效!
🎯 问题分析:为什么会"水土不服"?
核心痛点识别
许多C#开发者在转Java时会遇到这些困扰:
- 文件组织方式:一个文件只能有一个public类?
- 访问修饰符:为什么没有internal?default又是什么鬼?
- 构造函数:语法相似但细节差异让人头疼
- 属性访问:getter/setter的冗长写法让人怀念C#的属性语法 (你能狠死Java)
💡 解决方案:5个关键对比点
🔥 文件组织与类声明差异
C#的灵活性
C#// PersonManager.cs - 一个文件可以包含多个public类
namespace MyApp.Models
{
public class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
public class PersonManager
{
public void ProcessPerson(Person person) { }
}
internal class Helper
{
// internal类,程序集内可访问
}
}
这种写法也不应该全堆一起,即使写这样,也是有最小规则与相关
Java的严格规则
Javapackage org.example;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
// 构造函数
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// getter/setter方法
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }
}
// 同一文件中的其他类只能是package-private
class Helper {
// 包级访问权限
}
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒
- Java中,一个文件只能有一个public类,且文件名必须与类名完全一致
- package语句必须是文件的第一行非注释代码
- 类名采用PascalCase,但包名全小写(与C#命名空间不同)
🔥 访问修饰符对比表
| 访问级别 | C# | Java | 适用范围 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 最严格 | private | private | 类内部 |
| 程序集内 | internal | (package-private) | C#:程序集 / Java:包 |
| 继承可见 | protected | protected | 子类 |
| 完全公开 | public | public | 所有地方 |
实战对比示例
C#// C# 访问修饰符示例
public class Account
{
private decimal balance; // 类内访问
internal string accountType; // 程序集内访问
protected int securityLevel; // 子类可访问
public string AccountNumber; // 公开访问
}
Java// Java 访问修饰符示例
public class Account {
private BigDecimal balance; // 类内访问
String accountType; // 包内访问(默认)
protected int securityLevel; // 子类可访问
public String accountNumber; // 公开访问
}
💡 Java独特点
- package-private(默认):不加修饰符就是包级访问
- 没有internal:用package-private替代
- protected范围更大:同包内的类也能访问
🔥 对象创建与初始化对比
C#的多样化初始化
C#// C# 对象初始化方式
public class Employee
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public decimal Salary { get; set; }
public Employee() { }
public Employee(string name, int age)
{
Name = name;
Age = age;
}
}
// 创建对象的多种方式
var emp1 = new Employee();
var emp2 = new Employee("张三", 30);
var emp3 = new Employee { Name = "李四", Age = 25, Salary = 8000 }; // 对象初始化器
var emp4 = new Employee("王五", 28) { Salary = 9000 }; // 混合初始化
Java的传统方式
Javapackage org.example;
import java.math.BigDecimal;// Java 对象初始化
public class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
private BigDecimal salary;
// 默认构造函数
public Employee() {}
// 参数构造函数
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 全参构造函数
public Employee(String name, int age, BigDecimal salary) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
// Builder模式(推荐用于多参数场景)
public static class Builder {
private String name;
private int age;
private BigDecimal salary;
public Builder name(String name) { this.name = name; return this; }
public Builder age(int age) { this.age = age; return this; }
public Builder salary(BigDecimal salary) { this.salary = salary; return this; }
public Employee build() {
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.name = this.name;
emp.age = this.age;
emp.salary = this.salary;
return emp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用默认构造函数
Employee emp1 = new Employee();
// 使用参数构造函数
Employee emp2 = new Employee("Alice", 30);
// 使用全参构造函数
Employee emp3 = new Employee("Bob", 25, new BigDecimal("5000.00"));
// 使用Builder模式
Employee emp4 = new Employee.Builder()
.name("Charlie")
.age(28)
.salary(new BigDecimal("6000.00"))
.build();
}
}
这块Java的有点麻烦了
🔥 属性与字段访问模式
C#的属性语法糖
C#public class Product
{
// 自动属性
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
// 只读属性
public string Category { get; }
// 计算属性
public decimal TaxAmount => Price * 0.1m;
// 带验证的属性
private int _quantity;
public int Quantity
{
get => _quantity;
set => _quantity = value > 0 ? value : throw new ArgumentException("数量必须大于0");
}
}
Java的getter/setter模式
Javapackage org.example;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Product {
private String name;
private BigDecimal price;
private final String category; // 只读字段
private int quantity;
public Product(String category) {
this.category = category;
}
// 标准getter/setter
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public BigDecimal getPrice() { return price; }
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) { this.price = price; }
// 只读属性(只有getter)
public String getCategory() { return category; }
// 计算属性
public BigDecimal getTaxAmount() {
return price != null ? price.multiply(new BigDecimal("0.1")) : BigDecimal.ZERO;
}
// 带验证的setter
public int getQuantity() { return quantity; }
public void setQuantity(int quantity) {
if (quantity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("数量必须大于0");
}
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product product = new Product("Electronics");
product.setName("Laptop");
product.setPrice(new BigDecimal("1500.00"));
product.setQuantity(5);
System.out.println("产品名称: " + product.getName());
System.out.println("产品类别: " + product.getCategory());
System.out.println("产品价格: " + product.getPrice());
System.out.println("税额: " + product.getTaxAmount());
System.out.println("数量: " + product.getQuantity());
}
}

🔥 实际应用场景对比
场景:用户管理系统
C#版本
C#// UserService.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace UserManagement
{
public class User
{
public Guid Id { get; } = Guid.NewGuid();
public string Username { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public DateTime CreatedAt { get; } = DateTime.Now;
public UserRole Role { get; set; } = UserRole.Member;
}
public enum UserRole { Member, Admin, SuperAdmin }
public class UserService
{
private readonly List<User> _users = new();
public User CreateUser(string username, string email)
{
var user = new User { Username = username, Email = email };
_users.Add(user);
return user;
}
internal void ValidateUser(User user) // 程序集内方法
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.Username))
throw new ArgumentException("用户名不能为空");
}
}
}
Java版本
Javapackage org.example.entity;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.UUID;
public class User {
private final UUID id;
private String username;
private String email;
private final LocalDateTime createdAt;
private UserRole role;
public User() {
this.id = UUID.randomUUID();
this.createdAt = LocalDateTime.now();
this.role = UserRole.MEMBER;
}
public User(String username, String email) {
this();
this.username = username;
this.email = email;
}
// getter方法
public UUID getId() { return id; }
public String getUsername() { return username; }
public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; }
public String getEmail() { return email; }
public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; }
public LocalDateTime getCreatedAt() { return createdAt; }
public UserRole getRole() { return role; }
public void setRole(UserRole role) { this.role = role; }
}
Java// UserRole.java
package com.userManagement.model;
public enum UserRole {
MEMBER, ADMIN, SUPER_ADMIN
}
Javapackage org.example.service;
import org.example.entity.User;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class UserService {
private final List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
public User createUser(String username, String email) {
User user = new User(username, email);
users.add(user);
return user;
}
// 包级访问方法(相当于C#的internal)
void validateUser(User user) {
if (user.getUsername() == null || user.getUsername().isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("用户名不能为空");
}
}
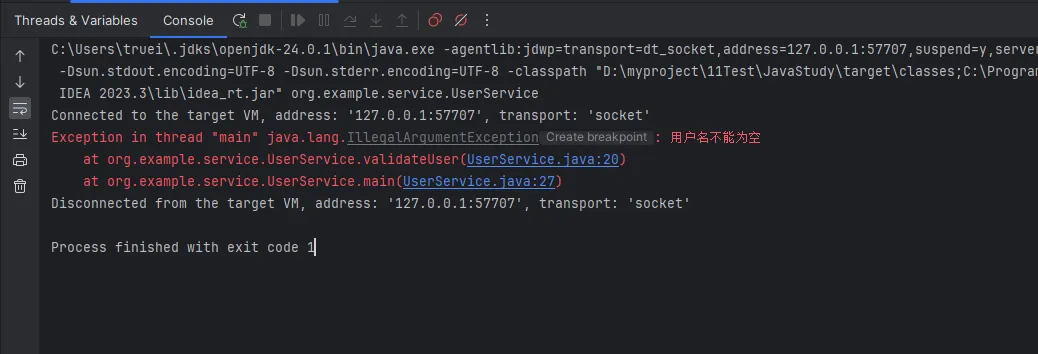
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserService userService = new UserService();
userService.createUser("rick","rick@163.com");
userService.validateUser(new User("",""));
}
}
🎯 转型要点总结
通过今天的深入对比,我们掌握了Java与C#在类与对象声明方面的三个核心差异:
- 文件组织规则:Java的"一文件一公开类"原则更严格,但换来了更清晰的代码组织
- 访问控制体系:Java用package-private替代了C#的internal,访问控制更细粒度
- 对象初始化模式:Java偏向传统的构造函数+getter/setter,虽然冗长但更明确
作为C#开发者,理解这些差异不仅能让你写出更地道的Java代码,更能深入理解两种语言的设计哲学。记住:Java强调明确性和一致性,C#追求简洁性和灵活性。
💬 互动讨论
- 你在从C#转Java的过程中,还遇到过哪些"似是而非"的语法陷阱?
- 对于Java冗长的getter/setter写法,你有什么提高效率的小技巧?
觉得这篇对比有价值?请转发给更多正在技术转型路上的同行!让我们一起在编程的道路上少走弯路,多写好代码!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录