目录
作为一名Windows下的Python开发者,你是否遇到过这样的情况:程序运行得好好的,突然就崩溃了?用户点击一个按钮,程序直接闪退?文件读取失败,整个应用卡死?这些问题的根源往往在于缺乏合适的异常处理机制。
今天我们就来深入探讨Python的异常处理机制(try/except/finally),帮你构建更加健壮、用户友好的Windows桌面应用程序。无论你是做数据处理、GUI开发还是上位机开发,掌握这套机制都将让你的Python开发水平上一个台阶。
🔍 问题分析:为什么需要异常处理?
💥 常见的"程序崩溃"场景
在实际的Python开发中,以下情况经常导致程序异常终止:
Python# 场景1:文件操作失败
def read_config():
file = open('config.txt', 'r') # 如果文件不存在,直接崩溃
content = file.read()
return content
Python# 场景2:数据类型错误
def calculate_average(numbers):
return sum(numbers) / len(numbers) # 如果numbers为空列表,除零错误
Python# 场景3:网络请求超时
import requests
def get_data():
response = requests.get('http://api.example.com/data') # 网络异常直接崩溃
return response.json()
这些代码在理想情况下运行良好,但一旦遇到异常情况,程序就会抛出错误并终止,用户体验极差。
🎯 异常处理的核心价值
异常处理机制不仅仅是为了防止程序崩溃,更重要的是:
- 提升用户体验:优雅地处理错误,给用户友好的提示
- 程序稳定性:保证核心功能在遇到问题时能够继续运行
- 问题定位:记录详细的错误信息,便于后期调试
- 业务连续性:在上位机开发中,设备通信异常不应影响整个系统
💡 解决方案:异常处理机制详解
🏗️ 基础语法结构
Python异常处理的核心是try/except/finally语句块:
Pythontry:
# 可能出现异常的代码
risky_operation()
except ExceptionType:
# 处理特定类型的异常
handle_exception()
except:
# 处理所有其他异常
handle_all_exceptions()
else:
# 没有异常时执行
success_operation()
finally:
# 无论是否有异常都会执行
cleanup_operation()
🔧 语句块详细说明
try块:放置可能抛出异常的代码
except块:捕获并处理异常
else块:当try块没有异常时执行
finally块:无论是否有异常都会执行,常用于资源清理
🚀 代码实战:从简单到复杂
📁 实战案例1:安全的文件操作
Pythondef safe_read_file(filename):
"""安全地读取文件内容"""
try:
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
print(f"成功读取文件:{filename}")
return content
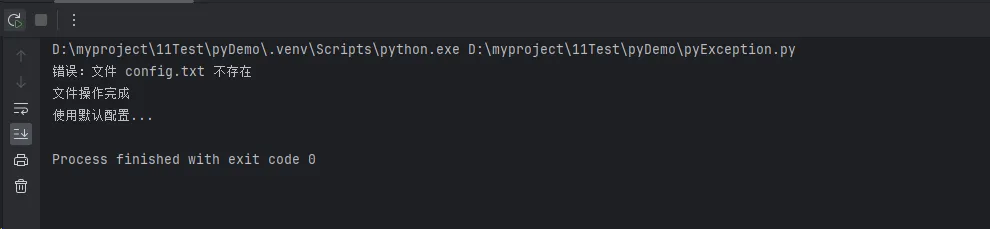
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"错误:文件 {filename} 不存在")
return None
except PermissionError:
print(f"错误:没有权限访问文件 {filename}")
return None
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print(f"错误:文件 {filename} 编码格式不正确")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"未知错误:{e}")
return None
finally:
print("文件操作完成")
# 使用示例
content = safe_read_file("config.txt")
if content:
print("文件内容获取成功,继续处理...")
else:
print("使用默认配置...")
📊 实战案例2:数据处理中的异常处理
Pythondef safe_data_processing(data_list):
"""安全地处理数据列表"""
results = []
error_count = 0
for i, item in enumerate(data_list):
try:
# 模拟复杂的数据处理
if isinstance(item, str):
processed = float(item) * 2
elif isinstance(item, (int, float)):
processed = item * 2
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的数据类型:{type(item)}")
results.append(processed)
except ValueError as e:
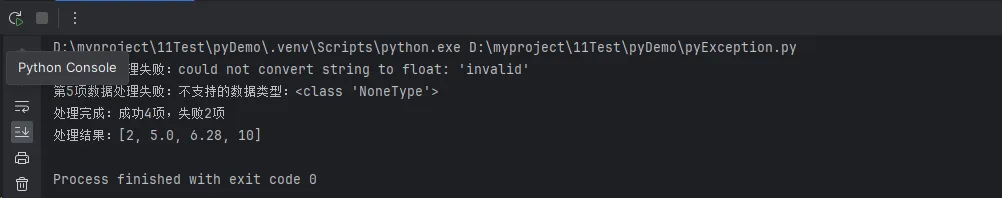
print(f"第{i+1}项数据处理失败:{e}")
error_count += 1
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"第{i+1}项发生未知错误:{e}")
error_count += 1
continue
print(f"处理完成:成功{len(results)}项,失败{error_count}项")
return results
# 测试数据
test_data = [1, "2.5", 3.14, "invalid", None, 5]
results = safe_data_processing(test_data)
print(f"处理结果:{results}")
🌐 实战案例3:网络请求的异常处理
Pythonimport requests
import time
from requests.exceptions import RequestException, Timeout, ConnectionError
def robust_api_request(url, max_retries=3, timeout=5):
"""健壮的API请求函数"""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
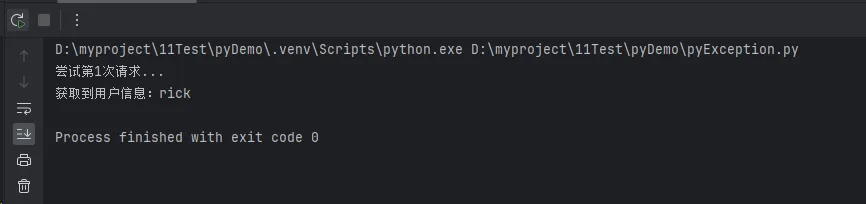
print(f"尝试第{attempt + 1}次请求...")
response = requests.get(url, timeout=timeout)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查HTTP状态码
return response.json()
except ConnectionError:
print(f"连接错误,第{attempt + 1}次尝试失败")
except Timeout:
print(f"请求超时,第{attempt + 1}次尝试失败")
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:
print(f"HTTP错误:{e}")
except ValueError: # JSON解析错误
print("响应不是有效的JSON格式")
except RequestException as e:
print(f"请求异常:{e}")
if attempt < max_retries - 1:
wait_time = 2 ** attempt # 指数退避
print(f"等待{wait_time}秒后重试...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
print("所有重试都失败了")
return None
# 使用示例
data = robust_api_request("https://api.github.com/users/rick9981")
if data:
print(f"获取到用户信息:{data.get('name', 'Unknown')}")
else:
print("使用缓存数据或提示用户检查网络...")
🏭 实战案例4:上位机开发中的设备通信
Pythonimport serial
import time
class DeviceCommunicator:
"""设备通信类,适用于上位机开发"""
def __init__(self, port, baudrate=9600):
self.port = port
self.baudrate = baudrate
self.connection = None
def connect(self):
"""连接设备"""
try:
self.connection = serial.Serial(
port=self.port,
baudrate=self.baudrate,
timeout=1
)
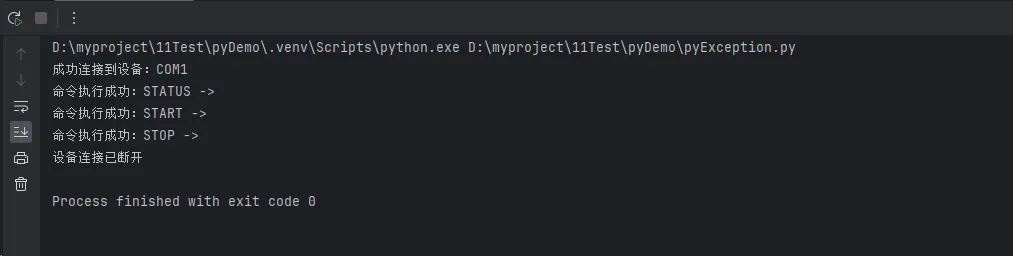
print(f"成功连接到设备:{self.port}")
return True
except serial.SerialException as e:
print(f"串口连接失败:{e}")
return False
except Exception as e:
print(f"连接设备时发生未知错误:{e}")
return False
def send_command(self, command, expected_response=None):
"""发送命令到设备"""
if not self.connection or not self.connection.is_open:
print("设备未连接")
return None
try:
# 发送命令
self.connection.write(command.encode())
time.sleep(0.1) # 等待设备响应
# 读取响应
response = self.connection.readline().decode().strip()
if expected_response and response != expected_response:
raise ValueError(f"设备响应异常:期望'{expected_response}',实际'{response}'")
print(f"命令执行成功:{command} -> {response}")
return response
except serial.SerialTimeoutException:
print("设备响应超时")
return None
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print("设备响应包含无效字符")
return None
except ValueError as e:
print(f"设备响应验证失败:{e}")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"命令执行失败:{e}")
return None
finally:
# 清理缓冲区
if self.connection and self.connection.is_open:
self.connection.reset_input_buffer()
def disconnect(self):
"""断开设备连接"""
try:
if self.connection and self.connection.is_open:
self.connection.close()
print("设备连接已断开")
except Exception as e:
print(f"断开连接时发生错误:{e}")
finally:
self.connection = None
# 使用示例
device = DeviceCommunicator("COM3")
if device.connect():
# 发送一系列命令
commands = ["STATUS", "START", "STOP"]
for cmd in commands:
result = device.send_command(cmd)
if result is None:
print(f"命令{cmd}执行失败,但程序继续运行...")
device.disconnect()
🛠️ 实战案例5:自定义异常类
Pythonclass DataValidationError(Exception):
"""数据验证异常"""
def __init__(self, message, error_code=None):
super().__init__(message)
self.error_code = error_code
class ConfigurationError(Exception):
"""配置错误异常"""
pass
def validate_user_input(data):
"""验证用户输入数据"""
try:
if not isinstance(data, dict):
raise DataValidationError("输入数据必须是字典格式", "TYPE_ERROR")
if "username" not in data:
raise DataValidationError("缺少用户名字段", "MISSING_FIELD")
if len(data["username"]) < 3:
raise DataValidationError("用户名长度不能少于3位", "LENGTH_ERROR")
print("数据验证通过")
return True
except DataValidationError as e:
print(f"数据验证失败:{e}")
if e.error_code:
print(f"错误代码:{e.error_code}")
return False
# 测试自定义异常
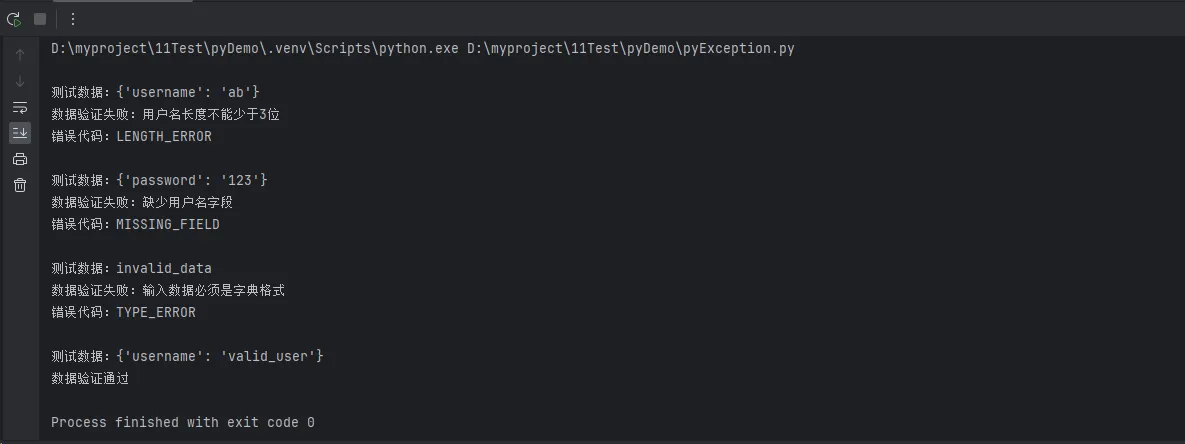
test_cases = [
{"username": "ab"}, # 长度不够
{"password": "123"}, # 缺少用户名
"invalid_data", # 类型错误
{"username": "valid_user"} # 正确数据
]
for test_data in test_cases:
print(f"\n测试数据:{test_data}")
validate_user_input(test_data)
🎯 编程技巧与最佳实践
⚡ 性能优化技巧
异常处理不是程序流控制
Python# ❌ 错误示例:用异常控制程序流程
def find_item_bad(items, target):
try:
return items.index(target)
except ValueError:
return -1
# ✅ 正确示例:先检查再操作
def find_item_good(items, target):
if target in items:
return items.index(target)
return -1
精确捕获异常类型
Python# ❌ 避免捕获所有异常
try:
risky_operation()
except: # 这样会掩盖真正的问题
pass
# ✅ 精确捕获特定异常
try:
risky_operation()
except FileNotFoundError:
handle_file_not_found()
except PermissionError:
handle_permission_error()
🔧 实用工具函数
Pythonimport functools
import logging
def exception_handler(default_return=None, log_error=True):
"""异常处理装饰器"""
def decorator(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
if log_error:
logging.error(f"函数 {func.__name__} 执行失败:{e}")
return default_return
return wrapper
return decorator
# 使用装饰器
@exception_handler(default_return=[], log_error=True)
def process_data(data):
# 可能出错的数据处理逻辑
return [x * 2 for x in data]
# 测试
result = process_data("invalid_data") # 返回[]而不是崩溃
print(result)
🎭 总结:构建健壮的Python应用
通过今天的深入学习,我们掌握了Python异常处理机制的三个核心要点:
1. 预防胜于治疗:合理使用try/except/finally语句块,让程序在面对异常时优雅降级而不是直接崩溃。
2. 精确处理异常:针对不同类型的异常采用不同的处理策略,避免一刀切的处理方式,这在上位机开发中尤为重要。
3. 用户体验至上:异常处理不仅仅是技术问题,更是用户体验问题。给用户清晰的错误提示,保持程序的稳定运行。
掌握这套编程技巧后,你的Python程序将更加健壮,用户体验也会显著提升。无论是处理文件操作、网络请求还是设备通信,都能游刃有余地应对各种异常情况。
下次开发Windows桌面应用时,记得为每个可能出错的地方都加上合适的异常处理机制,让你的Python开发更加专业!
想了解更多Python开发技巧?欢迎关注我们的公众号,每周分享实用的编程经验和项目实战案例!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!