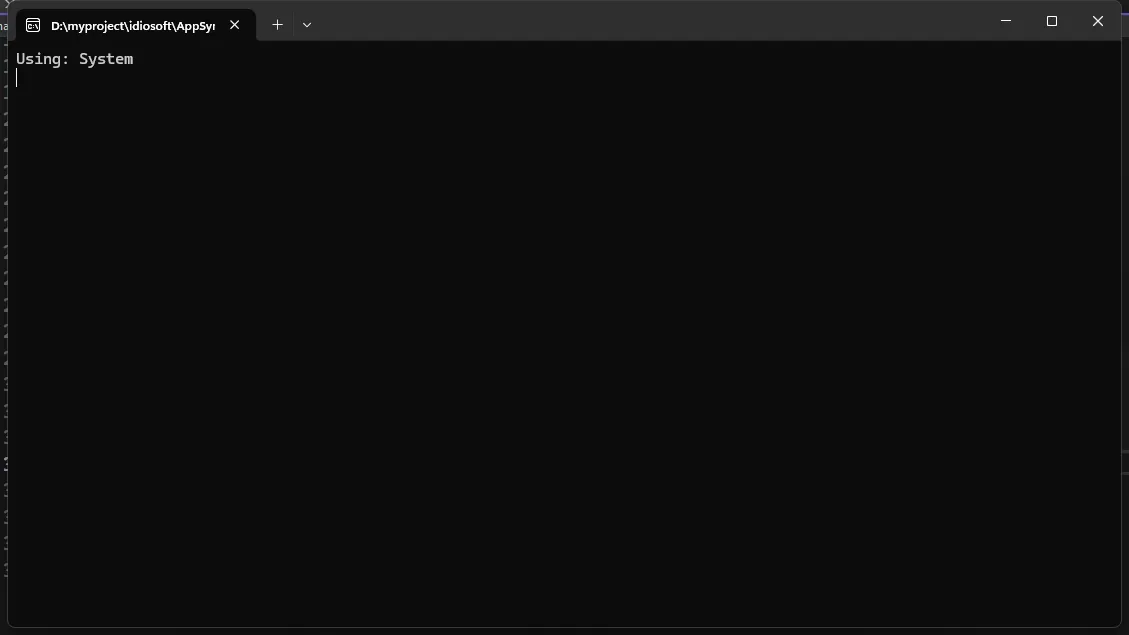
语法分析是理解和处理C#代码的基础。通过.NET Compiler Platform SDK (也称为Roslyn),我们可以分析、理解和转换C#代码的结构。
语法树的基本概念
语法树是编译器用来理解代码的数据结构。它具有以下特点:
- 完整性:代表源代码中的所有信息
- 不可变性:创建后无法修改
- 线程安全:可以在多个线程中并发访问
语法树的主要组成部分
C#// 四个主要构建块
1. SyntaxTree // 表示整个解析树
2. SyntaxNode // 表示语法结构(如声明、语句等)
3. SyntaxToken // 表示关键字、标识符、运算符等
4. SyntaxTrivia // 表示空白、注释等
实战示例
基础示例 - 解析Hello World
C#using Microsoft.CodeAnalysis;
using Microsoft.CodeAnalysis.CSharp;
using Microsoft.CodeAnalysis.CSharp.Syntax;
namespace AppSyntaxAnalysis
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 要分析的代码
string sourceCode = @"
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(""Hello World!"");
}
}";
// 解析代码生成语法树
SyntaxTree tree = CSharpSyntaxTree.ParseText(sourceCode);
// 获取根节点
CompilationUnitSyntax root = tree.GetCompilationUnitRoot();
// 分析using指令
foreach (UsingDirectiveSyntax usingDirective in root.Usings)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Using: {usingDirective.Name}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
在进行WinForm到WPF的转型时,CheckBox是常用的控件之一。它允许用户进行布尔选项的选择或取消选择。本文将介绍在WPF环境下如何使用CheckBox并自定义它的样式,并与WinForm做简单对比。
基础概念
在WinForm中,你可以直接从工具箱拖拽一个CheckBox到Form上,然后在属性面板设置Text、Checked等属性。WPF的工作流程更偏向于界面与逻辑分离:
- XAML文件中负责定义界面
- C#后台代码(.cs)中实现逻辑
以下将展示一个基本的CheckBox示例代码与样式定制示例,帮助理解WPF中CheckBox的用法。
基本示例
这里展示一个最简单的CheckBox示例,包含以下功能:
- 一个CheckBox,绑定点击事件
- 在文本下方使用一个TextBlock来显示CheckBox的选择状态
XAML文件
XML<Window x:Class="AppCheckbox.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppCheckbox"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
<!-- 这是一个简单的CheckBox -->
<CheckBox x:Name="myCheckBox"
Content="选中我"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
Checked="CheckBox_Checked"
Unchecked="CheckBox_Unchecked">
</CheckBox>
<!-- 用来显示当前CheckBox的状态 -->
<TextBlock x:Name="tbStatus"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Top"
Margin="0,30,0,0"
FontSize="16"
Text="当前状态:未选中">
</TextBlock>
</Grid>
</Window>
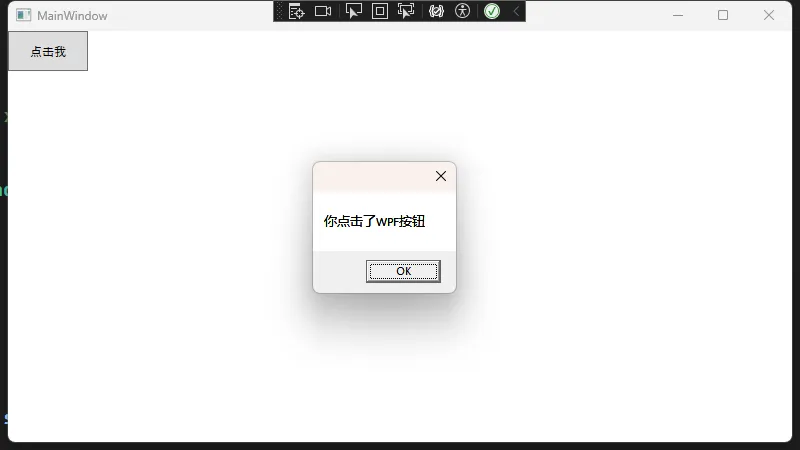
WinForm 中最常见的操作之一就是放置一个 Button(按钮),给它设置上适当的事件与属性即可完成点击操作。转到 WPF 之后,Button 依旧是实现交互和触发事件的主要控件之一,但 WPF 的优势在于更灵活强大的样式和布局系统。下面通过几个示例来说明如何将 WinForm 的思路迁移到 WPF,并进一步使用 WPF 的样式(Style)和模板(Template)功能来定制化按钮外观与交互行为。
基础 Button 示例
在 WinForm 中,你可能会这样写:
C#// WinForm 示例
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Button btnWinForm = new Button();
btnWinForm.Text = "点击我";
btnWinForm.Location = new Point(50, 50);
btnWinForm.Click += BtnWinForm_Click;
this.Controls.Add(btnWinForm);
}
private void BtnWinForm_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("你点击了WinForm按钮");
}
在 WPF 中,即使你也可以在后台代码里使用类似方式生成 Button,通常我们更倾向于在 XAML 中编写:
XML<Window x:Class="AppButton.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppButton"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
<!-- 定义一个Button -->
<Button x:Name="btnWPF"
Content="点击我"
Width="80" Height="40"
HorizontalAlignment="Left" VerticalAlignment="Top"
Click="btnWPF_Click"/>
</Grid>
</Window>
然后在后台代码 MainWindow.xaml.cs 中处理事件:
C#using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppButton
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnWPF_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("你点击了WPF按钮");
}
}
}
在现代.NET开发中,Reflection(反射)和LINQ(语言集成查询)是两个极其强大的特性。本文将深入探讨如何将这两种技术巧妙结合,实现更加灵活和高效的编程解决方案。
什么是Reflection?
Reflection是.NET框架提供的一种机制,允许在运行时动态地检查、调用和操作类型、方法、属性等元数据。它为开发者提供了极大的灵活性和动态性。
什么是LINQ?
LINQ是一种强大的数据查询和转换技术,可以对各种数据源(如集合、数据库、XML)进行标准化的查询操作。
实战案例:动态属性映射与过滤
下面是一个详细的示例,展示如何结合Reflection和LINQ实现复杂的数据处理:
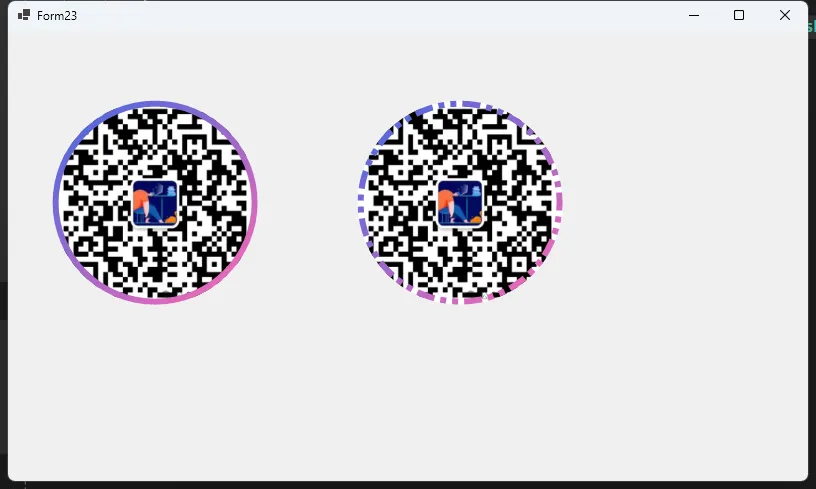
在Windows窗体应用程序开发中,我们经常需要展示圆形的图片,比如用户头像等。本文将详细介绍如何通过继承PictureBox控件,使用GDI+技术来实现一个支持渐变边框的圆形图片控件。
控件特性
- 支持圆形显示图片
- 可自定义边框粗细
- 支持双色渐变边框
- 可调整渐变角度
- 支持多种边框线型
- 具有抗锯齿效果
完整代码实现
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppControls
{
public class CircularPictureBox : PictureBox
{
private int borderSize = 2;
private Color borderColor = Color.RoyalBlue;
private Color borderColor2 = Color.HotPink;
private DashStyle borderLineStyle = DashStyle.Solid;
private DashCap borderCapStyle = DashCap.Flat;
private float gradientAngle = 50F;
public CircularPictureBox()
{
this.Size = new Size(100, 100);
this.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage;
this.BackColor = Color.Transparent;
}
// 优化双缓冲设置
protected override void OnHandleCreated(EventArgs e)
{
base.OnHandleCreated(e);
this.SetStyle(ControlStyles.AllPaintingInWmPaint |
ControlStyles.UserPaint |
ControlStyles.OptimizedDoubleBuffer |
ControlStyles.ResizeRedraw, true);
}
public int BorderSize
{
get
{
return borderSize;
}
set
{
borderSize = value;
this.Invalidate();
}
}
public Color BorderColor
{
get
{
return borderColor;
}
set
{
borderColor = value;
this.Invalidate();
}
}
public Color BorderColor2
{
get
{
return borderColor2;
}
set
{
borderColor2 = value;
this.Invalidate();
}
}
public DashStyle BorderLineStyle
{
get
{
return borderLineStyle;
}
set
{
borderLineStyle = value;
this.Invalidate();
}
}
public DashCap BorderCapStyle
{
get
{
return borderCapStyle;
}
set
{
borderCapStyle = value;
this.Invalidate();
}
}
public float GradientAngle
{
get
{
return gradientAngle;
}
set
{
gradientAngle = value;
this.Invalidate();
}
}
protected override void OnResize(EventArgs e)
{
base.OnResize(e);
this.Size = new Size(this.Width, this.Height);
}
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs pe)
{
base.OnPaint(pe);
Rectangle rectSurface = this.ClientRectangle;
Rectangle rectBorder = Rectangle.Inflate(rectSurface, -borderSize, -borderSize);
int smoothSize = 2;
if (borderSize > 0)
smoothSize = borderSize;
using (GraphicsPath pathSurface = GetCirclePath(rectSurface))
using (GraphicsPath pathBorder = GetCirclePath(rectBorder))
using (Pen penSurface = new Pen(this.Parent.BackColor, smoothSize))
{
// 设置绘图品质
pe.Graphics.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.AntiAlias;
// 设置区域
this.Region = new Region(pathSurface);
// 绘制图片
if (this.Image != null)
{
using (TextureBrush textureBrush = new TextureBrush(this.Image))
{
textureBrush.WrapMode = WrapMode.Clamp;
// 配置图片缩放
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
if (this.SizeMode == PictureBoxSizeMode.Zoom)
{
float scale = Math.Min((float)this.Width / this.Image.Width,
(float)this.Height / this.Image.Height);
float x = (this.Width - (this.Image.Width * scale)) / 2;
float y = (this.Height - (this.Image.Height * scale)) / 2;
matrix.Translate(x, y);
matrix.Scale(scale, scale);
}
else
{
matrix.Scale((float)this.Width / this.Image.Width,
(float)this.Height / this.Image.Height);
}
textureBrush.Transform = matrix;
pe.Graphics.FillPath(textureBrush, pathSurface);
}
}
// 绘制表面边缘
pe.Graphics.DrawPath(penSurface, pathSurface);
// 绘制边框
if (borderSize >= 1)
{
using (LinearGradientBrush borderGColor = new LinearGradientBrush(
rectBorder, borderColor, borderColor2, gradientAngle))
using (Pen penBorder = new Pen(borderGColor, borderSize))
{
penBorder.DashStyle = borderLineStyle;
penBorder.DashCap = borderCapStyle;
penBorder.Alignment = PenAlignment.Center;
pe.Graphics.DrawPath(penBorder, pathBorder);
}
}
}
}
private GraphicsPath GetCirclePath(Rectangle rect)
{
GraphicsPath path = new GraphicsPath();
path.AddEllipse(rect);
return path;
}
}
}